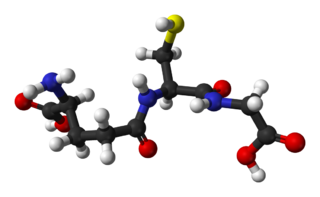
Glutathione is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOCOCH(NH2)CH2CH2CONHCH(CH2SH)CONHCH2COOH. It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine.
Protein disulfide isomerase, or PDI, is an enzyme in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in eukaryotes and the periplasm of bacteria that catalyzes the formation and breakage of disulfide bonds between cysteine residues within proteins as they fold. This allows proteins to quickly find the correct arrangement of disulfide bonds in their fully folded state, and therefore the enzyme acts to catalyze protein folding.

Glutathione disulfide (GSSG) is a disulfide derived from two glutathione molecules.

Glutathione reductase (GR) also known as glutathione-disulfide reductase (GSR) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSR gene. Glutathione reductase catalyzes the reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to the sulfhydryl form glutathione (GSH), which is a critical molecule in resisting oxidative stress and maintaining the reducing environment of the cell. Glutathione reductase functions as dimeric disulfide oxidoreductase and utilizes an FAD prosthetic group and NADPH to reduce one molar equivalent of GSSG to two molar equivalents of GSH:

Glutaredoxins are small redox enzymes of approximately one hundred amino-acid residues that use glutathione as a cofactor. In humans this oxidation repair enzyme is also known to participate in many cellular functions, including redox signaling and regulation of glucose metabolism. Glutaredoxins are oxidized by substrates, and reduced non-enzymatically by glutathione. In contrast to thioredoxins, which are reduced by thioredoxin reductase, no oxidoreductase exists that specifically reduces glutaredoxins. Instead, glutaredoxins are reduced by the oxidation of glutathione. Reduced glutathione is then regenerated by glutathione reductase. Together these components compose the glutathione system.
Arsenate reductase (glutaredoxin) (EC 1.20.4.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Adenylyl-sulfate reductase (glutathione) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Adenylyl-sulfate reductase (thioredoxin) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CoA-glutathione reductase (EC 1.8.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an enzyme-thiol transhydrogenase (glutathione-disulfide) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathione—CoA-glutathione transhydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathione—cystine transhydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) (EC 1.8.5.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathione—homocystine transhydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein-disulfide reductase (EC 1.8.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a thiosulfate-thiol sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Thioredoxins are small disulfide-containing redox proteins that have been found in all the kingdoms of living organisms. Thioredoxin serves as a general protein disulfide oxidoreductase. It interacts with a broad range of proteins by a redox mechanism based on reversible oxidation of 2 cysteine thiol groups to a disulfide, accompanied by the transfer of 2 electrons and 2 protons. The net result is the covalent interconversion of a disulfide and a dithiol.
Glutathione amide reductase (EC 1.8.1.16, GAR) is an enzyme with systematic name glutathione amide:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glutathione amide-dependent peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.17) is an enzyme with systematic name glutathione amide:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dissimilatory sulfite reductase is an enzyme that participates in sulfur metabolism in dissimilatory sulfate reduction.






