
New Sweden was a Swedish colony along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now the United States from 1638 to 1655, established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a great military power. New Sweden formed part of the Swedish efforts to colonize the Americas. Settlements were established on both sides of the Delaware Valley in the region of Delaware, New Jersey, Maryland, and Pennsylvania, often in places where Swedish traders had been visiting since about 1610. Fort Christina in Wilmington, Delaware, was the first settlement, named after the reigning Swedish monarch. The settlers were Swedes, Finns, and a number of Dutch. New Sweden was conquered by the Dutch Republic in 1655 during the Second Northern War and incorporated into the Dutch colony of New Netherland.

The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, forming the border between Pennsylvania and Delaware and New Jersey on its eastern shore.

Nyack is a village located primarily in the town of Orangetown in Rockland County, New York, United States. Incorporated in 1872, it retains a very small western section in Clarkstown. The village had a population of 7,265 as of the 2020 census. It is a suburb of New York City lying approximately 15 miles (24 km) north of the Manhattan boundary near the west bank of the Hudson River, situated north of South Nyack, east of Central Nyack, south of Upper Nyack, and southeast of Valley Cottage.

The Mid-Atlantic is a region of the United States generally located in the overlap between the Northeastern and Southeastern states. Its exact definition differs upon source, but the region typically includes seven states: Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Virginia, West Virginia, and Washington, D.C., the nation's capital.
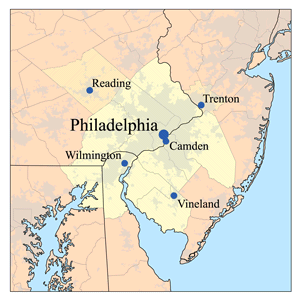
The Delaware Valley, sometimes referred to as Greater Philadelphia or the Philadelphia metropolitan area, is a metropolitan region in the Northeast on the East Coast of the United States that centers on Philadelphia and spans four U.S. states: Southeastern Pennsylvania, southern New Jersey, northern Delaware, and the northern Eastern Shore of Maryland. According to the 2020 census, the core metropolitan statistical area of the Delaware Valley had a total population of 6.288 million, making it the nation's seventh largest and world's 35th largest metropolitan area, while the combined statistical area of the Delaware Valley contains a total population of 7.366 million.

The Province of New Jersey was one of the Middle Colonies of Colonial America and became the U.S. state of New Jersey in 1783. The province had originally been settled by Europeans as part of New Netherland but came under English rule after the surrender of Fort Amsterdam in 1664, becoming a proprietary colony. The English renamed the province after the island of Jersey in the English Channel. The Dutch Republic reasserted control for a brief period in 1673–1674. After that it consisted of two political divisions, East Jersey and West Jersey, until they were united as a royal colony in 1702. The original boundaries of the province were slightly larger than the current state, extending into a part of the present state of New York, until the border was finalized in 1773.

Delaware Colony in the North American Middle Colonies consisted of land on the west bank of the Delaware River Bay. In the early 17th century. the area was inhabited by Lenape and possibly Assateague Native American Indian tribes. The first European settlers were Swedes, who established the colony of New Sweden at Fort Christina in present-day Wilmington, Delaware, in 1638. The Dutch captured the colony in 1655 and annexed it to New Netherland to the north. Great Britain subsequently took control of it from the Dutch in 1664. In 1682, William Penn, the Quaker proprietor of the Province of Pennsylvania to the north leased the three lower counties on the Delaware River from James, the Duke of York, who went on to become King James II.

South Jersey comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of New Jersey located between the lower Delaware River and the Atlantic Ocean. The designation of South Jersey with a distinct toponym is a colloquialism rather than an administrative definition and reflects geographical and perceived cultural and other differences between South Jersey and the northern part of the state. South Jersey is part of the Philadelphia metropolitan area, the seventh largest metropolitan region in the nation with 6.288 million residents in the core metropolitan statistical area and 7.366 million residents in the combined statistical area as of 2020.

Fort Nya Elfsborg was a fortification and settlement established as a part of New Sweden. Built in 1643 and named after the Älvsborg Fortress off Gothenburg, Fort Nya Elfsborg was located on the New Jersey side of the Delaware River, between present day Salem and Alloway Creek.

Mongarlowe is a village in the Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, Australia in Queanbeyan-Palerang Regional Council. In former times, it was also known, in various contexts, as Little River, Monga, and Sergeants Point.

The Pequest River is a 35.7-mile-long (57.5 km) tributary of the Delaware River in the Skylands Region in northwestern New Jersey in the United States.

The Paulins Kill is a 41.6-mile (66.9 km) tributary of the Delaware River in northwestern New Jersey in the United States. With a long-term median flow rate of 76 cubic feet of water per second (2.15 m³/s), it is New Jersey's third-largest contributor to the Delaware River, behind the Musconetcong River and Maurice River. The river drains an area of 176.85 square miles (458.0 km2) across portions of Sussex and Warren counties and 11 municipalities. It flows north from its source near Newton, and then turns southwest. The river sits in the Ridge and Valley geophysical province.
Eric Pålsson Mullica was an early Finnish settler to New Sweden. He and his family were the source of the name of several geographic features and places in New Jersey.

European colonization of New Jersey started soon after the 1609 exploration of its coast and bays by Henry Hudson. Dutch and Swedish colonists settled parts of the present-day state as New Netherland and New Sweden.

Fort Casimir or Fort Trinity was a Dutch fort in the seventeenth-century colony of New Netherland. It was located on a no-longer existing barrier island at the end of Chestnut Street in what is now New Castle, Delaware.

Pavonia was the first European settlement on the west bank of the North River that was part of the seventeenth-century province of New Netherland in what would become the present Hudson County, New Jersey.

Bergen was a part of the 17th century province of New Netherland, in the area in northeastern New Jersey along the Hudson and Hackensack Rivers that would become contemporary Hudson and Bergen Counties. Though it only officially existed as an independent municipality from 1661, with the founding of a village at Bergen Square, Bergen began as a factory at Communipaw circa 1615 and was first settled in 1630 as Pavonia. These early settlements were along the banks of the North River across from New Amsterdam, under whose jurisdiction they fell.
Old York Road is a roadway that was built during the 18th century to connect Philadelphia with New York City. Through New Jersey it was built along the Raritan "Naraticong Trail", also known as the Tuckaraming Trail. A memorial plaque to the friendship of the Naraticong Indians, who permitted the road to be built over their trail, is at the intersection of Old York Road and Canal in Raritan, NJ. The Swift Sure Stage Coach Line completed the journey between the two cities in two days and cost a few dollars.

Middlebrook is an unincorporated community within the borough of Bound Brook in Somerset County, New Jersey. It is named after the Middle Brook, a tributary of the Raritan River, on the western side of the community. The early-18th-century Old York Road, connecting Philadelphia to New York City, passed through here.

The Van Veghten House is a historic building in the Finderne section of Bridgewater Township, New Jersey, United States. The house was built c. 1725 and served as the headquarters of Quartermaster General Nathanael Greene during the second Middlebrook encampment (1778–79) in the American Revolutionary War. The Somerset County Historical Society owns the house and uses it as its headquarters, including a museum and library. The early-18th-century Old York Road, connecting Philadelphia to New York City, passed by here. The house was added to the National Register of Historic Places on October 10, 1979, and noted as representing "one of the few remaining Raritan River mansions".




















