
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be specialized to develop flowers or short shoots or may have the potential for general shoot development. The term bud is also used in zoology, where it refers to an outgrowth from the body which can develop into a new individual.

Caryophyllaceae, commonly called the pink family or carnation family, is a family of flowering plants. It is included in the dicotyledon order Caryophyllales in the APG III system, alongside 33 other families, including Amaranthaceae, Cactaceae, and Polygonaceae. It is a large family, with 81 genera and about 2,625 known species.

Paronychia is an inflammation of the skin around the nail, which can occur suddenly, when it is usually due to the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, or gradually when it is commonly caused by the fungus Candida albicans. The term is from Greek: παρωνυχία from para 'around', onyx 'nail', and the abstract noun suffix -ia.

In botany, a rosette is a circular arrangement of leaves or of structures resembling leaves.

Erinus alpinus, the fairy foxglove, alpine balsam, starflower, or liver balsam, is a species of flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae, native to Central and Southern Europe and also to Morocco and Algeria.

Paronychia is a genus of plants in the family Caryophyllaceae with over 110 species worldwide, mostly from warm-temperate North America, Eurasia, South America and Africa. They are herbs that are annual or biennial or perennial in life span. Some species have a woody base. For the most part they have small, white to yellow-white colored flowers that are often hidden within the paired bracts.
This page provides a glossary of plant morphology. Botanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. The accompanying page—Plant morphology—provides an overview of the science of the external form of plants. There is also an alphabetical list: Glossary of botanical terms. In contrast, this page deals with botanical terms in a systematic manner, with some illustrations, and organized by plant anatomy and function in plant physiology.

A leaf is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus, palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata, the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll which is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light energy from the sun. A leaf with lighter-colored or white patches or edges is called a variegated leaf.

Polygonum paronychia is a species of flowering plant in the knotweed family known by the common names dune knotweed, black knotweed, and beach knotweed. It is native to the coastline of western North America from British Columbia to California, where it grows in sandy coastal habitat such as beaches, dunes, and scrub.

Swertia perennis is a species of flowering plant in the gentian family known by the common names felwort and star swertia. It is native to several regions of the northern hemisphere, including much of Eurasia and western North America. It is a plant of wetlands, particularly calcareous fens. It is common to abundant in many areas, but it is known to be negatively impacted by habitat fragmentation and other habitat destruction, and human activity has led to its extirpation from some areas where it was once common. It is a perennial herb producing usually one erect stem growing 10 to 50 centimeters tall. The basal leaves are spoon-shaped with rounded tips, and leaves higher on the plant are widely lance-shaped or somewhat oval, with pointed tips. The inflorescence is an open panicle of flowers atop the stem. Each flower has a calyx of four or five pointed sepals and a corolla of four or five pointed lobes each up to 1.3 centimeters long. The corolla is dull blue to violet in color with darker purplish veining or stippling. There are two rounded nectary pits at the base of each lobe of the corolla. Stamens tipped with large anthers surround a central ovary.

Bonamia grandiflora is a rare species of flowering plant in the morning glory family known by the common names Florida lady's nightcap, Florida bonamia, and scrub morning glory. It is endemic to Central Florida, where there are about 100 known populations remaining, many of which are within the bounds of the Ocala National Forest. The plant has declined in recent decades primarily due to the development of its habitat, which is being converted to urban zones and citrus groves. This is the primary reason that the plant was federally listed as a threatened species in 1987.

Nolina brittoniana is a rare species of flowering plant in the asparagus family known by the common name Britton's beargrass. It is endemic to Florida, where there are 72 known populations, only a few of which are large enough to be considered viable. It is federally listed as an endangered species of the United States.

Paronychia chartacea is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common names papery Whitlow-wort and paper nailwort. It is endemic to Florida in the United States. There are two subspecies of the plant; ssp. chartacea occurs in Central Florida, especially the Lake Wales Ridge, and ssp. minima is native to the Florida Panhandle. The two subspecies are geographically separated and do not occur together. Both are included on the federal Endangered Species List, on which the species is designated threatened.
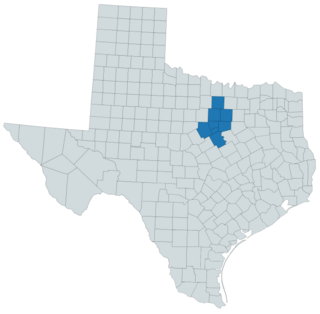
Dalea reverchonii is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common name Comanche Peak prairie-clover. It is endemic to Texas in the United States, where it is known from Bosque, Erath, Hood, Johnson, Parker, Somervell, Tarrant, and Wise counties. This species was first collected by Julien Reverchon at the top of Comanche Peak. As of 2015 the species still grows there.

Paronychia franciscana is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common names San Francisco nailwort, California Whitlow-wort, Franciscan paronychia, and Chilean nailwort. It is native to Chile, but it was first described from specimens collected in San Francisco, California, in the United States, where it is an introduced species.

Physaria pallida is a rare species of flowering plant in the mustard family known by the common name white bladderpod. It is endemic to Texas in the United States, where it is known only from San Augustine County. It is federally listed as an endangered species.

Paronychia rugelii, common name Rugel's nailwort, is a plant native to the US states of Georgia and Florida. It can be found in woodlands and on disturbed sites at elevations below 200 m. They are sometimes referred to as sand squares.

Paronychia argyrocoma, the silvery nailwort or silverling, is a plant species native to the eastern United States. It has a disjunct distribution, found in New England and the Appalachian Mountains of the Southeast but not from New York, New Jersey or Pennsylvania in between. The species grows on rocky sites at elevations of 200–1800 m.

Paronychia argentea is an herbaceous plant from the family Caryophyllaceae that grows in sandy areas, ways, abandoned fields and dry terrains.

Paronychia drummondii, commonly called Drummond's nailwort, is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae. It is native to the United States where it is restricted to the South Central region in the states of Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas. Its natural habitat is in sandy woodlands and openings.


















