
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year.

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.
Celluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common for its use as photographic film before the advent of safer methods, celluloid's common present-day uses are for manufacturing table tennis balls, musical instruments, combs, office equipment, fountain pen bodies, and guitar picks.

Celanese Corporation, formerly known as Hoechst Celanese, is an American technology and specialty materials company headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is a Fortune 500 corporation. The company is the world's leading producer of acetic acid, producing about 1.95 million tonnes per year, representing approximately 25% of global production. Celanese is also the world's largest producer of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM).

Phthalates, or phthalate esters, are esters of phthalic acid. They are mainly used as plasticizers, i.e., substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity. They are used primarily to soften polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Note that while phthalates are usually plasticizers, not all plasticizers are phthalates. The two terms are specific and unique and cannot be used interchangeably.

In biochemistry, cellulose acetate refers to any acetate ester of cellulose, usually cellulose diacetate. It was first prepared in 1865. A bioplastic, cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and as a frame material for eyeglasses; it is also used as a synthetic fiber in the manufacture of cigarette filters and playing cards. In photographic film, cellulose acetate film replaced nitrate film in the 1950s, being far less flammable and cheaper to produce.

Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materials, such as plastic. A laminate is a layered object or material assembled using heat, pressure, welding, or adhesives. Various coating machines, machine presses and calendering equipment are used.
Polymer chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that focuses on the structures of chemicals, chemical synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules. The principles and methods used within polymer chemistry are also applicable through a wide range of other chemistry sub-disciplines like organic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and physical chemistry. Many materials have polymeric structures, from fully inorganic metals and ceramics to DNA and other biological molecules. However, polymer chemistry is typically related to synthetic and organic compositions. Synthetic polymers are ubiquitous in commercial materials and products in everyday use, such as plastics, and rubbers, and are major components of composite materials. Polymer chemistry can also be included in the broader fields of polymer science or even nanotechnology, both of which can be described as encompassing polymer physics and polymer engineering.

A plasticizer is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.

Otto fuel II is a monopropellant mixture of chiefly propylene glycol dinitrate that is used to drive torpedoes and other weapon systems. It was invented by Otto Reitlinger in 1963. Otto fuel II, sometimes known simply as Otto fuel, is not related to the Otto cycle; it is named after Reitlinger and for being the second iteration of the fuel. It was developed by the US Navy and the first torpedo to use it was the Mark 48 torpedo in the 1960s.

Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), also known as poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) (PEVA), is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. The weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 50%, with the remainder being ethylene. There are three different types of EVA copolymer, which differ in the vinyl acetate (VA) content and the way the materials are used.

Cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP), also known as cellacefate (INN) and cellulosi acetas phthalas, is a commonly used polymer phthalate in the formulation of pharmaceuticals, such as the enteric coating of tablets or capsules and for controlled release formulations. It is a cellulose polymer where about half of the hydroxyls are esterified with acetyls, a quarter are esterified with one or two carboxyls of a phthalic acid, and the remainder are unchanged. It is a hygroscopic white to off-white free-flowing powder, granules, or flakes. It is tasteless and odorless, though may have a weak odor of acetic acid. Its main use in pharmaceutics is with enteric formulations. It can be used together with other coating agents, e.g. ethyl cellulose. Cellulose acetate phthalate is commonly plasticized with diethyl phthalate, a hydrophobic compound, or triethyl citrate, a hydrophilic compound; other compatible plasticizers are various phthalates, triacetin, dibutyl tartrate, glycerol, propylene glycol, tripropionin, triacetin citrate, acetylated monoglycerides, etc.

Soft plastic bait, commonly known as soft lure, soft plastics, plastic bait, worm lure or just worm, is any of a range of elastomer-based fishing lures termed so because of their flexible, flesh-like texture. Soft lures are available in a large range of colours, sizes and particularly shapes, and are typically impaled directly onto a fishing hook like an ordinary bait.
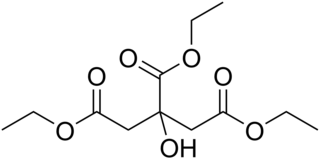
Triethyl citrate is an ester of citric acid. It is a colorless, odorless liquid used as a food additive, emulsifier and solvent to stabilize foams, especially as whipping aid for egg white. It is also used in pharmaceutical coatings and plastics.

Zinc borate is an inorganic compound, a borate of zinc. It is a white crystalline or amorphous powder insoluble in water. Its toxicity is low. Its melting point is 980 °C.

Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin plastic membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces.

Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be molded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to their widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives.

Conservation and restoration of objects made from plastics is work dedicated to the conservation of objects of historical and personal value made from plastics. When applied to cultural heritage, this activity is generally undertaken by a conservator-restorer.
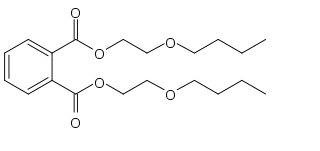
Dibutoxy ethyl phthalate is an organic compound and phthalate ester, baring 2-butoxyethanol groups. It is used as a plasticizer in polyvinyl chloride, polyvinyl acetate and cellulose acetate. Like most phthalates it is non-volatile, and remains liquid over a wide range of temperatures. Although its water solubility is low, it remains one of the most water soluble of the common phthalates.
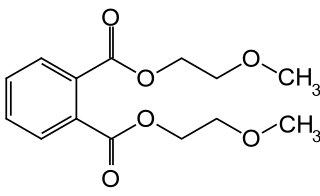
Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate, also commonly di(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate (DMEP), is a phthalate ester baring 2-methoxyethanol groups. Historically it was used as a plasticizer in cellulose acetate plastics, it is now largely banned owing to concerns over its effects to human health.


















