
Waikato is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, the northern King Country, much of the Taupo District, and parts of Rotorua District. It is governed by the Waikato Regional Council.

Cambridge is a town in the Waipa District of the Waikato Region of the North Island of New Zealand. Situated 24 kilometres (15 mi) southeast of Hamilton, on the banks of the Waikato River, Cambridge is known as "The Town of Trees & Champions". The town has a population of 19,150, making it the largest town in the Waipa District, and third largest urban area in the Waikato.

Rodney District was a local government area in the northernmost part of New Zealand's Auckland Region from 1989 to 2010. It included Kawau Island. It was created from the amalgamation of Helensville Borough and Rodney County in 1989. The seat of Rodney District Council was at Orewa. Rodney District and Rodney County each took their names from Cape Rodney, which Captain James Cook named on 24 November 1769 after Admiral Sir George Brydges Rodney.
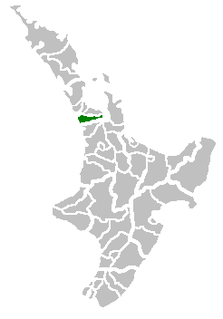
Franklin District was a New Zealand territorial authority that lay between the Auckland metropolitan area and the Waikato Plains. As a formal territory it was abolished on 31 October 2010 and divided between Auckland Council in the Auckland Region to the north and Waikato and Hauraki districts in the Waikato Region to the south and east. The Auckland portion is now part of the Franklin ward, which also includes rural parts of the former Manukau City.

Te Awamutu is a town in the Waikato region in the North Island of New Zealand. It is the council seat of the Waipa District and serves as a service town for the farming communities which surround it. Te Awamutu is located some 30 kilometres (19 mi) south of Hamilton on State Highway 3, one of the two main routes south from Auckland and Hamilton.

The Waipa River is in the Waikato region of the North Island of New Zealand. The headwaters are in the Rangitoto Range east of Te Kuiti. It flows north for 115 kilometres (71 mi), passing through Otorohanga and Pirongia, before flowing into the Waikato River at Ngaruawahia. It is the Waikato's largest tributary. The Waipa's main tributary is the Puniu River.

Waikato District is a territorial authority of New Zealand, in the northern part of Waikato Region, North Island. Waikato District is administered by the Waikato District Council, with headquarters in Ngaruawahia.
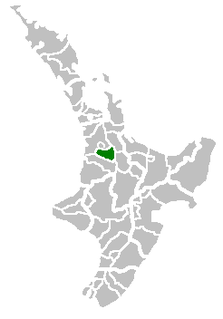
Waipa District is a municipality in the Waikato region of New Zealand that is administered by the Waipa District Council. Its most populous town is Cambridge. The seat of the council is at the second most populous town, Te Awamutu. The district is south and south-east of the city of Hamilton. It has five wards: Te Awamutu, Cambridge, Pirongia, Maungatautari and Kakepuku.

South Waikato District is a local government district in the Waikato Region of the North Island of New Zealand. It is located between the cities of Hamilton to the north, Rotorua to the east, Taupo to the south and Ruapehu District to the west.
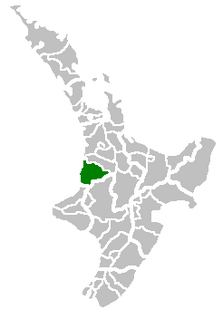
Waitomo District is a territorial authority, located in the Waikato region, at the north of the King Country area in the North Island of New Zealand. A small part of the district, the town of Tiroa, however, lies in the Manawatu-Wanganui region.

Ruapehu District is a territorial authority in the centre of New Zealand's North Island.
The Taupo District Council is a territorial authority that administers the Taupo District in the Central North Island of New Zealand. The district stretches from the small town of Mangakino in the northwest to the Tongariro National Park in the south, and east into the Kaingaroa Forest, covering 6,970 km2. It had a population of 37,200 as of the June 2018.

The Taupo District is a district in New Zealand. It covers 6,350 km² of land, as well as a further 610 km² of lake area, both in Lake Taupo, New Zealand's largest lake, and also in the smaller Lake Rotoaira. The district stretches from the small town of Mangakino in the northwest to the Tongariro National Park in the south, and east into the Kaingaroa Forest. The district's population is largely located in the two main centres, Taupo and Turangi.
The Waikato and King Country regions of New Zealand are built upon a basement of greywacke rocks, which form many of the hills. Much of the land to the west of the Waikato River and in the King Country to the south has been covered by limestone and sandstone, forming bluffs and a karst landscape. The volcanic cones of Karioi and Pirongia dominate the landscape near Raglan and Kawhia Harbours. To the east, the land has been covered with ignimbrite deposits from the Taupo Volcanic Zone. Large amounts of pumice from the Taupo Volcanic Zone have been deposited in the Waikato Basin and Hauraki Plains.

A district in New Zealand is a territorial authority area governed by a district council as a second-tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. They were formed as a result of local government reforms in 1989. There are 53 districts in New Zealand, and they do not include the 13 city councils, and the Chatham Islands Council. District councils serve a combination of rural and urban communities, while city councils administer the larger urban areas. Three districts are unitary authorities also performing the functions of a regional council.

Gore District is a municipality in the Southland region of the South Island of New Zealand.
State Highway 39 (SH 39) is a New Zealand state highway that forms a western bypass of the city of Hamilton. Gazetted in 1999, it is a generally quicker route to get between Auckland and New Plymouth as well as connecting to the Waitomo Caves, just south of the SH 39 southern terminus. The southernmost 14 km section has a concurrency with SH 31, as this highway has existed for much longer.

John William Ellis was a New Zealand businessman and mayor of Hamilton from 1917 to 1918.





















