Priene was an ancient Greek city of Ionia located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) north of what was then the course of the Maeander River. It was 67 kilometres (42 mi) from ancient Anthea, 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) from ancient Aneon and 25 kilometres (16 mi) from ancient Miletus. The city was built on the sea coast, overlooking the former Latmian Gulf of the Aegean. It was developed on steep slopes and terraces extending from sea level to a height of 380 metres (1,250 ft) above sea level at the top of the escarpment. Because of siltation from the river filling the bay over several centuries, the city is now an inland site. It is located at a short distance west of the modern village Güllübahçe Turun in the Söke district of Aydın Province, Turkey.

The archaeology of Israel is the study of the archaeology of the present-day Israel, stretching from prehistory through three millennia of documented history. The ancient Land of Israel was a geographical bridge between the political and cultural centers of Mesopotamia and Egypt.

Tel Rehov or Tell es-Sarem, is an archaeological site in the Bet She'an Valley, a segment of the Jordan Valley, Israel, approximately 5 kilometres (3 mi) south of Beit She'an and 3 kilometres (2 mi) west of the Jordan River. It was occupied in the Bronze Age and Iron Age.

The Dura-Europos synagogue was an ancient Jewish former synagogue discovered in 1932 at Dura-Europos, Syria. The former synagogue contained a forecourt and house of assembly with painted walls depicting people and animals, and a Torah shrine in the western wall facing Jerusalem. It was built backing on to the city wall, which was important in its survival. The last phase of construction was dated by an Aramaic inscription to 244 CE, making it one of the oldest synagogues in the world. It was unique among the many ancient synagogues that have emerged from archaeological excavations as the structure was preserved virtually intact, and it had extensive figurative wall-paintings, which came as a considerable surprise to scholars. These paintings are now displayed in the National Museum of Damascus.

Benjamin Mazar was a pioneering Israeli historian, recognized as the "dean" of biblical archaeologists. He shared the national passion for the archaeology of Israel that also attracts considerable international interest due to the region's biblical links. He is known for his excavations at the most significant biblical site in Israel: south and south west of the Temple Mount in Jerusalem. In 1932 he conducted the first archaeological excavation under Jewish auspices in Israel at Beit She'arim and in 1948 was the first archaeologist to receive a permit granted by the new State of Israel. Mazar was trained as an Assyriologist and was an expert on biblical history, authoring more than 100 publications on the subject. He developed the field of historical geography of Israel. For decades he served as the chairman of the Israel Exploration Society and of the Archaeological Council of Israel. Between 1951 and 1977, Mazar served as Professor of Biblical History and Archaeology at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. In 1952 he became Rector of the university and later its president for eight years commencing in 1953.

Gamla, also Gamala, was an ancient Jewish town on the Golan Heights. Believed to have been founded as a Seleucid fort during the Syrian Wars, it transitioned into a predominantly Jewish settlement that came under Hasmonean rule in 81 BCE. The town's name reflects its location on a high, elongated ridge with steep slopes resembling a camel's hump.

Theodor Wiegand was a German archaeologist.

Carl Humann was a German engineer, architect and archaeologist. He discovered the Pergamon Altar.

The Sardis Synagogue is a former ancient Jewish synagogue, that was discovered in the modern-day town of Sardis, in the Manisa Province, in the Aegean Region of western Turkey. The former synagogue building is now an archaeological site and Jewish museum. The archaeological site is the largest Jewish site known from antiquity.

Naaran was an ancient Jewish village dating to the 5th and 6th century CE, located in the modern-day West Bank, in the State of Palestine. Remains of the village have been excavated north-west of Jericho. Naaran is archeologically notable for the mosaic floor of a synagogue, featuring a large zodiac design, which was discovered at the site.

Kursi is an archaeological site in the Golan Heights containing the ruins of a Byzantine monastery and identified by tradition as the site of Jesus' "Miracle of the Swine". Part of the archaeological site is now an Israeli national park. Kursi takes its name from the Talmudic site. A marble slab with Aramaic text discovered in December 2015 seems to indicate that the settlement had, as of c. 500 CE, a Jewish or Judeo-Christian population.

The Kfar Bar'am Synagogue, also known as the Kafar Berem Synagogue, is the archaeological ruins of two former ancient Jewish synagogues, located at the site of Kafr Bir'im, a depopulated Palestinian village, in what is today, the Bar'am National Park, in the Galilee region of the Northern District of Israel, approximately 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) from the border with Lebanon. It is estimated that the former synagogue was completed in the 3rd century, during the Roman period, likely by c. 220 CE, and was located in the medieval Jewish village of Kfar Bar'am.

Levantine archaeology is the archaeological study of the Levant. It is also known as Syro-Palestinian archaeology or Palestinian archaeology. Besides its importance to the discipline of Biblical archaeology, the Levant is highly important when forming an understanding of the history of the earliest peoples of the Stone Age.

Meiron was a Palestinian village, located 5 kilometers (3.1 mi) west of Safad. Associated with the ancient Canaanite city of Merom, excavations at the site have found extensive remains from the Hellenistic and Early Roman periods. The remains include a 3rd-century synagogue, and Meiron served as a prominent local religious centre at the time.

Chorazin or Korazim was an ancient village in the Roman and Byzantine periods, best known from the Christian Gospels. It stood on the Korazim Plateau in the Upper Galilee on a hill above the northern shore of the Sea of Galilee, 2.5 mi (4.0 km) from Capernaum in what is now the territory of modern Israel.

Ancient synagogues in Palestine refers to synagogues and their remains in the Land of Israel/Palestine region, built by the Jewish and Samaritan communities from the time of the Hasmonean dynasty during the Late Hellenistic period, to the Late Byzantine period.

Huqoq or Hukkok was an ancient Jewish village, located 12.5 km north of Tiberias. The area had been settled since ancient times and is mentioned in the Book of Joshua. The Palestinian village of Yaquq later stood at Huqoq's location, and a fort named Hukok was built near the site on 11 July 1945, later followed by a kibbutz.
Johann (Hans) Hermann Schrader was a German classical archaeologist and art historian.

The Temple of Athena Polias in Priene was an Ionic Order temple located northwest of Priene’s agora, inside the sanctuary complex. It was dedicated to Athena Polias, also the patron deity of Athens. It was the main temple in Priene, although there was a temple of Zeus. Built around 350 BC, its construction was sponsored by Alexander the Great during his anabasis to the Persian Empire. Its ruins sit at the foot of an escarpment of mount Mycale. It was believed to have been constructed and designed by Pytheos, who was the architect of the great Mausoleum of Halikarnassos, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was one of the Hellenistic temples that was not reconstructed by Romans.

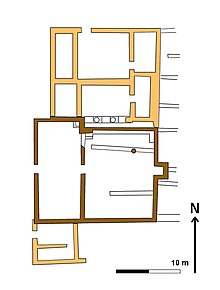
The Gamla synagogue is an ancient former Jewish synagogue, located in the ancient Jewish city of Gamla on the western slope of the Golan Heights, approximately 18 km (11 mi) northeast of Lake Kinneret, in Israel. The synagogue was built between the 1st century BCE and the 1st century CE.