
The Exocoetidae are a family of marine fish in the order Beloniformes class Actinopterygii, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven to nine genera. While they cannot fly in the same way a bird does, flying fish can make powerful, self-propelled leaps out of the water where their long wing-like fins enable gliding for considerable distances above the water's surface. The main reason for this behavior is thought to be to escape from underwater predators, which include swordfish, mackerel, tuna, and marlin, among others, though their periods of flight expose them to attack by avian predators such as frigate birds.

Hypostomus plecostomus, also known as the suckermouth catfish or the common pleco, is a tropical fish belonging to the armored catfish family (Loricariidae), named for the armor-like longitudinal rows of scutes that cover the upper parts of the head and body. Although the name Hypostomus plecostomus is often used to refer to common plecostomus sold in aquarium shops, most are actually members of other genera.

Exocoetus is a genus of flying fishes. It is a bony fish. The body is covered with cycloid scales. The mouth is wide, and the jaws bear teeth. It is a marine fish. The tail has hypobatic fins as the ventral lobe.

Hirundichthys is a genus of flying fish. They have elongated, moderately thick, ventrally flattened bodies. The pectoral branch of the lateral line is absent. The upper jaw is not protrusible. The dorsal fin has fewer or equal rays than the anal fin; the dorsal fin is low, with the anterior rays the longest, the pectoral fins are strikingly long, reaching to or almost to caudal fin base; pelvic fins are long, reaching beyond the anal fin origin, and their insertion is closer to the anal fin origin than to the pectoral fin insertion.

Pterygoplichthys or commonly known as Janitor fish is a genus of South American armored catfishes. These fish are commonly known as sailfin armoured catfish or sailfin plecs.

Cheilopogon is a genus of flyingfishes.

Leiarius is a genus of long-whiskered catfishes native to South America. Most of the genus' species are found in the aquarium hobby as ornamental fish.

The sailfin grouper, also known as the bacalao grouper, colorado grouper or yellow grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found off islands in the eastern Pacific.

The mirrorwing flyingfish is a flying fish of the family Exocoetidae. It was first described by the French zoologist, Achille Valenciennes in a 22-volume work titled Histoire naturelle des poissons, which was a collaboration with Georges Cuvier.

The Atlantic flyingfish is a flying fish in the family Exocoetidae. It was first described by the French zoologist, Achille Valenciennes in a 22-volume work entitled Histoire naturelle des poissons, which was a collaboration with fellow zoologist Georges Cuvier.
Emblemaria is a genus of chaenopsid blennies found throughout the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.

Fodiator is a genus of flying fishes. It is the only genus in the subfamily Fodiatorinae.
Prognichthys is a genus of flying fishes.

Myersina is a genus of ray-finned fish from the family Gobiidae, the true gobies which are found from the Atlantic coast of South Africa through the Indian Ocean to the western Pacific Ocean. The generic name honours the American ichthyologist George S. Myers (1905-1985) who was a younger colleague of Herre's at the time at which he described the genus and who went on to be president of the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists, the head of the Division of Fishes at the United States National Museum and an ichthyologist for the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.

The sailfin flying fish is a member of the flying fish family (Exocoetidae). As is typical of other members of its family, this species has the ability to jump out of the water and glide on hypertrophied fins in order to evade predators. It is considered a “two-winged” flying fish, meaning that it only has enlarged pectoral fins, as opposed to “four-winged” flying fish, which have both enlarged pectoral and pelvic fins.

Cheilopogon nigricans, the blacksail flyingfish, also known as African flyingfish, or leaping flyingfish, is a flying fish in the family Exocoetidae. It is an oceanodromous, plankton-eating marine fish which has commercial value.

Parexocoetus mento; also known as the African sailfin flying fish, Cuvier's flying fish, the yellow belly flying fish or the short-winged flying fish; is a species of flying fish from the family Exocoetidae which is found in the Indo-pacific region and which has colonised the eastern Mediterranean.

Exocoetus obtusirostris, commonly known as the oceanic two-wing flyingfish or the blunt-snouted flyingfish, is a species of ray-finned fish native to the tropical and subtropical western Atlantic Ocean. It has the ability to glide above the surface of the water to escape from predators.

Parexocoetus hillianus is a species of flying fish from the genus Parexocoetus. It is found in the western Atlantic in the waters of the Gulf Stream off the southeastern United States and Bermuda south through the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea to northern Brazil. In the eastern Atlantic a separate population, which may be a subspecies, is found from Guinea-Bissau south to Angola.
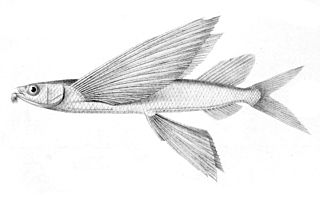
Cheilopogon pinnatibarbatus, Bennett's flying fish, is a species of flying fish which has a circumglobal distribution in tropical and subtropical seas. It is an epiplegaic species which feeds on zooplankton and small fishes and is capable of leaping out of the water and gliding over the surface.
















