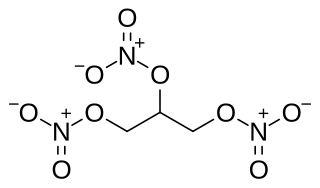
Nitroglycerin (NG), also known as trinitroglycerol (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless or pale yellow, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating glycerol with white fuming nitric acid under conditions appropriate to the formation of the nitric acid ester. Chemically, the substance is a nitrate ester rather than a nitro compound, but the traditional name is retained. Discovered in 1846 by Ascanio Sobrero, nitroglycerin has been used as an active ingredient in the manufacture of explosives, namely dynamite, and as such it is employed in the construction, demolition, and mining industries. It is combined with nitrocellulose to form double-based smokeless powder, used as a propellant in artillery and firearms since the 1880s.
Monopropellants are propellants consisting of chemicals that release energy through exothermic chemical decomposition. The molecular bond energy of the monopropellant is released usually through use of a catalyst. This can be contrasted with bipropellants that release energy through the chemical reaction between an oxidizer and a fuel. While stable under defined storage conditions, monopropellants decompose very rapidly under certain other conditions to produce a large volume of its own energetic (hot) gases for the performance of mechanical work. Although solid deflagrants such as nitrocellulose, the most commonly used propellant in firearms, could be thought of as monopropellants, the term is usually reserved for liquids in engineering literature.
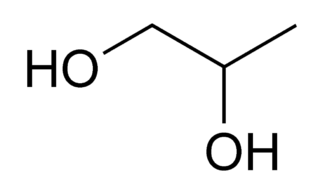
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid. It is almost odorless and has a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. As it contains two alcohol groups, it is classified as a diol. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.

1,2-Dibromoethane, also known as ethylene dibromide (EDB), is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula C
2H
4Br
2. Although trace amounts occur naturally in the ocean, where it is probably formed by algae and kelp, substantial amounts are produced industrially. It is a dense colorless liquid with a faint, sweet odor, detectable at 10 ppm. It is a widely used and sometimes-controversial fumigant. The combustion of 1,2-dibromoethane produces hydrogen bromide gas that is significantly corrosive.
Monomethylhydrazine (MMH) is a highly toxic, volatile hydrazine derivative with the chemical formula CH6N2. It is used as a rocket propellant in bipropellant rocket engines because it is hypergolic with various oxidizers such as nitrogen tetroxide and nitric acid. As a propellant, it is described in specification MIL-PRF-27404.
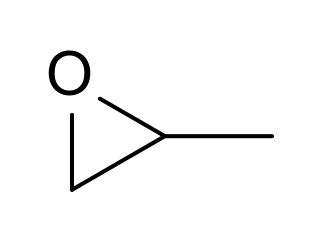
Propylene oxide is an acutely toxic and carcinogenic organic compound with the molecular formula C3H6O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture.

Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion, is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. In response to safety concerns, the less toxic but still dangerous analogue parathion methyl was later developed.

Otto fuel II is a monopropellant mixture of chiefly propylene glycol dinitrate that is used to drive torpedoes and other weapon systems. It was invented by Otto Reitlinger in 1963. Otto fuel II, sometimes known simply as Otto fuel, is not related to the Otto cycle; it is named after Reitlinger and for being the second iteration of the fuel. It was developed by the US Navy and the first torpedo to use it was the Mark 48 torpedo in the 1960s.

Pentaborane(9) is an inorganic compound with the formula B5H9. It is one of the most common boron hydride clusters, although it is a highly reactive compound. Because of its high reactivity with oxygen, it was once evaluated as rocket or jet fuel. Like many of the smaller boron hydrides, pentaborane is colourless, diamagnetic, and volatile. It is related to pentaborane(11).

Chloroprene (IUPAC name 2-chlorobuta-1,3-diene) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH2=CCl−CH=CH2. Chloroprene is a colorless volatile liquid, almost exclusively used as a monomer for the production of the polymer polychloroprene, better known as neoprene, a type of synthetic rubber.
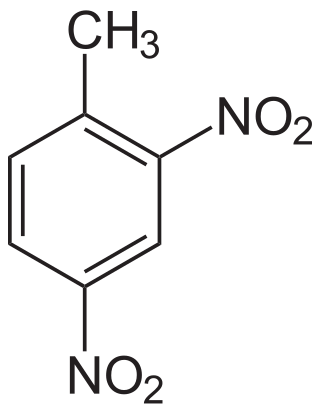
2,4-Dinitrotoluene (DNT) or dinitro is an organic compound with the formula C7H6N2O4. This pale yellow crystalline solid is well known as a precursor to trinitrotoluene (TNT) but is mainly produced as a precursor to toluene diisocyanate.

Ethylene glycol dinitrate, abbreviated EGDN and NGC, also known as Nitroglycol, is a colorless, oily, explosive liquid obtained by nitrating ethylene glycol. It is similar to nitroglycerine in both manufacture and properties, though it is more volatile and less viscous. Unlike nitroglycerine, the chemical has a perfect oxygen balance, meaning that its ideal exothermic decomposition would completely convert it to low energy carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen gas, with no excess unreacted substances, without needing to react with anything else.

Allyl alcohol is an organic compound with the structural formula CH2=CHCH2OH. Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers. Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols.
2-Chloroethanol (also called ethylene chlorohydrin or glycol chlorohydrin) is an organic chemical compound with the chemical formula HOCH2CH2Cl and the simplest beta-halohydrin (chlorohydrin). This colorless liquid has a pleasant ether-like odor. It is miscible with water. The molecule is bifunctional, consisting of both an alkyl chloride and an alcohol functional group.
Perchloryl fluoride is a reactive gas with the chemical formula ClO
3F. It has a characteristic sweet odor that resembles gasoline and kerosene. It is toxic and is a powerful oxidizing and fluorinating agent. It is the acid fluoride of perchloric acid.

Nitroethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula C2H5NO2. Similar in many regards to nitromethane, nitroethane is an oily liquid at standard temperature and pressure. Pure nitroethane is colorless and has a fruity odor.
Tetranitromethane or TNM is an organic oxidizer with chemical formula C(NO2)4. Its chemical structure consists of four nitro groups attached to one carbon atom. In 1857 it was first synthesised by the reaction of sodium cyanoacetamide with nitric acid.

Ethyl acrylate is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHCO2CH2CH3. It is the ethyl ester of acrylic acid. It is a colourless liquid with a characteristic acrid odor. It is mainly produced for paints, textiles, and non-woven fibers. It is also a reagent in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical intermediates.

1,2-Dichloropropane is an organic compound classified as a chlorocarbon. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet odor. it is obtained as a byproduct of the production of epichlorohydrin, which is produced on a large scale.
Diglycidyl ethers are chemical compounds used as a reactive diluents for epoxy resin. Other uses include treating textiles and stabilizing chlorinated organic compounds. Diglycidyl ether itself is extremely toxic, and can prove fatal or cause permanent damage if inhaled or consumed orally. As a class of compounds, there are a number of them available commercially with much lower toxicity profiles. One such example is epoxy resin itself Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether.














