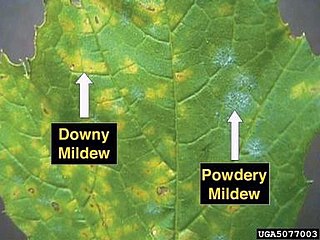
Downy mildew refers to any of several types of oomycete microbes that are obligate parasites of plants. Downy mildews exclusively belong to the Peronosporaceae family. In commercial agriculture, they are a particular problem for growers of crucifers, grapes and vegetables that grow on vines. The prime example is Peronospora farinosa featured in NCBI-Taxonomy and HYP3. This pathogen does not produce survival structures in the northern states of the United States, and overwinters as live mildew colonies in Gulf Coast states. It progresses northward with cucurbit production each spring. Yield loss associated with downy mildew is most likely related to soft rots that occur after plant canopies collapse and sunburn occurs on fruit. Cucurbit downy mildew only affects leaves of cucurbit plants.

Agrostemma githago, the common corn-cockle, is a herbaceous annual flowering plant in the pink and carnation family Caryophyllaceae.

Peronosporaceae are a family of water moulds that contains 21 genera, comprising more than 600 species. Most of them are called downy mildews.

Hyaloperonospora parasitica is an oomycete from the family Peronosporaceae. It has been considered for a long time to cause downy mildew of a variety of species within the Brassicaceae, on which the disease can cause economically important damage by killing seedlings or affecting the quality of produce intended for freezing. Hyaloperonospora parasitica causes downy mildew on a wide range of many different plants. It belongs to the Kingdom Chromista, the phylum Oomycota, and the family Peronosporaceae. The former name for H. parasitica was Peronospora parasitica until it was reclassified and put in the genus Hyaloperonospora. It is an especially vicious disease on crops of the family Brassicaceae. It is most famous for being a model pathogen of Arabidopsis thaliana which is a model organism used for experimental purposes. Accordingly, the former Hyaloperonospora parasitica has been split into a large number of species. For instance, the taxonomically correct name of the parasite of the well-known model organism Arabidopsis thaliana is Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis, not H. parasitica, whereas the pathogen of Brassica has to be called Hyaloperonospora brassicae.
Peronospora sparsa is an oomycete plant pathogen that causes downy mildew in berry producing plants; especially in the genus's Rubus and Rosa. Downy mildew plant pathogens are often host specific and cause problems in cloudberries, blackberries, boysenberries, strawberries, and arctic bramble. Since they are host specific, Peronospora sparsa will not cause downy mildew in grapes because a different plant pathogen causes downy mildew in grapes; Plasmopara viticola. Although it depends on the cultivar, symptoms do not normally start until later stages of disease and can look different on different plants. The most common symptoms include red lesions in the veins of leaves, with dry and deformed berries.
Peronospora trifoliorum, commonly known as downy mildew of alfalfa, is an oomycete plant pathogen infecting alfalfa.

Peronospora farinosa is a species name that has been widely applied to downy mildew on leaves of wild and cultivated Amaranthaceae: Amaranthus, Atriplex, Bassia, Beta, Chenopodium, Halimione, Salsola, Spinacia, etc. However, the species name has been taxonomically rejected as the original description contained reference to multiple species and could not unequivocally be attributed to a species of Peronospora. In the past, some of the species on important crop plants have been given names as formae speciales, notably f.sp. betae on sugar beet and f.sp. spinaciae on spinach. However, phylogentic reconstructions have revealed that these "forms" of Peronospora on different genera and their subdivisions, are distinct species, most of which already have previously published scientific names. Such host specialization possibly also exists with respect to the various wild amaranthaceous species given as hosts of P. farinosa.

Peronospora manshurica is a plant pathogen. It is a widespread disease on the leaves of soybeans and other crop plants. The fungi is commonly referred to as downy mildew, "leafspot", or "leaf-spot".

Blackstonia perfoliata or more commonly known as the yellow-wort is a species of flowering plant in the family Gentianaceae found around the Mediterranean Basin, but extending into northwestern Europe.

Veronica polita, or grey field-speedwell, is a herbaceous flowering plant species in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. It has hairy stems, is either prostrate or ascending, with dull green leaves that are one of petiolate, serrate, ovate (rounded) and usually wider than long.The flowers are small and bright blue. The plant has solitary axillary peduncles that are shorter or slightly longer than the leaves. It is native to Eurasia, possibly including the British Isles, western Asia, northern Africa, and North America, but has been introduced into suitable habitats worldwide as a weed of cultivation. It is susceptible to downy mildew disease caused by the oomycete species Peronospora agrestis.

Melampyrum pratense, the common cow-wheat, is a plant species in the family Orobanchaceae.

Peronospora is a genus of oomycetes that are obligate plant pathogens of many eudicots. Most species in this group produce a downy mildew disease, which can cause severe damage to many different cultivated crops, as well as wild and ornamental plants. There are 19 genera that produce downy mildew, and Peronospora has been placed alongside Pseudoperonospora in the group of downy mildews with coloured conidia. Peronospora has far more species than any other genus of the downy mildews. However, many species have been moved from this genus to be reclassified to other or new genera. Among these was the most famous Peronospora species, formerly known as Peronospora parasitica, and now known as Hyaloperonospora parasitica. Now, the Peronospora species of most importance is likely the Peronospora tabacina. Peronospora tabacina causes blue mold on tobacco plants and can severely reduce yields of this economically important crop to the point where it has been classified as a bioweapon.

Peronospora hyoscyami f.sp. tabacina is a plant pathogen infecting tobacco that causes blue mold. It is an oomycete that is highly destructive toward seed plants. It is very prevalent in humid farming zones, like the southeastern and Eastern U.S., Canada, and countries bordering the Caribbean. The disease was first identified in 1921 in Florida and Georgia. Ten years later the same disease was found once again in the same region of the U.S. The disease began to spread into Virginia, Maryland, and North Carolina. A few years later, the disease reached Kentucky and Tennessee. In 1960, a blue mold epidemic spread in approximately eleven countries. There was approximately twenty five million dollars in losses which is nearly thirty percent of tobacco plants at the time. Each year, Peronospora hyoscyami is introduced as blue mold as windblown spores from outside the region by infected transplants.

Agrimonia striata is a species of perennial forb belonging to the rose family (Rosaceae). It grows to about 40 inches (1m) producing a dense cluster (raceme) of 5-parted yellow flowers on a hairy stalk above pinnately-divided leaves. It is native to the United States, Canada, and Saint Pierre and Miquelon. It is susceptible to downy mildew caused by the oomycete species Peronospora agrimoniae.

Androsace septentrionalis is a species of annual herbaceous plant in the Primrose family (Primulaceae), native to North America, Asia, and Europe.

Peronospora destructor is a plant pathogen. It causes downy mildew on leaves of cultivated and wild Allium. Allium cepa is most often affected, while Allium schoenoprasum (chives) and Allium porrum (leek) are only occasionally affected.
Peronospora anemones is a plant pathogen. It causes downy mildew on leaves of anemone. It occurs on various wild and garden forms of anemone, and has particular commercial importance on Anemone coronaria grown for cut flowers, for example in France and Italy.
Peronospora arborescens is a plant pathogen. It causes downy mildew on leaves of Papaver spp. It has economic importance on Papaver somniferum grown as an oilseed crop, for example in central and eastern Europe. It is controlled by sanitation, crop rotation, use of clean seed and fungicide sprays of the foliage. There are other species of Peronospora which occur on Papaver: Peronospora argemones (Gäum.), Peronospora cristata (Tranzschel), and Peronospora papaveris-pilosi (Vienn.-Bourg.).
Eremophila conglomerata is a flowering plant in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae and is endemic to central areas of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with small, serrated leaves and mauve to blue flowers that extend well beyond the foliage.

Eucalyptus conglomerata, commonly known as the swamp stringybark, is a species of straggly tree or mallee that is endemic to Queensland. It has rough, fibrous "stringybark" lance-shaped to oblong adult leaves, flower buds in groups of eleven or more, white flowers and more or less barrel-shaped fruit.














