
The Cupedidae are a small family of beetles, notable for the square pattern of "windows" on their elytra, which give the family their common name of reticulated beetles.

The Cerophytidae are a family of Coleoptera known as the rare click beetles. Adults are infrequently encountered, and larvae are found within wood, where they are believed to feed on fungi. The family contains over 20 species in five genera, primarily distributed in the New World: 17 fossil genera are known extending to the Early Jurassic.

Bittacidae is a family of scorpionflies commonly called hangingflies or hanging scorpionflies.

Anaxyelidae is a family of incense cedar wood wasps in the order Hymenoptera. It contains only one living genus, Syntexis, which has only a single species, native to Western North America. Fossils of the family extend back to the Middle Jurassic, belonging to over a dozen extinct genera, with a particularly high diversity during the Early Cretaceous. Syntexis lay eggs in the sapwood of conifers, preferring recently burnt wood.

Nemonychidae is a small family of weevils, placed within the primitive weevil group because they have straight rather than geniculate (elbowed) antennae. They are often called pine flower weevils. As in the Anthribidae, the labrum appears as a separate segment to the clypeus, and the maxillary palps are long and projecting. Nemonychidae have all ventrites free, while Anthribidae have ventrites 1-4 connate or partially fused. Nemonychidae lack lateral carinae on the pronotum, while these are usually present, though may be short, in Anthribidae.

The Berothidae are a family of winged insects of the order Neuroptera. They are known commonly as the beaded lacewings. The family was first named by Anton Handlirsch in 1906.
Protodiplatys is an extinct genus of earwigs, in the family Protodiplatyidae, the suborder Archidermaptera, and the order Dermaptera. It is known from three species, P. fortis and P. gracilis, which are known from the Middle-Late Jurassic Karabastau Formation in Kazakhstan, and P. mongoliensis from the Aptian aged Gurvan-Eren Formation of Mongolia.
Archidermapteron martynovi is an extinct species of earwig, in the genus Archidermapteron, family Protodiplatyidae, the suborder Archidermaptera, the order Dermaptera, and is the only species in the genus Archidermapteron, which simply means "ancient member of the Dermaptera". It had long, segmented cerci unlike modern species of Dermaptera, but tegmina and hind wings that folded up into a "wing package" that are like modern earwigs. The only clear fossil of the species was found in Russia.

Ithonidae, commonly called moth lacewings and giant lacewings, is a small family of winged insects of the insect order Neuroptera. The family contains a total of ten living genera, and over a dozen extinct genera described from fossils. The modern Ithonids have a notably disjunct distribution, while the extinct genera had a more global range. The family is considered one of the most primitive living neuropteran families. The family has been expanded twice, first to include the genus Rapisma, formerly placed in the monotypic family Rapismatidae, and then in 2010 to include the genera that had been placed into the family Polystoechotidae. Both Rapismatidae and Polystoechotidae have been shown to nest into Ithonidae sensu lato. The larvae of ithonids are grub-like, subterranean and likely phytophagous.

Heloridae is a family of wasps in the order Hymenoptera known primarily from fossils, and only one extant genus, Helorus, with 12 species found worldwide. Members of Helorus are parasitic on green lacewings.

Roproniidae is a family of wasps in the order Hymenoptera, of which only two genera are still extant, the others being fossils.

Aneuretopsychidae is an extinct family of scorpionflies known from the Mesozoic. Fossils are known from the Jurassic (Callovian-Oxfordian) to the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian). It is part of Mesopsychoidea, a group of scorpionflies with siphonate proboscis. They are suggested to have been nectarivores, feeding off the liquid pollination drops of and acting as pollinators for now extinct insect pollinated gymnosperms such as Bennettitales.

Dermapteridae is an extinct family of earwigs known from the Late Triassic to Mid Cretaceous, it is part of the extinct suborder Archidermaptera, alongside Protodiplatyidae and Turanovia. It was first named as a subfamily by Vishniakova in 1980, and elevated to family status by Engel in 2003 without discussion.
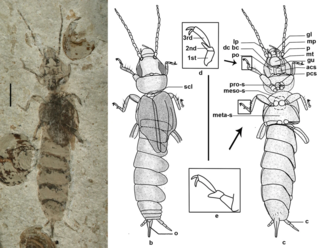
Eodermaptera is an extinct suborder of earwigs known from the Middle Jurassic to Mid Cretaceous. Defining characteristics include "tarsi three-segmented, tegmina retain venation, 8th and 9th abdominal tergite in females are narrowed, but separate from 10th tergite and not covered by 7th tergite and exposed ovipositor" They are considered to be more closely related to Neodermaptera than the more basal Archidermaptera.
Blattulidae is an extinct family of cockroaches known from the Triassic to the Late Cretaceous. Their distinguishing characteristics include "forewing has long Sc, regular venation with distinct intercalaries and hindwing has simple CuP, branched A1."

Archisargidae is an extinct family of brachyceran flies known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. It is part of the extinct superfamily Archisargoidea. Most members of the family are known from the Callovian-Oxfordian Daohugou biota of Inner Mongolia, China, and the equivalently aged Karabastau Formation of Kazakhstan. The family has been found to be paraphyletic with respect to Eremochaetidae in a cladistic analysis.
Praeaulacidae is an extinct family of Mesozoic parasitic wasps in the suborder Evanioidea. It among the earliest known families of the group and is characterised by more complete wing venation in comparison to other members of the suborder. It has been found that Othniodellithidae is nested within Praeaulacidae via cladistic analysis.
Mesochrysopidae is an extinct family of lacewings known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. They are considered to be closely related to green lacewings of the family Chrysopidae. The family are also alternatively considered a paraphyletic grade leading up to crown Chrysopidae.

Orthophlebiidae is an extinct family of scorpionflies known from the Triassic to Cretaceous, belonging to the superfamily Panorpoidea. The family is poorly defined and is probably paraphyletic, representing many primitive members of Panorpoidea with most species only known from isolated wings, and has such been considered a wastebasket taxon.

Peipiaosteidae is an extinct family of fish, known from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Asia. They are members of Acipenseriformes, related to sturgeons (Acipenseridae) and paddlefish (Polyodontidae). Fossils have been found in freshwater deposits in China, Russia, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia. They are generally considered either the earliest diverging group of Acipenseriformes, or the sister group to the clade containing Acipenseridae and Polyodontidae. At least Yanosteus was likely to have been piscivorous, based on a specimen of Lycoptera found in the mouth of one specimen.















