History
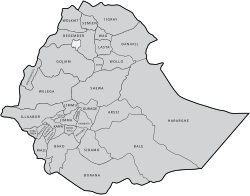
Pre-1936
Older provinces (existing prior to the 1936–41 fascist Italian occupation), are still frequently used to indicate locations within Ethiopia. These include:
1942–1974

Ethiopia was divided into 12 provinces or governates-general (taklai ghizat) by Imperial Ethiopian Government Decree No. 1 of 1942 and later amendments. [3] The 12 provinces were:
Bale was created as a 13th province when it was split off from Harrarghe in 1960. Eritrea was united with Ethiopia and made a 14th province in 1962. [3]
1974–1991
When the Derg took power in 1974 they relabelled the provinces as regions (kifle hager). [4] : 222 By 1981 Addis Ababa had become a separate administrative division from Shewa, and Aseb was split off from Eritrea in 1981, making 16 administrative divisions in total. [4] : 334 With the exception of Arsi (whose name derives from the eponymous Oromo subgroup, and which initially included majority-Gurage area later transferred to Shewa province (becoming Southern Shewa), all of the provinces were deliberately drawn to include multiple "tribes" (or ethnicities) so as to better facilitate national cohesion.[ verification needed ]
Under the 1987 Constitution of Ethiopia, the military rule of the Derg evolved into the civilian government of the People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, and chapter 8 of the Constitution determined that the state would be subdivided into "autonomous regions" and "administrative regions". Chapter 9 gave to the National Shengo (the legislature) the power to establish the regions. [5] The Shengo established the regions in Proclamation No. 14 of 1987, on 18 September. There were thirty regions, consisting of five autonomous regions, and twenty-five administrative regions. The five autonomous regions were: [4] : 223
The twenty-five administrative regions were: [4] : xxiii
