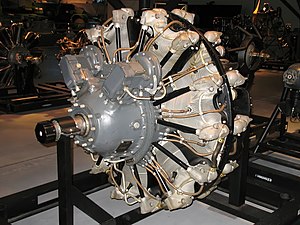
Design and development
The R-2000 was an enlarged version of the Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp, with focus on reducing the manufacturing costs and fuel requirements. The bore was increased to 5.75 in (146 mm), while it still retained the 5.5 in (140 mm) stroke. This brought displacement up to 2,000 in3 (32.8 L). There were a number of detail changes from the R-1830, such as front-mounted instead of rear-mounted magnetos (as with the larger, and earlier Double Wasp), plain bearings for the crankshaft rather than roller bearings, and 87 octane fuel (specified because there were fears wartime supplies of 100 octane might fall short, but those fears were groundless).
The R-2000 produced 1,300 hp (970 kW) at 2,700 rpm with 87 octane fuel, 1,350 hp (1,010 kW) with 100 octane fuel and 1,450 hp (1,080 kW) at 2,800 rpm with 100/130-grade fuel. [1]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.