The Puebloans, or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Among the currently inhabited Pueblos, Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zuni, and Hopi are some of the most commonly known. Pueblo people speak languages from four different language families, and each Pueblo is further divided culturally by kinship systems and agricultural practices, although all cultivate varieties of corn (maize).

Rio Arriba County is a county in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2020 census, the population was 40,363. Its county seat is Tierra Amarilla. Its northern border is the Colorado state line.

Los Ranchos de Albuquerque, known locally simply as "Los Ranchos" or "The Village," is a village in Bernalillo County, New Mexico. The population was 6,024 at the time of the 2010 Census.

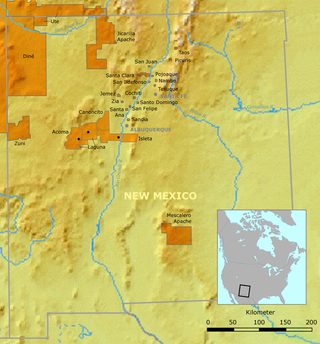
Santo Domingo Pueblo, also known Kewa Pueblo is a federally-recognized tribe of Native American Pueblo people in northern New Mexico. A population of 2,456 live in structures some of which date from circa 1700; in Sandoval County described by the U.S. Census Bureau as a census-designated place.

Socorro is a city in Socorro County in the U.S. state of New Mexico. It is in the Rio Grande Valley at an elevation of 4,579 feet (1,396 m). In 2010 the population was 9,051. It is the county seat of Socorro County. Socorro is located 74 miles (119 km) south of Albuquerque and 146 miles (235 km) north of Las Cruces.
Tiwa is a group of two, possibly three, related Tanoan languages spoken by the Tiwa Pueblo, and possibly Piro Pueblo, in the U.S. state of New Mexico.

San Antonio is a census-designated place in Socorro County, New Mexico, United States, roughly in the center of the state, on the Rio Grande.
The Pueblo Revolt of 1680, also known as Popé's Rebellion or Po'pay's Rebellion, was an uprising of most of the indigenous Pueblo people against the Spanish colonizers in the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, larger than present-day New Mexico. Incidents of brutality and cruelty, coupled with persistent Spanish policies that stoked animosity, gave rise to the eventual Revolt of 1680. The persecution and mistreatment of Pueblo people who adhered to traditional religious practices was the most despised of these. The Spaniards were resolved to abolish "pagan" forms of worship and replace them with Christianity. The Pueblo Revolt killed 400 Spaniards and drove the remaining 2,000 settlers out of the province. The Spaniards returned to New Mexico twelve years later.
The Piro people were a Native American tribe who lived in New Mexico during the 16th and 17th century. The Piros lived in a number of pueblos in the Rio Grande Valley around modern Socorro, New Mexico, USA. The now extinct Piro language may have been a Tanoan language. Numbering several thousand at the time of first contact with the Spanish, by the time of the Pueblo Revolt in 1680 the Piro had been decimated by European-introduced diseases and Apache attacks and most of the survivors resettled near El Paso, Texas.
Luis Lopez is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in Socorro County, New Mexico, United States. It lies between Socorro and San Antonio along the Rio Grande.

San Miguel de Socorro is the Catholic church in Socorro, New Mexico, built on the ruins of the old Nuestra Señora de Socorro mission. The old mission was built around 1627, but was destroyed in 1680 during the Pueblo Revolt. A portion of the adobe wall of the old church remains today and still can be seen behind glass just left of the altar. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2016.
Teypana was the first pueblo to be called Socorro. This Piro pueblo was located close to present-day Socorro, New Mexico. A reference from 1598 suggests Teypana was on the west bank of the Rio Grande, downriver from the pueblo of Pilabó. Found in a partly flawed list of Piro pueblos, the reference is somewhat problematic. In 1598, Juan de Oñate and an advance party of his colonists were given food and water by the people of Teypana. In response, they named the settlement Socorro, which means “help” or “aid” in Spanish. By 1626, the name had become associated with the Piro pueblo of Pilabó, site of the first permanent mission in Piro territory, now buried under the town of Socorro, NM.
The Piro pueblo of Senecú was the southernmost occupied pueblo in New Mexico prior to the Pueblo Revolt of 1680. It was located on the west bank of the Rio Grande within sight of the Piro pueblo of San Pasqual. Colonial Spanish documents consistently place the pueblo opposite of Black Mesa, which is near San Marcial. Due to changes in the floodplain and the establishment of San Marcial, however, no surface remains of the pueblo survive in the area.

Interstate 25 (I-25) in the US state of New Mexico follows the north–south corridor through Albuquerque and Santa Fe. It replaced U.S. Route 85 (US 85), which is no longer signed, but still exists in route logs sharing most of the I-25 alignment. I-25 starts in New Mexico at an interchange with I-10 in Las Cruces and extends roughly 460 miles (740 km) before reaching Colorado. I-25 passes through principally rural land through central New Mexico and passes through or near the cities of Las Cruces, Truth or Consequences, Socorro, Belen, Albuquerque, Santa Fe, Las Vegas, and Raton.

New Mexico has a long history of wine production, within American wine, especially along the Rio Grande, from its capital Santa Fe, the city of Albuquerque with its surrounding metropolitan area, and in valleys like the Mesilla and the Mimbres River valleys. In 1629, Franciscan friar García de Zúñiga and a Capuchín friar named Antonio de Arteaga planted the first wine grapes in Santa Fe de Nuevo México, in what would become the modern Middle Rio Grande Valley AVA. Today, wineries exist in the aforementioned Middle Rio Grande Valley, as well as the Mesilla Valley AVA and the Mimbres Valley AVA.
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of New Mexico.
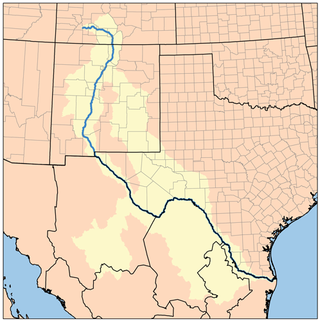
The Rio Grande Trail is a proposed long distance trail along the Rio Grande in the U.S. state of New Mexico. The river extends over 1,800 total miles, some 700 miles (1,100 km) of which pass through the heart of New Mexico. It is the state's primary drainage feature and most valuable natural and cultural resource. The river and its bosque provide a wide variety of recreation, including hunting and fishing, birdwatching, river rafting, hiking, biking, and horseback riding. The river also flows through or beside numerous spectacular and geologically interesting landforms, the result of extensive volcanism and erosion of the valley within the Rio Grande Rift. Although some trail advocates would like to see the trail extended the full distance through New Mexico, from the Colorado border to the United States–Mexico border, the portion proposed for initial development extends 300 miles (480 km), from Bernalillo south to Las Cruces.
Tortugas, New Mexico or Tortugas Pueblo is a community in Doña Ana County, New Mexico, just outside of Las Cruces, New Mexico. As of the 2020 census, the CDP's population was 579.
San Pascual Pueblo was a Piro pueblo south and east of Socorro, in Socorro County, New Mexico, United States. Its ruins lie on the east bank of the Rio Grande, on a butte, on the western slope of the Little San Pascual Mountain, overlooking the river, near the eastern boundary of the Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge.

The Rio Grande Valley is the river valley carved out by the Rio Grande as it flows through the American Southwest and northeastern Mexico, forming a part of the border region. In the US state of New Mexico, the river flows mostly north to south, and forms a valley near Cochiti Pueblo to the state line near El Paso, Texas along the floors of the large sedimentary basins of the Rio Grande Rift, and includes the narrow sections between the basins. It has been historically settled first by the Pueblo peoples, the Spanish, the Mexicans, and finally Anglo-Americans. As the largest river in the state, some of its most populous cities are located wholly or partially in the valley, including Albuquerque, New Mexico's largest city.













