Related Research Articles

Alexander I of Epirus, also known as Alexander Molossus, was a king of Epirus (343/2–331 BC) of the Aeacid dynasty. As the son of Neoptolemus I and brother of Olympias, Alexander I was an uncle, and a brother-in-law, of Alexander the Great. He was also an uncle of Pyrrhus of Epirus,.

Alexander II was a king of Epirus, and the son of Pyrrhus and Lanassa, the daughter of the Sicilian tyrant Agathocles.
This article concerns the period 279 BC – 270 BC.
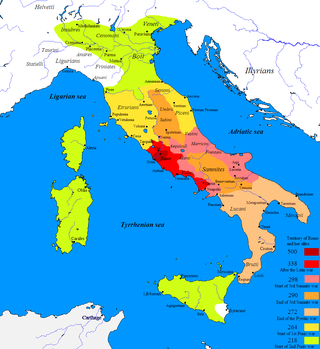
Year 272 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cursor and Maximus. The denomination 272 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Pyrrhus was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period. He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he became king of Epirus. He was one of the strongest opponents of early Rome, and had been regarded as one of the greatest generals of antiquity. Several of his victorious battles caused him unacceptably heavy losses, from which the term "Pyrrhic victory" was coined.

Antigonus II Gonatas was a Macedonian Greek ruler who solidified the position of the Antigonid dynasty in Macedon after a long period defined by anarchy and chaos and acquired fame for his victory over the Gauls who had invaded the Balkans.
Bardylis was an Illyrian king, and the founder of the first attested Illyrian dynasty. During his reign, Bardylis aimed to made Illyria a regional power interfering with Macedon. He united many southern Illyrian tribes under his realm and defeated the Macedonians and Molossians several times, expanding his dominion over Upper Macedonia and Lynkestis, and ruling over Macedon through a puppet king. Before the Rise of Macedon Illyrians were the dominant power in the region. Bardylis also led raids against Epirus, but his soldiers were eventually expelled from the region.
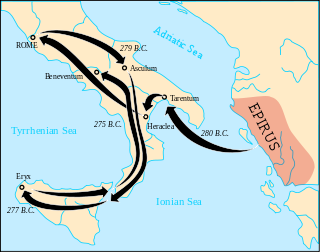
The Battle of Heraclea took place in 280 BC between the Romans under the command of consul Publius Valerius Laevinus, and the combined forces of Greeks from Epirus, Tarentum, Thurii, Metapontum, and Heraclea under the command of Pyrrhus, king of Epirus. Although the battle was a victory for the Greeks and their casualties were lower than the Romans, they had lost many veteran soldiers that would be hard to replace on foreign soil.
Ptolemy, king of Epirus was the second son of Alexander II, king of Epirus, and Olympias, grandson of the great Pyrrhus and brother of Phthia of Macedon. He was named in honour of his late uncle Ptolemy. He succeeded to the throne on the death of his elder brother, Pyrrhus II of Epirus, but reigned only a very short time, having set out on a military expedition, during the course of which he fell sick and died or, according to Polyaenus, he was treasonably assassinated. The date of his reign cannot be fixed with certainty, but as he was a contemporary of Demetrius II, king of Macedonia, it may be placed between 239 and 229 BC. He was succeeded by Deidamia II or Pyrrhus III.
Neoptolemus II was king of Epirus from 302 BC until his death. He was the son of king Alexander I of Epirus and Cleopatra of Macedonia, his maternal grandparents were Philip II of Macedon and Olympias. His maternal uncles included Alexander the Great and Philip III of Macedon. His maternal aunts included Thessalonike and Cynane.
Alcetas II, king of Epirus, was the son of Arybbas, and grandson of Alcetas I. On account of his ungovernable temper, he was banished by his father, who appointed his younger son, Aeacides, to succeed him. On the death of Aeacides, who was killed in a battle fighting against Cassander in 313 BC, the Epirotes recalled Alcetas. Cassander sent an army against him under the command of Lyciscus, but in 312 BC entered into an alliance with him. The Epirotes, incensed at the outrages of Alcetas, rose against him and put him to death, together with his two sons. As a result, in 306 BC Pyrrhus, the son of Aeacides, was placed upon the throne by his protector King Glaukias of the Illyrians.
Mytilos or Mytilus was an Illyrian king who reigned in southern Illyria, around the hinterland of Dyrrhachion and Apollonia. He was the successor of Monunios, and probably his son. Mytilus is mentioned by Pompeius Trogus and Frontinus reporting the events of the military conflict between the Illyrians and the Epirotes under Alexander II, son of Pyrrhus. From around 270 BC Mytilus minted in Dyrrhachion his own bronze coins bearing the king's name and the symbol of the city.

The Epirote League was an ancient Greek coalition, or koinon, of Epirote tribes.
Glaucias was a ruler of the Taulantian kingdom which dominated southern Illyrian affairs in the second half of the 4th century BC. Glaucias is first mentioned as bringing a considerable force to the assistance of Bardylis' son Cleitus, an Illyrian prince who revolted against Alexander the Great, in the battle of Pelium 335 BC. They were, however, both defeated, and Cleitus was forced to take refuge within the Taulantian territories, whither Alexander did not pursue him, his attention being called elsewhere by the news of the revolt of Thebes.

Epirus was an ancient Greek kingdom, and later republic, located in the geographical region of Epirus, in parts of north-western Greece and southern Albania. Home to the ancient Epirotes, the state was bordered by the Aetolian League to the south, Ancient Thessaly and Ancient Macedonia to the east, and Illyrian tribes to the north. The Greek king Pyrrhus is known to have made Epirus a powerful state in the Greek realm that was comparable to the likes of Ancient Macedonia and Ancient Rome. Pyrrhus' armies also attempted an assault against the state of Ancient Rome during their unsuccessful campaign in what is now modern-day Italy.
Deidamia or Deidameia or Laodamia was the Queen regnant of Epirus in 234 - 233 BC. She was the daughter of Pyrrhus II of Epirus, king of Epirus.
Bardylis II was an Illyrian king, and presumably the son of Cleitus, and grandson of Bardylis. He was the father of Bircenna, wife of Pyrrhus of Epirus. Bardylis II is the only attested Illyrian king after Glaucias' death. He may have succeeded Glaucias on the throne as the grandson of Bardylis I, or alternatively he may have reigned independently after his father Cleitus somewhere in Dassaretia, in an area located nearer the Macedonian border. At that time Bardylis II was evidently the most powerful king in Illyria who could unite the largest number of Illyrian tribes under his rule.

Pyrrhus' invasion of the Peloponnese in 272 BC was an invasion of south Greece by Pyrrhus, King of Epirus. He was opposed by Macedon and a coalition of Greek city-states (poleis), most notably Sparta. The war ended in a joint victory by Macedonia and Sparta.

This is a list of Illyrian rulers from the Enchelean and Taulantian kingdoms (dynasty):
References
- ↑ Sampson, Gareth C. (2020-08-05). Rome and Parthia: Empires at War: Ventidius, Antony and the Second Romano-Parthian War, 40-20 BC. Pen and Sword Military. p. 272. ISBN 978-1-5267-1016-1.