The Phasianidae are a family of heavy, ground-living birds, which includes pheasants, partridges, junglefowl, chickens, turkeys, Old World quail, and peafowl. The family includes many of the most popular gamebirds. The family is a large one and includes 185 species divided into 54 genera. It was formerly broken up into two subfamilies, the Phasianinae and the Perdicinae. However, this treatment is now known to be paraphyletic and polyphyletic, respectively, and more recent evidence supports breaking it up into two subfamilies: Rollulinae and Phasianinae, with the latter containing multiple tribes within two clades. The New World quail (Odontophoridae) and guineafowl (Numididae) were formerly sometimes included in this family, but are now typically placed in families of their own; conversely, grouse and turkeys, formerly often treated as distinct families, are now known to be deeply nested within Phasianidae, so they are now included in the present family.

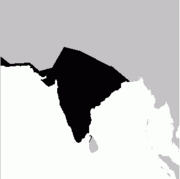
Galloperdix is a genus of three species of bird in the pheasant family, Phasianidae. These terrestrial birds are restricted to the Indian Subcontinent, with the red spurfowl and painted spurfowl in forest and scrub in India, and the Sri Lanka spurfowl in forests of Sri Lanka. They share the common name "spurfowl" with the members of the genus Pternistis which are widely distributed in Africa.

Francolins are birds in the tribe Gallini that traditionally have been placed in the genus Francolinus, but now commonly are divided into multiple genera.

The double-spurred spurfowl is a gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. Like most spurfowls, it is restricted to Africa. It is a resident breeder in tropical west Africa, but there is a small and declining isolated population in Morocco.

The red-necked spurfowl or red-necked francolin, is a gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae that is a resident species in southern Africa.

The grey francolin is a species of francolin found in the plains and drier parts of the Indian subcontinent and Iran. This species was formerly also called the grey partridge, not to be confused with the European grey partridge. They are mainly ground-living birds and are found in open cultivated lands as well as scrub forest and their local name of teetar is based on their calls, a loud and repeated Ka-tee-tar...tee-tar which is produced by one or more birds. The term teetar can also refer to other partridges and quails. During the breeding season calling males attract challengers, and decoys were used to trap these birds especially for fighting.

The swamp francolin, also called swamp partridge, is a francolin species native to the foothills of the Himalayas in northern India and Nepal. It is considered extinct in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta in Bangladesh. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.

Arborophila is a bird genus in the family Phasianidae. The genus has the second most members within the Galliformes after Pternistis, although Arborophila species vary very little in bodily proportions with different species varying only in colouration/patterning and overall size. These are fairly small, often brightly marked partridges found in forest of eastern and southern Asia. Some species in this genus have small ranges, and are threatened by habitat loss and hunting.

Erckel's spurfowl, also known as Erckel's francolin, is a species of game bird in the family Phasianidae.

Harwood's spurfowl, also known as Harwood's Francolin, is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae. It is a grey-brown bird with red bill and tail, and red bare skin around the eyes. Both sexes have similar coloring, although the female is paler in color with a more extensive buff belly.

Hildebrandt's spurfowl is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae. It is found in Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Zambia. The species is named for Johann Maria Hildebrandt, who collected the first specimens in Kenya. The sexes differ markedly in their plumage and females are smaller than males.

Heuglin's spurfowl is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae. It is found in Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, and Uganda. The German explorer Theodor von Heuglin first described the species.

The Natal spurfowl or Natal francolin is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae. It is found in Botswana, Eswatini, Mozambique, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.

The grey-breasted spurfowl or grey-breasted francolin is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae. It is found only in Tanzania.

The crested francolin is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae. It is found in southern Africa. One of its subspecies, Ortygornis sephaena rovuma, is sometimes considered a separate species, Kirk's francolin.

The scaly spurfowl is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae. It is found in Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Kenya, Malawi, Nigeria, Rwanda, São Tomé and Príncipe, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda.

Rhizothera is a bird genus in the family Phasianidae, native to Malaysia and Indonesia. They are the only genus in the tribe Rhizotherini. Established by George Robert Gray in 1841, it contains the following species:

The Phasianinae are a subfamily of the pheasant family (Phasianidae) of landfowl, the order Galliformes. The subfamily includes true pheasants, tragopans, grouse, turkey and similar birds. Although this subfamily was considered monophyletic and separated from the partridges, francolins, and Old World quails (Perdicinae) till the early 1990s, molecular phylogenies have shown that this placement is paraphyletic. For example, some partridges (genus Perdix) are more closely affiliated to pheasants, whereas Old World quails and partridges from the genus Alectoris are closer to junglefowls. There are two clades in the Phasianinae: the erectile clade and the non-erectile clades. Both clades are believed to have diverged during the early Oligocene, about 30 million years ago.

Pternistis is a genus of galliform birds formerly classified in the spurfowl group of the partridge subfamily of the pheasant family. They are described as "partridge-francolins" in literature establishing their phylogenetic placement outside the monophyletic assemblage of true spurfowls. All species are endemic to Sub-Saharan Africa, excepted the double-spurred spurfowl. They are commonly known as spurfowls or francolins, but are closely related to jungle bush quail, Alectoris rock partridges, and Coturnix quail. The species are strictly monogamous, remaining mated indefinitely. They procure most of their food by digging. Spurfowls subsist almost entirely on roots, beans of leguminous shrubs and trees, tubers, and seeds, and feasting opportunistically on termites, ants, locusts, flowers, and fruit. Important predators are jackals, caracals, servals, and birds of prey, as well as herons and marabou storks.

Rollulinae is a bird subfamily containing the jungle and wood partridges. They are the most basal member of the family Phasianidae, having diverged during the late Eocene or early Oligocene, about 30-35 million years ago. Many taxonomists formerly placed this subfamily within the Perdicinae, but more recent studies have affirmed its existence, and it is accepted by taxonomic authorities such as the International Ornithological Congress.