
Tube-dwelling anemones or ceriantharians look very similar to sea anemones but belong to an entirely different subclass of anthozoans. They are solitary, living buried in soft sediments. Tube anemones live inside and can withdraw into tubes, which are composed of a fibrous material made from secreted mucus and threads of nematocyst-like organelles known as ptychocysts. Within the tubes of these ceriantharians, more than one polyp is present, which is an exceptional trait because species that create tube systems usually contain only one polyp per tube. Ceriantharians were formerly classified in the taxon Ceriantipatharia along with the black corals but have since been moved to their own subclass, Ceriantharia.

Zoanthids are an order of cnidarians commonly found in coral reefs, the deep sea and many other marine environments around the world. These animals come in a variety of different colonizing formations and in numerous colors. They can be found as individual polyps, attached by a fleshy stolon or a mat that can be created from small pieces of sediment, sand and rock. The term "zoanthid" refers to all animals within this order Zoantharia, and should not be confused with "Zoanthus", which is one genus within Zoantharia.

Edwardsia is a genus of sea anemones, the type of the family Edwardsiidae. They have eight mesenteries and live in tubes in the sand. The name, in New Latin, commemorates the French zoologist Henri Milne-Edwards.

Rhodactis is genus of "mushroom corals", which are characterized by large individual polyps that are often reminiscent of a mushroom. Rhodactis are related to stony corals but do not produce a stony skeleton.

Alicia is a genus of sea anemones in the family Aliciidae and contains the following species:

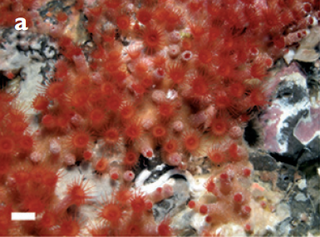
Corynactis is a genus of colonial anthozoans similar in appearance to sea anemones and in body format to scleractinian stony corals. These animals are cnidarians in the family Corallimorphidae. Large unidentified polyps of this genus feed on the crown-of-thorns seastar Acanthaster planci and may help control the crown-of-thorns population.

Amphianthus is a genus of sea anemones. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Amphianthidae.

Hormathiidae is a family of sea anemones in the class Anthozoa.

Anthothoe is a genus of sea anemones in the family Sagartiidae.

Isozoanthus is a genus of anemone-like anthozoans in the order Zoantharia.

Parazoanthidae is a family of cnidarians.

Parazoanthus swiftii, commonly known as the golden zoanthid, is a species of coral in the order Zoantharia which grows symbiotically on several species of sponge. It is found in shallow waters in the Caribbean Sea and western Atlantic Ocean.

Zoanthus is a genus of anthozoans in the family Zoanthidae. It is the type genus for its family and order.

Palythoa is a genus of anthozoans in the order Zoantharia.

Brachycnemina is a suborder of zoanthids in the order Zoantharia. Genetic analysis has been used to suggest Brachycnemina is a monophyletic group diverging within the paraphyletic Macrocnemina.

Arachnanthus is a genus of tube-dwelling anemones in the family Arachnactidae. Members of the genus are found worldwide.

Parazoanthus darwini is a species of macrocnemic zoanthid first found in the Galapagos. It can be distinguished by its association with sponges, by having about 24–30 tentacles and polyps embedded in a well-developed coenenchyme.

Pachycerianthus is a genus of marine tube-dwelling anemones in the family Cerianthidae.
Terrazoanthus is a genus of corals belonging to the family Hydrozoanthidae.
Paraphellia is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Hormathiidae.


















