
Odonata is an order of predatory flying insects that includes the dragonflies and damselflies. The two groups are distinguished with dragonflies usually being bulkier with large compound eyes together and wings spread up or out at rest, while damselflies are usually more slender with eyes placed apart and wings folded together along body at rest. Adult odonates can land and perch, but rarely walk.

The order Diplura is one of three orders of non-insect hexapods within the class Entognatha. The name "diplura", or "two tails", refers to the characteristic pair of caudal appendages or filaments at the terminal end of the body.

The insects of the beetle family Chrysomelidae are commonly known as leaf beetles, and include over 37,000 species in more than 2,500 genera, making up one of the largest and most commonly encountered of all beetle families. Numerous subfamilies are recognized, but the precise taxonomy and systematics are likely to change with ongoing research.

The caddisflies, or order Trichoptera, are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the basis of the adult mouthparts. Integripalpian larvae construct a portable casing to protect themselves as they move around looking for food, while annulipalpian larvae make themselves a fixed retreat in which they remain, waiting for food to come to them. The affinities of the small third suborder Spicipalpia are unclear, and molecular analysis suggests it may not be monophyletic. Also called sedge-flies or rail-flies, the adults are small moth-like insects with two pairs of hairy membranous wings. They are closely related to the Lepidoptera which have scales on their wings; the two orders together form the superorder Amphiesmenoptera.

Byrrhoidea is a superfamily of beetles belonging to Elateriformia that includes several families which are either aquatic or associated with a semi-aquatic habitat. Other than the superfamily Hydrophiloidea, most of the remaining Polyphagan beetles which are aquatic are in this superfamily.
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, tarsus, ischium, metatarsus, carpus, dactylus, patella.

The family Leptoceridae are a family of caddisflies often called "long-horned caddisflies" or "silverhorns". Leptoceridae is the second largest family of caddisflies with over 1850 species in approximately 68 genera. The main identifying feature of most Leptoceridae is that their antennae are much longer than those of other caddisflies. There is one genus with relatively short antennae (Ceraclea), but it is easily identified by the pair of dark curved lines on the mesonotum.

Latridiidae is a family of tiny, little-known beetles commonly called minute brown scavenger beetles or fungus beetles. The number of described species currently stands at around 1050 in 29 genera but the number of species is undoubtedly much higher than this and increases each time a new estimate is made.

Melolonthinae is a subfamily of the scarab beetles. It is a very diverse group; distributed over most of the world, it contains over 11,000 species in over 750 genera. Some authors include the scarab subfamilies Euchirinae and Pachypodinae as tribes in the Melolonthinae.

The Ecnomidae are a family of caddisflies comprising 9 genera with a total of 375 species.
The Glossosomatidae are a family of the class Insecta and order Trichoptera.The family contains 23 genera in three subfamilies. In the US alone, there are 76 spp. in 6 different genera.

Trombidiidae, also known as red velvet mites, true velvet mites, or rain bugs, are small arachnids found in plant litter and are known for their bright red color.
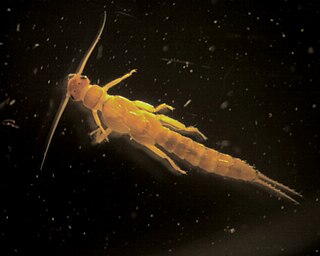
Chloroperlidae are a family of stoneflies, commonly known as green stoneflies, with more than 200 species and 22 genera. They appear green to yellow in colour, and are popularly used among fisherman as bait for trout fishing. Green stoneflies live in the benthic zone of the cold streams and rivers of five continents and four zoogeographical regions, emerging from the water to live in the riparian zone as adults. They are sensitive to pollutants, making them an indicator species for determining the quality of water bodies. Chloroperlidae are hemimetabolous, having no pupal stage, but instead hatch from eggs as nymphs and mature directly into adults. They are omnivorous, feeding on small organisms and plant particles, and become more carnivorous as they mature. The classification of Chloroperlidae is contested, with some believing that they should be considered as members of different orders, as opposed to the order Plecoptera that they currently belong to.

The Erebidae are a family of moths in the superfamily Noctuoidea. The family is among the largest families of moths by species count and contains a wide variety of well-known macromoth groups. The family includes the underwings (Catocala); litter moths (Herminiinae); tiger, lichen, and wasp moths (Arctiinae); tussock moths (Lymantriinae), including the arctic woolly bear moth ; fruit-piercing moths ; micronoctuoid moths (Micronoctuini); snout moths (Hypeninae); and zales, though many of these common names can also refer to moths outside the Erebidae. Some of the erebid moths are called owlets.

Dryomyza anilis is a common fly from the family Dryomyzidae. The fly is found through various areas in the Northern hemisphere and has brown and orange coloration with distinctive large red eyes. The life span of the fly is not known, but laboratory-reared males can live 28–178 days. D. anilis has recently been placed back in the genus Dryomyza, of which it is the type species. Dryomyzidae were previously part of Sciomyzidae but are now considered a separate family with two subfamilies.

Polyxenida is an order of millipedes readily distinguished by a unique body plan consisting of a soft, non-calcified body ornamented with tufts of bristles. These features have inspired the common names bristly millipedes or pincushion millipedes. This order includes about 148 species in four families worldwide, which represent the only living members of the subclass Penicillata.
Dolophilodes distinctus is a species of caddisfly in the Philopotamidae family. The larvae are found in streams in eastern North America where they build net-like retreats.

Kinnaridae is a family of fulgoroid planthoppers. This is a small family with a little more than 20 genera and about a 100 species. The family was erected by Muir in 1925 and most members are found in the Oriental and Neotropical regions and only a few in the Nearctic and Palaearctic regions.

Agrypnia is a genus of giant caddisflies in the family Phryganeidae. There are about 19 described species in Agrypnia.

















