
An explosive is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances.
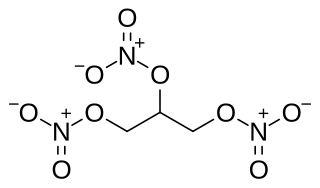
Nitroglycerin (NG), also known as trinitroglycerol (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless or pale yellow, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating glycerol with white fuming nitric acid under conditions appropriate to the formation of the nitric acid ester. Chemically, the substance is a nitrate ester rather than a nitro compound, but the traditional name is retained. Discovered in 1846 by Ascanio Sobrero, nitroglycerin has been used as an active ingredient in the manufacture of explosives, namely dynamite, and as such it is employed in the construction, demolition, and mining industries. It is combined with nitrocellulose to form double-based smokeless powder, used as a propellant in artillery and firearms since the 1880s.
Monopropellants are propellants consisting of chemicals that release energy through exothermic chemical decomposition. The molecular bond energy of the monopropellant is released usually through use of a catalyst. This can be contrasted with bipropellants that release energy through the chemical reaction between an oxidizer and a fuel. While stable under defined storage conditions, monopropellants decompose very rapidly under certain other conditions to produce a large volume of its own energetic (hot) gases for the performance of mechanical work. Although solid deflagrants such as nitrocellulose, the most commonly used propellant in firearms, could be thought of as monopropellants, the term is usually reserved for liquids in engineering literature.
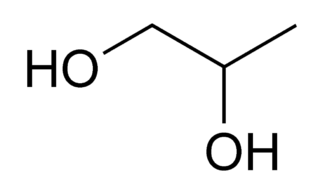
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid. It is almost odorless and has a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. As it contains two alcohol groups, it is classified as a diol. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.
Nitromethane, sometimes shortened to simply "nitro", is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH
3NO
2. It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel additive in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft.

A plasticizer is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.

Smokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to black powder. Because of their similar use, both the original black powder formulation and the smokeless propellant which replaced it are commonly described as gunpowder. The combustion products of smokeless powder are mainly gaseous, compared to around 55% solid products for black powder. In addition, smokeless powder does not leave the thick, heavy fouling of hygroscopic material associated with black powder that causes rusting of the barrel.

Hydroxylammonium nitrate or hydroxylamine nitrate (HAN) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula [NH3OH]+[NO3]−. It is a salt derived from hydroxylamine and nitric acid. In its pure form, it is a colourless hygroscopic solid. It has potential to be used as a rocket propellant either as a solution in monopropellants or bipropellants. Hydroxylammonium nitrate (HAN)-based propellants are a viable and effective solution for future "green" propellant-based missions, as it offers 50% higher performance for a given propellant tank compared to commercially used hydrazine.
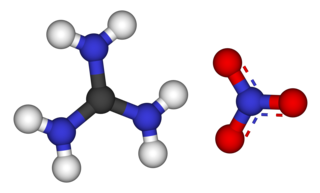
Guanidine nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula [C(NH2)3]NO3. It is a colorless, water-soluble salt. It is produced on a large scale and finds use as precursor for nitroguanidine, fuel in pyrotechnics and gas generators. Its correct name is guanidinium nitrate, but the colloquial term guanidine nitrate is widely used.
Glycol ethers are a class of chemical compounds consisting of alkyl ethers that are based on glycols such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. They are commonly used as solvents in paints and cleaners. They have good solvent properties while having higher boiling points than the lower-molecular-weight ethers and alcohols.
Dibutyl sebacate (DBS) is an organic chemical, a dibutyl ester of sebacic acid. Its main use is as a plasticizer in production of plastics, namely cellulose acetate butyrate, cellulose acetate propionate, ethyl cellulose, polyvinyl butyral, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, and many synthetic rubbers and other plastics. It can be used for plastics in use in the food packaging industry, in plastics used for medical devices, and for pharmaceutical applications, e.g. as a plasticizer for film coating of tablets, beads, and granules. It is also used as a lubricant in shaving lotions, and a flavoring additive in non-alcoholic beverages, ice cream, ices, candy, and baked goods. It provides excellent compatibility with a range of plastic materials, superior properties at low temperatures, and good oil resistivity. Its other names include Morflex, Kodaflex, polycizer, Proviplast 1944 and PX 404. Dibutyl sebacate is also used as a desensitizer in Otto fuel II, a torpedo monopropellant.

Propylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN, 1,2-propylene glycol dinitrate, or 1,2-propanediol dinitrate) is an organic chemical, an ester of nitric acid and propylene glycol. It is structurally similar to nitroglycerin, except that it has one fewer nitrate group. It is a characteristically and unpleasantly smelling colorless liquid, which decomposes at 121 °C, below its boiling point. It is flammable and explosive. It is shock-sensitive and burns with a clean flame producing water vapor, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen gas.

2-Nitrodiphenylamine is an organic chemical with the formula C6H5NHC6H4NO2. It is a nitrated derivative of diphenylamine. It is a red solid, usually found in form of flakes or powder. It is polar but hydrophobic.
A pyrotechnic composition is a substance or mixture of substances designed to produce an effect by heat, light, sound, gas/smoke or a combination of these, as a result of non-detonative self-sustaining exothermic chemical reactions. Pyrotechnic substances do not rely on oxygen from external sources to sustain the reaction.
Tetranitromethane or TNM is an organic oxidizer with chemical formula C(NO2)4. Its chemical structure consists of four nitro groups attached to one carbon atom. In 1857 it was first synthesised by the reaction of sodium cyanoacetamide with nitric acid.

Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN) is an explosive nitrated alcohol ester with the formula C4H8N2O7. While chemically similar to numerous other high explosives, pure diethylene glycol dinitrate is difficult to ignite or detonate. Ignition typically requires localized heating to the decomposition point unless the DEGDN is first atomized.
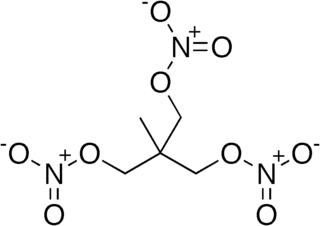
Trimethylolethane trinitrate (TMETN), also known as metriol trinitrate or nitropentaglycerin, is a nitrate ester. It is a high explosive similar to nitroglycerin. It is a transparent oily liquid, colorless to light brown. It is odorless. It is used in some solid propellants and smokeless powders as a plasticizer. Its chemical formula is CH3−C(CH2−O−NO2)3.
Nitrous oxide fuel blend propellants are a class of liquid rocket propellants that were intended in the early 2010s to be able to replace hydrazine as the standard storable rocket propellent in some applications.
Bulk loaded liquid propellants are an artillery technology that was pursued at the U.S. Army Research Laboratory and U.S. Naval Weapons Center from the 1950s through the 1990s. The advantages would be simpler guns and a wider range of tactical and logistic options. Better accuracy and tactical flexibility would theoretically come from standard shells with varying propellant loads, and logistic simplification by eliminating varying powder loads.
Cavea-B is a mixture of 1,4-Diaza-1,2,4-trimethyl bicyclo[2.2.2]octane dinitrate, dissolved in white fuming nitric acid. It was researched during the 1960s by teams working at the Naval Air Rocket Test Station as an alternative to the more commonly used hydrazine monopropellant for use in spacecraft's attitude control and thruster systems. It was derived from an earlier, similar formulation which came to be called Cavea-A, which showed less promise due to its excessively high melting point.











