Related Research Articles

Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.

CATIA is a multi-platform software suite for computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), computer-aided engineering (CAE), 3D modeling and product lifecycle management (PLM), developed by the French company Dassault Systèmes.
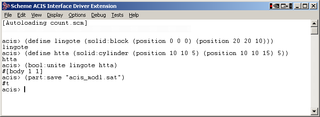
The 3D ACIS Modeler (ACIS) is a geometric modeling kernel developed by Spatial Corporation, part of Dassault Systemes. ACIS is used by many software developers in industries such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), computer-aided engineering (CAE), architecture, engineering and construction (AEC), coordinate-measuring machine (CMM), 3D animation, and shipbuilding. ACIS provides software developers and manufacturers the underlying 3D modeling functionality.

Dassault Systèmes SE is a French multinational software corporation which develops software for 3D product design, simulation, manufacturing and other 3D related products.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises.

SolidWorks is a brand within Dassault Systèmes that develops and markets solid modeling computer-aided design, computer-aided engineering, 3D CAD design and collaboration, analysis, and product data management software. It developed the world's first 3D CAD application that ran on a desktop PC.

Computervision, Inc. (CV) was an early pioneer in Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM). Computervision was founded in 1969 by Marty Allen and Philippe Villers, and headquartered in Bedford, Massachusetts, United States. Its early products were built on a Data General Nova platform. Starting around 1975, Computervision built its own "CGP" Nova-compatible 16-bit computers with added instructions optimized for graphics applications and using its own operating system known as Computervision Graphic Operating System (CGOS). In the 1980s, Computervision rewrote their code to operate on Unix-based platforms.
Martin Edward Newell is a British-born computer scientist specializing in computer graphics who is perhaps best known as the creator of the Utah teapot computer model.
Collaborative product development (CPD) is a business strategy, work process and collection of software applications that facilitates different organizations to work together on the development of a product. It is also known as collaborative product definition management (cPDM).
A geometric modeling kernel is a solid modeling software component used in computer-aided design (CAD) packages. Available modelling kernels include:

AVEVA Group plc is a British multinational information technology consulting company headquartered in Cambridge, England. The company started as the Computer-Aided Design Centre which was created in Cambridge in 1967 by the UK Ministry of Technology and Cambridge University.
Delcam is a supplier of advanced CAD/CAM software for the manufacturing industry. The company has grown steadily since being founded formally in 1977, after initial development work at Cambridge University, UK. It is now a global developer of product design and manufacturing software, with subsidiaries and joint ventures in North America, South America, Europe and Asia with a total staff of over 800 people and local support provided from over 300 re-seller offices worldwide. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange until 6 February 2014, when it was acquired by Autodesk. It now operates as a wholly owned, independently operated subsidiary of Autodesk.
Richard G. Newell is a British businessman and technologist in the software industry in Computer aided design (CAD) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
Vellum Investment Partners, LLC, dba Ashlar-Vellum, is an American software company that develops Computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D modeling software for both the Macintosh and Microsoft Windows platforms. Ashlar-Vellum's interface, designed in 1988 by Dr. Martin Newell and Dan Fitzpatrick, featured an automated Drafting Assistant that found useful points in the geometry and allowed the artist to quickly connect to locations like the "midpoint" or "tangent".

Quantapoint, Inc. is a technology and services company that develops and uses patented 3D laser scanning hardware and software. Quantapoint creates a Digital Facility using 3D laser scanning and then provides visualization, analysis, quality control, decision support and documentation services for buildings, museums, refineries, chemical plants, nuclear and fossil-fuel power plants, offshore platforms and other structures.
MEDUSA4 is a CAD program used in the areas of mechanical and plant engineering by manufacturers and Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) companies. The system's history is closely tied to the beginnings of mainstream CAD and the research culture fostered by Cambridge University and the UK government as well as the resulting transformation of Cambridge into a world-class tech centre in the 1980s.
MPDS, the MEDUSA Plant Design System, is a suite of plant engineering applications for 2D/3D layout, design, and modeling of process plants, factories, or installations. The system's history is closely tied to the very beginnings of mainstream CAD and the research culture fostered by Cambridge University and the UK government including the resulting "Cambridge Phenomenon " MPDS was initially developed for 3D plant design and layout and piping design. Today, the software includes modules for 2D/3D factory layout, process, instrumentation diagrams (P&ID), mechanical handling systems design, steel design, ducting (HVAC) design, electrical design, and hangers and supports Design. The latest version, MPDS4 5.2.1, was released for Microsoft Windows and Sun Solaris in February 2014.
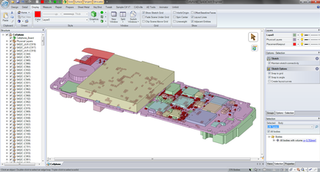
SpaceClaim is a solid modeling CAD software that runs on Microsoft Windows and developed by SpaceClaim Corporation. The company is headquartered in Concord, Massachusetts.
References
- ↑ "Exploding the Myths of UK Innovation Policy: How 'Soft Companies' and R&D Contracts for Customers Drive the Growth of the Hi-Tech Economy" (PDF). aveva.com. January 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 December 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2012. by David Connell and Jocelyn Probert Centre for Business Research, University of Cambridge
- ↑ "AVEVA PDMS - Full release history". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2015.