San Marino is a small European republic, with limited public transport facilities. It is an enclave in central Italy. The principal public transport links involve buses, helicopters, and an aerial tramway. There was a public electric railway network, a small part of which has been preserved and returned to service in 2012 as a tourist attraction.

Milano Centrale is the main railway station of the city of Milan, Italy, and is the largest railway station in Europe by volume. The station is a terminus and located at the northern end of central Milan. It was officially inaugurated in 1931 to replace the old central station, which was a transit station but with a limited number of tracks and space, so could not handle the increased traffic caused by the opening of the Simplon Tunnel in 1906.

Pianoro is a town and comune in the province of Bologna in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy, in the hills of the Tusco-Emilian Apennines, 200 metres (660 ft) above sea level.

The Towers of Bologna are a group of medieval structures in Bologna, Italy. The two most prominent ones remaining, known as the Two Towers, are a landmark of the city.

Vittorio Emanuele is a station on Line A of the Rome Metro. The station was inaugurated in 1980 and is sited underground, beneath Piazza Vittorio Emanuele II, which gives it its name, in the Esquilino rione.

The Gruppo Torinese Trasporti (GTT) is a public benefit corporation responsible for public transportation in the provinces of Alessandria, Cuneo, Asti and the Metropolitan City of Turin. It was created in 2003 from the merge of ATM and SATTI, the latter responsible for railway connection in the province of Turin as well as for the Turin metro. GTT is now wholly owned by the Turin City Hall.

Turin is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is mainly on the western bank of the Po River, below its Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 847,287 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million.

The current tram system in Rome, Italy, is a leftover from what once was the largest tram system in Italy. With its fragmented structure, it does not currently function as a backbone of the city's public transport. The system is owned and operated by Azienda Tranvie e Autobus del Comune di Roma.

Duomo is an interchange station serving Lines 1 and 3 of the Milan Metro.

The Milan tramway network is part of the public transport network of Milan, Italy, operated by Azienda Trasporti Milanesi (ATM).

The Bologna trolleybus system is part of the public transport network of the city and comune of Bologna, in the region of Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy. While being in operation since 1991, the current system comprises five urban routes: 13, 14, 15, 32 and 33. Additional routes are presently under construction.

Messina Marittima railway station is an interchange station for train and ferry services into and out of the city and comune of Messina, on the island of Sicily, Italy. Opened in 1889 and was rebuilt between 1937 and 1939. It forms part of the Palermo–Messina and Messina–Syracuse railways.

The Bologna–Ancona railway is an Italian railway that connects the city of Bologna with the city of Ancona, passing through the Po Valley to Rimini and along the Adriatic coast for the rest of the line.

The Porta Saragozza of Bologna was one of the gates or portals in the medieval walls of this city.

The Piazza di Porta Ravegnana is a city square in the central of Bologna, region of Emilia-Romagna, Italy. The Piazza, located some four blocks east of the Piazza Maggiore and Cathedral of Bologna, is the site of the Two Towers of Bologna.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Treviso in the Veneto region of Italy.
Trasporto Passeggeri Emilia-Romagna is a public company overseeing public transportation in the Metropolitan City of Bologna, in the province of Ferrara and in parts of the provinces of Modena and Ravenna, Italy.
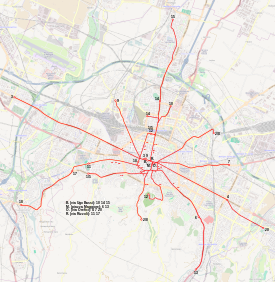
The Bologna tramway network is a tramway network under construction in Bologna, Italy.