Nitric oxide synthase, inducible is an enzyme which is encoded by the NOS2 gene in humans and mice. [5]
Nitric oxide synthase, inducible is an enzyme which is encoded by the NOS2 gene in humans and mice. [5]
Three related pseudogenes are located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [6]
Nitric oxide synthase is expressed in epithelial cells of the liver, lung and bone marrow. It is inducible by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and certain cytokines.[ citation needed ]
Nitric oxide is a reactive free radical mediating in neurotransmission, antimicrobial and antitumoral activities.[ citation needed ] In mice, the function of Nos2 in immunity against a number of viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites has been well characterized, whereas in humans the role of NOS2 has remained elusive and controversial. [7] Nos2 is important for protective immunity against CMV. [8]
Caveolin 1 has been shown to interact with Nitric oxide synthase 2A. [9] and Rac2. [10]
Autosomal recessive NOS2 deficiency has been described in mice. They lack the gene encoding nitric oxide synthase 2 (Nos2) and are susceptible to murine CMV infection. [11]
In February 2020, the same autosomal recessive, complete NOS2 deficiency was described in a human. A 51-year-old previously healthy person died after 29 months of progressive CMV infection due to respiratory failure secondary to CMV pneumonitis, CMV encephalitis, and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Whole-exome sequencing on genomic DNA from his blood showed he had homozygous variants in five genes. The only loss-of-function variant was a homozygous frameshift mutation in nitric oxide synthase 2. This condition is extremely rare, occurring in fewer than 1 per million persons. [8]

Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and peristalsis, and is involved in angiogenesis and neural development. It may function as a retrograde neurotransmitter. Nitric oxide is mediated in mammals by the calcium-calmodulin controlled isoenzymes eNOS and nNOS. The inducible isoform, iNOS, involved in immune response, binds calmodulin at physiologically relevant concentrations, and produces NO as an immune defense mechanism, as NO is a free radical with an unpaired electron. It is the proximate cause of septic shock and may function in autoimmune disease.
In molecular biology, caveolins are a family of integral membrane proteins that are the principal components of caveolae membranes and involved in receptor-independent endocytosis. Caveolins may act as scaffolding proteins within caveolar membranes by compartmentalizing and concentrating signaling molecules. They also induce positive (inward) membrane curvature by way of oligomerization, and hairpin insertion. Various classes of signaling molecules, including G-protein subunits, receptor and non-receptor tyrosine kinases, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), and small GTPases, bind Cav-1 through its 'caveolin-scaffolding domain'.
Gasotransmitters is a class of neurotransmitters. The molecules are distinguished from other bioactive endogenous gaseous signaling molecules based on a need to meet distinct characterization criteria. Currently, only nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide are accepted as gasotransmitters.
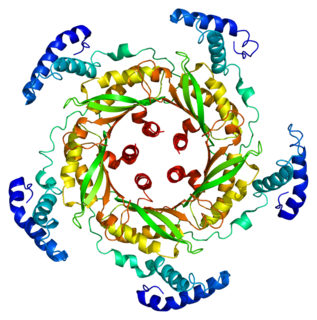
GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH) (EC 3.5.4.16) is a member of the GTP cyclohydrolase family of enzymes. GTPCH is part of the folate and biopterin biosynthesis pathways. It is responsible for the hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate (7,8-DHNP-3'-TP, 7,8-NH2-3'-TP).

Caveolin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAV3 gene. Alternative splicing has been identified for this locus, with inclusion or exclusion of a differentially spliced intron. In addition, transcripts utilize multiple polyA sites and contain two potential translation initiation sites.
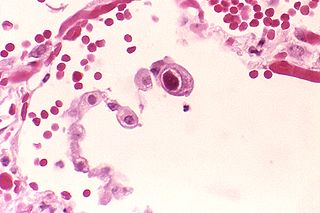
Human betaherpesvirus 5, also called human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), is species of virus in the genus Cytomegalovirus, which in turn is a member of the viral family known as Herpesviridae or herpesviruses. It is also commonly called CMV. Within Herpesviridae, HCMV belongs to the Betaherpesvirinae subfamily, which also includes cytomegaloviruses from other mammals. CMV is a double-stranded DNA virus.

Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STAT2 gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. This protein is critical to the biological response of type I interferons (IFNs). STAT2 sequence identity between mouse and human is only 68%.

Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases. eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. Therefore, a functional eNOS is essential for a healthy cardiovascular system.

Caveolin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAV1 gene.
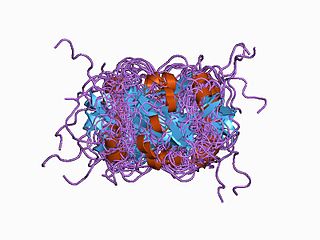
Nitric oxide synthase 1 (neuronal), also known as NOS1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS1 gene.

ATP synthase F1 subunit alpha, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5F1A gene.

Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HNRNPL gene.

Nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein (NOS1AP) also known as carboxyl-terminal PDZ ligand of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein (CAPON) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOS1AP gene.

Para-hydroxybenzoate—polyprenyltransferase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the COQ2 gene.

Cavin-2 or Serum deprivation-response protein (SDPR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDPR gene. Cavin-2 is highly expressed in a variety of human endothelial cells.

NF-kappa-B-repressing factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NKRF gene.

Nitric oxide synthase-interacting protein is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOSIP gene.
Nitric oxide is a molecule and chemical compound with chemical formula of NO. In mammals including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule involved in several physiological and pathological processes. It is a powerful vasodilator with a half-life of a few seconds in the blood. Standard pharmaceuticals such as nitroglycerine and amyl nitrite are precursors to nitric oxide. Low levels of nitric oxide production are typically due to ischemic damage in the liver.
In molecular biology mir-939 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
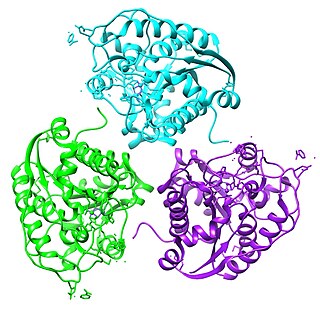
Arginase, type II is an arginase protein that in humans is encoded by the ARG2 gene.