| Potamilus amphichaenus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Bivalvia |
| Order: | Unionida |
| Family: | Unionidae |
| Genus: | Potamilus |
| Species: | P. amphichaenus |
| Binomial name | |
| Potamilus amphichaenus (Frierson, 1898) | |
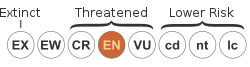
Potamilus amphichaenus, the Texas heelsplitter, is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. Freshwater Drum (Aplodinotus grunniens) were confirmed as the host fish species for the glochidia reproductive stage of the Texas Heelsplitter. [2]
This species is endemic to the United States.