The Naples Metro is the rapid transit system serving the city of Naples, Italy. The system comprises three underground rapid transit lines.

The Genoa Metro is a rapid transit consisting of a single line that connects the centre of Genoa, Italy with the suburb of Rivarolo Ligure, to the north-west of the city centre. The service is currently managed by Azienda Mobilità e Trasporti (AMT), which provides public transport for the city of Genoa.

Palermo Centrale is the main railway station of the Italian city of Palermo, capital of Sicily. It is one of the most important "FS" stations of Italy. Along with Catania Centrale, Messina Centrale and Syracuse it is one of the most important stations of its region. It is owned by the Ferrovie dello Stato, the national rail company of Italy.

The Bari–Barletta railway is a regional railway line in Apulia, Italy, managed by the private company Ferrotramviaria.
Ferrotramviaria is a private railway company of Italy. Based in Bari, in the Apulia region, it manages the Ferrovie del Nord Barese network, composed by the Bari–Barletta railway and the Bari metropolitan railway service.

The Livorno–Rome railway is one of the trunk lines of the Italian railway network. It connects Italy’s northwest with its south, running along the Tyrrhenian coast between the Italian regions of Tuscany and Lazio, through the provinces of Livorno, Grosseto, Viterbo and Rome. The line is double track and is fully electrified at 3,000 V DC. Passenger traffic is managed by Trenitalia.

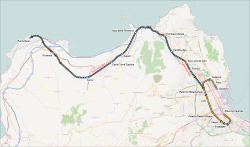
Punta Raisi railway station, is located within Palermo Airport in Cinisi, near Palermo, Sicily, Italy. Opened in 2004, the station is the northwestern terminus of the Palermo Passante railway, and forms part of the Palermo Metro.

Palermo Notarbartolo is one of the main railway stations serving the city and comune of Palermo, capital of the region of Sicily in Italy. Opened in 1974, it is the second most important station in Palermo, after Palermo Centrale. It forms part of the Palermo–Trapani railway, and is also the junction station for a branch line to Palermo Giachery.

The Bari metropolitan railway service is a commuter rail service in the Italian city Bari. It consists of two lines, joining the central railway station, located in the city centre, with the dormitory suburb San Paolo and with the ″Karol Wojtyła″ Airport and the city of Bitonto.
The Trento–Venice railway is an Italian state-owned railway line connecting Trento, in Trentino-Alto Adige, to Mestre, a suburb of Venice, in the Veneto region. At Mestre, it connects to the main line from Verona.

The Genoa urban railway service is operated by Trenitalia on the lines around the city of Genoa.

The Venice–Trieste railway is a railway line in Italy.

The Bologna–Ancona railway is an Italian railway that connects the city of Bologna with the city of Ancona, passing through the Po Valley to Rimini and along the Adriatic coast for the rest of the line.

Reggio di Calabria Santa Caterina railway station is a railway station of the Italian city of Reggio Calabria, Calabria. Part of the Battipaglia–Reggio di Calabria railway, it serves the quartiere of Santa Caterina and the port of Reggio.

The Empoli–Siena–Chiusi railway is an Italian railway that connects Empoli and Siena to the Florence–Rome railway at Chiusi. The route between Empoli and Siena follows the valleys of Elsa river as far as Poggibonsi and then the Staggia stream, which were very convenient when the line was planned. The route is in fact flat and substantially straight from Empoli to Poggibonsi, then ascends with wide and long curves through the hills of central Tuscany to Siena.

The Rome–Fiumicino railway is an urban railway line in Rome.
The Parma–La Spezia railway is the railway line that connects Parma, Italy with the Genoa–Pisa railway near La Spezia over the Cisa Pass through the Apennines. The route is approximately 120 kilometres long. Its Italian name derives from the town of Pontremoli, one of the main towns it passes through.

The Udine–Trieste railway is an Italian state railway line that connects Udine and Trieste running through the central and eastern part of Friuli Venezia Giulia.

The Terontola–Foligno railway is an electrified, standard-gauge Italian railway that connects the Florence–Rome railway in Terontola-Cortona with the Rome–Ancona railway in Foligno, passing through Perugia and Assisi.