
Ponca is a city and county seat of Dixon County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 961 at the 2010 census.

Ponca City is a city in Kay County in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The city was named after the Ponca tribe. Ponca City had a population of 24,424 in the 2020 census, down from 25,387 at the time of the 2010 census.

Carlo Gesualdo da Venosa was an Italian nobleman and composer. Though both the Prince of Venosa and Count of Conza, he is better known for writing madrigals and pieces of sacred music that use a chromatic language not heard again until the late 19th century. He is also known for killing his first wife and her aristocratic lover upon finding them in flagrante delicto.
The Ponca people are a nation primarily located in the Great Plains of North America that share a common Ponca culture, history, and language, identified with two Indigenous nations: the Ponca Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma or the Ponca Tribe of Nebraska.

Standing Bear was a Ponca chief and Native American civil rights leader who successfully argued in U.S. District Court in 1879 in Omaha that Native Americans are "persons within the meaning of the law" and have the right of habeas corpus, thus becoming the first Native American judicially granted civil rights under American law. His first wife Zazette Primeau (Primo), daughter of Lone Chief, mother of Prairie Flower and Bear Shield, was also a signatory on the 1879 writ that initiated the famous court case.

Venosa is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the southern Italian region of Basilicata, in the Vulture area. It is bounded by the comuni of Barile, Ginestra, Lavello, Maschito, Montemilone, Palazzo San Gervasio, Rapolla and Spinazzola. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia.

Ernest Whitworth Marland was an American lawyer, oil businessman in Pennsylvania and later Oklahoma, and politician who was a United States Representative (congressman) and 10th Governor of Oklahoma. He served in the United States House of Representatives from a district in northern Oklahoma, 1933 to 1935, and as the tenth Governor of Oklahoma from 1935 to 1939. As a Democrat, he initiated a "Little Deal" in Oklahoma during the Great Depression of the 1930s, working to relieve the distress of unemployed people and the economic hardships affecting the state and nation-wide and to build infrastructure as investment for the future.
Ponca State Park is a public recreation area located on the banks of the Missouri River four miles (6.4 km) north of Ponca, Nebraska, in the northeastern corner of the state. The state park's approximately 2,100 acres (850 ha) are situated among high bluffs and steep, forested hills adjacent to the Missouri National Recreational River. The park is managed by the Nebraska Game and Parks Commission.

Rapana venosa, common name the veined rapa whelk or Asian rapa whelk, is a species of large predatory sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc or whelk, in the family Muricidae, the rock shells.
The Kansas–Oklahoma–Missouri League was a name of an American minor league baseball league which was established in 1946 and played through 1952. As the name indicates, the Class D level league had franchises based in Kansas, Missouri and Oklahoma. Baseball Hall of Fame members Mickey Mantle played in the league for the 1949 Independence Yankees and Burleigh Grimes managed the 1948 Independence Yankees.

Omaha–Ponca is a Siouan language spoken by the Omaha (Umoⁿhoⁿ) people of Nebraska and the Ponca (Paⁿka) people of Oklahoma and Nebraska. The two dialects differ minimally but are considered distinct languages by their speakers.
Nanza is the Ponca name for what is now called Ponca Fort. It was a fortified village built by the Ponca in the vicinity of present-day Niobrara, Nebraska, USA, in circa 1700 and occupied until about 1865.
The Ponca Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma, also known as the Ponca Nation, is one of two federally recognized tribes of Ponca people. The other is the Ponca Tribe of Nebraska. Traditionally, peoples of both tribes have spoken the Omaha-Ponca language, part of the Siouan language family. They share many common cultural norms and characteristics with the Omaha, Osage, Kaw, and Quapaw peoples.

The Ponca Tribe of Nebraska is one of two federally recognized tribes of the Ponca people. The other is the Ponca Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma. As of 2023, the Ponca Tribe of Nebraska’s total population is 5,334 citizens, of which 1,923 reside in Nebraska.
Ponca City, Oklahoma was home to numerous minor league baseball teams between 1923 and 1957, playing at Conoco Park. Ponca City played as members of the Oklahoma State League (1923–1924), Southwestern League (1926), Western Association (1934–1938), Kansas–Oklahoma–Missouri League (1947–1952) and Western Association (1954). Ponca City was an affiliate of the Chicago Cubs (1934–1938), Brooklyn Dodgers (1947–1952) and Chicago Cubs (1955–1957).
The Ponca Reservation of the Ponca Tribe of Nebraska is located in northeast Nebraska, with the seat of tribal government located in Niobrara, Knox County. The Indian reservation is also the location of the historic Ponca Fort called Nanza. The Ponca tribe does not actually have a reservation because the state of Nebraska will not allow them to have one. However, they do in fact have a 15-county service delivery area, including counties spread throughout Nebraska, South Dakota and Iowa.

Ponca City High School is a public high school that serves approximately 1,500 students in grades 9–12, located in Ponca City, Oklahoma. The current main principal is Thad Dilbeck.
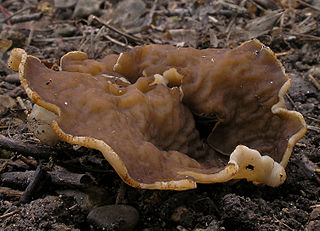
Disciotis venosa, commonly known as the bleach cup, veiny cup fungus, or the cup morel is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae. Fruiting from April, they are often difficult to locate because of their nondescript brown color.
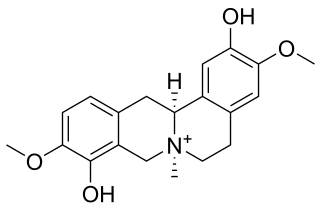
Cyclanoline is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Stephania venosa tuber.

Fontainea venosa, also commonly known as southern blushwood, veiny fontainea, Queensland fontainea and formerly named as Bahrs scrub fontainea is a rare rainforest shrub or tree of the family Euphorbiaceae. It is found in southeastern Queensland, Australia, extending from Boyne Valley to Cedar Creek and is considered vulnerable due to several contributing threats. The total population size is around 200 plants.













