
The French Southern and Antarctic Lands is an overseas territory of France. It consists of:
SothoSesotho, also known as Southern Sotho or Sesotho sa Borwa is a Southern Bantu language of the Sotho–Tswana ("S.30") group, spoken in Lesotho, and South Africa where it is an official language.
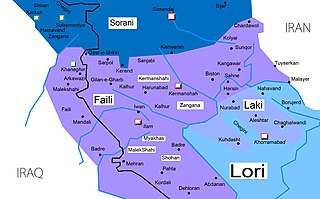
Southern Kurdish is one of the dialects of the Kurdish language, spoken predominantly in northeastern Iraq and western Iran. The Southern Kurdish-speaking region spans from Khanaqin in Iraq to Dehloran southward and Asadabad eastward in Iran.

Litoria is a genus of hylid tree frogs, sometimes collectively referred to as Australasian treefrogs.

The southern brown tree frog, also known as the brown tree frog, whistling tree frog, or Ewing's tree frog, is a species of tree frog native to Australia: most of southern Victoria, eastern South Australia, southern New South Wales from about Ulladulla—although this species is reported to occur further north—and throughout Tasmania including the Bass Strait Islands, in which state it is the most frequently encountered frog. It has been introduced to New Zealand, where it can be locally abundant.

Littlejohn's tree frog, also called a heath frog or orange-bellied tree frog, is a species of tree frog native to eastern Australia from Wyong, New South Wales, to Buchan, Victoria.

Ehrlichiosis is a tick-borne bacterial infection, caused by bacteria of the family Anaplasmataceae, genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. These obligate intracellular bacteria infect and kill white blood cells.

Ehrlichia is a genus of Rickettsiales bacteria that are transmitted to vertebrates by ticks. These bacteria cause the disease ehrlichiosis, which is considered zoonotic, because the main reservoirs for the disease are animals.

The Tasmanian Thornbill is a small bushland member of the Acanthizidae family, endemic to Tasmania and the Bass Strait Islands. It is a common bird in these regions and is often found occupying the colder, wetter portions of them. The brown thornbill will typically occupy the correspondingly drier portions of habitat.

Ehrlichia ewingii is a species of rickettsiales bacteria. It has recently been associated with human infection, and can be detected via PCR serological testing. The name Ehrlichia ewingii was proposed in 1992.

Human monocytotropic ehrlichiosis is a form of ehrlichiosis associated with Ehrlichia chaffeensis. This bacterium is an obligate intracellular pathogen affecting monocytes and macrophages.
Ehrlichiosis ewingii infection is an infectious disease caused by an intracellular bacteria, Ehrlichia ewingii. The infection is transmitted to humans by the tick, Amblyomma americanum. This tick can also transmit Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the bacteria that causes human monocytic ehrlichiosis (HME).

Persectania is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae.

Southern Alta, is a distinctive Aeta language of the mountains of northern Philippines. Southern Alta is one of many endangered languages that risks being lost if it is not passed on by current speakers. Most speakers of Southern Alta also speak Tagalog.
The brown frog (Rana) is a genus of about 50 species of true frogs found through much of Eurasia, North America, Africa, Central America, and the northern half of South America.

Persectania aversa, commonly known as the southern armyworm, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It was first described in 1856 by Francis Walker. It is endemic to New Zealand and can be found throughout the country including the North, South, Stewart and Chatham Islands. This species inhabits open grasslands. Larvae feed on grass species including commercial crops such as oats and barley and as a result this species is regarded as an agricultural pest. Adults are nocturnal and are attracted to light. They are on the wing throughout the year.
The Southern Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in an area stretching from the southern shore of Lingayen Gulf to the highlands of Quirino province. The most widely spoken Southern Cordilleran language is Pangasinan, one of the eight major languages of the Philippines.

The Tasmanian Central Highland forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in Australia. It covers Tasmania's Central Highlands region.
Watson's tree frog, also known as the large brown tree frog or southern heath frog, is a species of tree frog endemic to south-eastern Australia.













