
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida.

Leonardo Fea was an Italian explorer, zoologist, painter, and naturalist.

Tord Tamerlan Teodor Thorell was a Swedish arachnologist.

Chrysilla is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1887. Several species formerly placed here were transferred to Phintella, and vice versa. Females are 3 to 4 millimetres long, and males are 4 to 9 millimetres long. The genus is Persian, derived from the Greek Χρύσιλλα.

Epocilla is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1887. The name comes from Ἐπόκιλλος (Epocillus), a soldier of Alexander the Great.

Telamonia is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1887. They are colorful spiders, with patterns that vary considerably between sexes and species. Two longitudinal stripes along the abdomen are common, and the carapace is often colored. They have a slender opisthosoma and long legs.
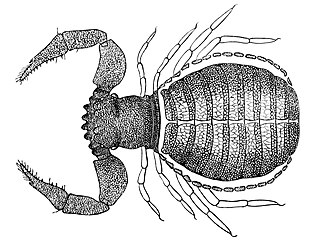
Feaellidae is a family of pseudoscorpions, first described by Edvard Ellingsen in 1906.

Feaella is a genus of pseudoscorpions in the family Feaellidae, first described by Edvard Ellingsen in 1906.
Anaxibia is a genus of cribellate araneomorph spiders in the family Dictynidae, and was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1898.
Jacaena is a genus of Asian liocranid sac spiders first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1897.
Timonoe is a monotypic genus of Burmese long-jawed orb-weavers containing the single species, Timonoe argenteozonata. It was first described by Tamerlan Thorell from a female found in 1898, and it has only been found in Myanmar.
Deione is a genus of Asian orb-weaver spiders first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1898.
Talthybia is a genus of Asian orb-weaver spiders containing the single species, Talthybia depressa. It was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1898, and has only been found in China and Myanmar.
Zelotes captator is a species of Southeast Asian ground spider. It was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1887, and has only been found in Myanmar. In 2022, it was moved from the monotypic genus Aracus to the genus Zelotes.

Camaricus is a genus of crab spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1887.

Asceua is a genus of Asian ant spiders first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1887.
Teutamus is a genus of Southeast Asian liocranid sac spiders first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1890.
Micythus is a genus of Southeast Asian ground spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1897. As of March 2022, it contains only three species: M. anopsis, M. pictus, and M. rangunensis.
Pseudochiridiidae is a family of pseudoscorpions. It was described in 1923 by American arachnologist Joseph Conrad Chamberlin. Pseudochiridiids are relatively small pseudoscorpions. They are found in plant litter or beneath tree bark. The family was sometimes treated as a subfamily of the Cheiridiidae, but has since been reinstated.
Pseudochiridium is a genus of pseudoscorpions in the Pseudochiridiidae family. It was described in 1906 by Danish arachnologist Carl Johannes With.








