
The Formicinae are a subfamily within the Formicidae containing ants of moderate evolutionary development.

Ponerinae, the ponerine ants, is a subfamily of ants in the Poneromorph subfamilies group, with about 1,600 species in 47 extant genera, including Dinoponera gigantea - one of the world's largest species of ant. Mated workers have replaced the queen as the functional egg-layers in several species of ponerine ants. In such queenless species, the reproductive status of workers can only be determined through ovarian dissections.

Tapinoma is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dolichoderinae. The genus currently comprises 74 described species distributed worldwide in tropical and temperate regions. Members of are generalized foragers, nesting in a wide variety of habitats, ranging from grasslands, open fields, woodlands, to inside buildings. The majority of species nest in the ground under objects such as stones or tree logs, other species build nests under bark of logs and stumps, in plant cavities, insect galls or refuse piles.

Paratrechina is one of seven ant genera in the Prenolepis genus-group from the subfamily Formicinae. Six species are included in Paratrechina; one of which, the longhorn crazy ant, is a widespread, pantropical pest.

Crematogaster is an ecologically diverse genus of ants found worldwide, which are characterised by a distinctive heart-shaped gaster (abdomen), which gives them one of their common names, the Saint Valentine ant. Members of this genus are also known as cocktail ants because of their habit of raising their abdomens when alarmed. Most species are arboreal (tree-dwelling). These ants are sometimes known as acrobat ants.
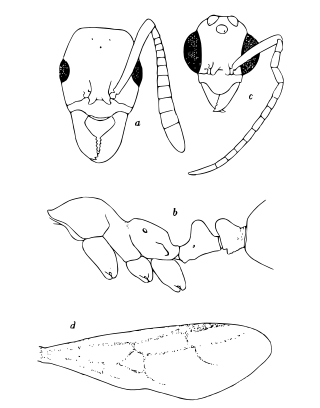
Megalomyrmex is a genus of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae. The genus is known only from the Neotropics, where some of the species are specialized parasites or predators of Attini.

Tetramorium is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae that includes more than 520 species. These ants are also known as pavement ants.

Acropyga is a genus of small formicine ants. Some species can be indirect pests. A. acutiventris, which is found from India to Australia, tends subterranean, root-feeding mealybugs of the species Xenococcus annandalei. Living, gravid females are carried in the jaws of A. acutiventris queens during their nuptial flight, to establish the symbiotic association in founding colonies. Other Acropyga species have relationships with different species of mealybugs, and it could be a trait common to the whole genus.

Aenictus is a large army ant genus distributed in the Old World tropics and subtropics. It contains about 181 species, making it one of the larger ant genera of the world.

Centromyrmex is a pantropical, though mainly Afrotropical, genus of ants in the subfamily Ponerinae. This ponerine ant was recorded for the first time in French Guiana and the most northerly point of recording was in Costa Rica. The specimens reported here were collected in a region of Amazon Forest with flight interception traps.

Stigmatomma is a genus of ants in the subfamily Amblyoponinae. The genus has a worldwide distribution, and like most other amblyoponines, Stigmatomma species are specialized predators. First described by Roger (1859), it was for a long time considered to be a synonym of Amblyopone until it was revived as an independent genus by Yoshimura & Fisher (2012) based on worker mandible morphology.

Technomyrmex is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dolichoderinae. With 98 species, it is one of the largest and most diverse ant genera in the Dolichoderinae. The genus distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical zones with most species occurring in the Oriental-Malesian and Afrotropical regions. One species, Technomyrmex albipes is a tramp ant now widespread throughout the tropics due to human activities.

Carebara is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae. It is one of the largest myrmicine genera with more than 200 species distributed worldwide in the tropics and the Afrotropical region. Many of them are very tiny cryptic soil and leaf-litter inhabitants. They nest in rotten wood to which the bark is still adherent in the Afrotropical region, or may be lestobiotic nesting near other ant species. Some species are known to exist parasitically within termite nests. Little is known about the biology of the genus, but they are notable for the vast difference in size between queens and workers.

Nylanderia is a large genus of ants in the subfamily Formicinae. The genus has a nearly cosmopolitan distribution with species inhabiting a wide array of habitats in almost all geographic regions. Nylanderia, currently containing over 110 species, is an ecologically important genus, with some species reported as being invasive. The ants are small to medium in size and range in color from pale yellow to black.

Meranoplus is an Old World genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae. With over 80 valid species, it is predicted that over half of the Meranoplus diversity remains undescribed, most of these from Australia.

Pseudolasius is a genus of ants in the subfamily Formicinae. The genus is known from southern Asia to northern Australia, where it appears to be restricted to tropical areas. These ants are commonly known as twig ants due to their habit of nesting in twigs or hollow stems.

Parasyscia is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dorylinae containing approximately 50 described species. The genus is distributed across the Afrotropical, Australasia, Indomalaya, Malagasy, Oceania, and Palearctic bioregions. Parasyscia was described by Carlo Emery (1882), moved to a subgenus of Cerapachys by Forel (1892) and finally placed as a junior synonym of Cerapachys by Kempf (1972). Parasyscia was resurrected as a valid genus by Borowiec (2016) during the redescription of the doryline genera.

Ectomomyrmex is a ponerine genus of ants found in Asia and Australia. Little is known about their biology, but they seem to be generalist predators of arthropod prey.

Lasiini is a tribe of ants in the family Formicidae. There are about 10 genera and more than 450 described species in Lasiini.



















