
Tylopoda is a suborder of terrestrial herbivorous even-toed ungulates belonging to the order Artiodactyla. They are found in the wild in their native ranges of South America and Asia, while Australian feral camels are introduced. The group has a long fossil history in North America and Eurasia. Tylopoda appeared during the Eocene around 50 million years ago.

Camelids are members of the biological family Camelidae, the only currently living family in the suborder Tylopoda. The seven extant members of this group are: dromedary camels, Bactrian camels, wild Bactrian camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos. Camelids are even-toed ungulates classified in the order Artiodactyla, along with species including whales, pigs, deer, cattle, and antelopes.

Diadectidae is an extinct family of early tetrapods that lived in what is now North America and Europe during the Late Carboniferous and Early Permian, and in Asia during the Late Permian. They were the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also the first fully terrestrial animals to attain large sizes. Footprints indicate that diadectids walked with an erect posture. They were the first to exploit plant material in terrestrial food chains, making their appearance an important stage in both vertebrate evolution and the development of terrestrial ecosystems.

Camelops is an extinct genus of camel that lived in North and Central America, ranging from Alaska to Honduras, from the middle Pliocene to the end of the Pleistocene. It is more closely related to living camels than to lamines, making it a true camel of the Camelini tribe. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek κάμηλος and ὄψ, i.e. "camel-face".
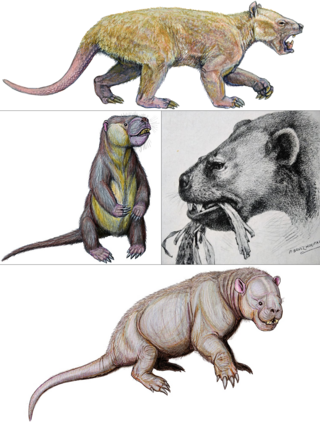
Stylinodontidae is an extinct family of mammals from extinct superfamily Stylinodontoidea within extinct order Taeniodonta, that lived in North America from the early Paleocene to middle Eocene.

Miacis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to middle Eocene.

Poebrotherium is an extinct genus of camelid, endemic to North America. They lived from the Eocene to Miocene epochs, 46.3—13.6 mya, existing for approximately 32 million years.

Orobates is an extinct genus of diadectid reptiliomorphs that lived during the Early Permian. Its fossilised remains were found in Germany. A combination of primitive and derived traits distinguish it from all other well-known members of Diadectidae, a family of herbivorous reptiliomorphs. It weighed about 4 kg and appears to have been part of an upland fauna, browsing on high fibre plants.

Hemiauchenia is a genus of laminoid camelids that evolved in North America in the Miocene period about 10 million years ago. This genus diversified and entered South America in the Late Pliocene about 3-2 million years ago, as part of the Great American Biotic Interchange. The genus became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene. The monophyly of the genus has been considered questionable, with phylogenetic analyses finding the genus to paraphyletic or polyphyletic, with some species suggested to be more closely related to living lamines than to other Hemiaucenia species.

Brachychampsa is an extinct genus of alligatorid, possibly a basal caiman. Specimens have been reported from New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, North and South Dakota, New Jersey, and Saskatchewan, though only those from Montana, Utah, and New Mexico are based on material sufficient to justify the referral. Some specimens have been reported from the Campanian-aged deposits of Central Asia, although the species status is indeterminate for these fossils. The genus first appeared during the late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous and became extinct during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous. Brachychampsa is distinguished by an enlarged fifth maxillary tooth in the upper jaw.
Aguascalientia is an extinct genus of miniature camelids, endemic to North America during the Early Miocene 23.0—20.4 mya existing for approximately 3 million years.
Hesperocamelus is an extinct genus of terrestrial herbivore in the family Camelidae, endemic to North America from the Miocene.
Megacamelus is an extinct genus of terrestrial herbivore in the family Camelidae, endemic to North America from the Miocene through Pliocene 10.3—4.9 mya, existing for approximately 5.4 million years.
Paracamelus is an extinct genus of camel in the family Camelidae. It originated in North America Around 8-7 Ma, and crossed the Beringian land bridge into Eurasia during the Late Miocene, about 6 million years ago (Ma). It is the presumed ancestor to living camels of the genus Camelus.

Palaeolama is an extinct genus of laminoid camelids that existed from the Late Pliocene to the Early Holocene. Their range extended from North America to the intertropical region of South America.

Hyopsodontidae is an extinct family of primitive mammals, initially assigned to the order Condylarthra, living from the Paleocene to the Eocene in North America and Eurasia. Condylarthra is now thought to be a wastebasket taxon; hyopsodontids have occasionally been speculated to be related to Afrotheria, but the most recent consensus is that they are related to Perissodactyla. Analysis of the inner ear shows shared characteristics with the Equoidea ; they may be a basal ungulate group near to perissodactyls.
The Willwood Formation is a sedimentary sequence deposited during the late Paleocene to early Eocene, or Clarkforkian, Wasatchian and Bridgerian in the NALMA classification.

A list of prehistoric and extinct species whose fossils have been found in the La Brea Tar Pits, located in present-day Hancock Park, a city park on the Miracle Mile section of the Mid-Wilshire district in Los Angeles, California.
The Washakie Formation is a geologic formation in northern Colorado and southern Wyoming. It preserves many mammal, bird, reptile and other fossils dating back to the Lutetian stage of the Eocene within the Paleogene period. The sediments fall in the Bridgerian and Uintan stages of the NALMA classification.

Oxyaeninae is an extinct subfamily of placental mammals from extinct family Oxyaenidae, that lived in Asia, North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.














