 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Verquvo |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Soluble guanylate cyclase activator |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.247.370 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
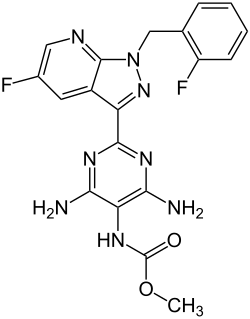
| Formula | C19H16F2N8O2 |
| Molar mass | 426.388 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Vericiguat, sold under the brand name Verquvo, is a medication used to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization in certain patients with heart failure after a recent acute decompensation event. [3] [4] [7] It is taken by mouth. [3] [4] [7] Vericiguat is a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator. [3]
Contents
- Medical uses
- Adverse effects
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacokinetics
- History
- Society and culture
- Legal status
- References
- Further reading
- External links
Common side effects include low blood pressure and low red cell count (anemia). [4] [7]
It was approved for medical use in the United States in January 2021, [4] [8] and for use in the European Union in July 2021. [7]