
Charadriiformes is a diverse order of small to medium-large birds. It includes about 390 species and has members in all parts of the world. Most charadriiform birds live near water and eat invertebrates or other small animals; however, some are pelagic (seabirds), others frequent deserts, and a few are found in dense forest. Members of this group can also collectively be referred to as shorebirds.

The mousebirds are birds in the order Coliiformes. They are the sister group to the clade Cavitaves, which includes the Leptosomiformes, Trogoniformes (trogons), Bucerotiformes, Piciformes and Coraciformes. This group is now confined to sub-Saharan Africa, and it is the only bird order confined entirely to that continent, with the possible exception of turacos which are considered by some as the distinct order Musophagiformes, and the cuckoo roller, which is the only member of the order Leptosomiformes, and which is found in Madagascar but not mainland Africa. Mousebirds had a wider range in the Paleogene, with a widespread distribution in Europe and North America during the Paleocene.

Gastornis is an extinct genus of large, flightless birds that lived during the mid-Paleocene to mid-Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Most fossils have been found in Europe, and possible specimens are known in North America and Asia. Several genera including Diatryma were historically considered to be congeneric with Gastornis, but recent interpretations challenged this referral.

Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct family of large carnivorous, mostly flightless birds that were among the largest apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era. Their definitive fossil records range from the Middle Eocene to the Late Pleistocene around 43 to 0.1 million years ago, though some specimens suggest that they were present since the Early Eocene.

Presbyornis is an extinct genus of presbyornithid bird from North America during the Paleogene period, between the Late Paleocene and Early Eocene.
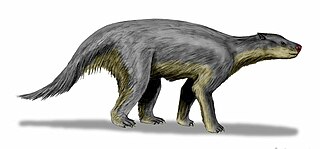
Pantodonta is an extinct suborder of eutherian mammals. These herbivorous mammals were one of the first groups of large mammals to evolve after the end of the Cretaceous. The last pantodonts died out at the end of the Eocene.

The Sophiornithidae are an extinct family of chicken-sized predatory birds that lived from the Paleocene to the Eocene periods of the Cenozoic, and were found primarily in Europe, and are thought to be primitive owls.

The Pelagornithidae, commonly called pelagornithids, pseudodontorns, bony-toothed birds, false-toothed birds or pseudotooth birds, are a prehistoric family of large seabirds. Their fossil remains have been found all over the world in rocks dating between the Early Paleocene and the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary.

Songzia is an extinct genus of gruiform bird related to rails. It lived in the Eocene epoch. Though many families traditionally assigned to the Gruiformes do not seem to actually belong there, this is apparently not the case with this animal. Its fossils have been found in Songzi county.

Odontopteryx is a genus of the extinct pseudotooth birds or pelagornithids. These were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.
Pseudodontornis is a rather disputed genus of the prehistoric pseudotooth birds. The pseudotooth birds or pelagornithids were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty. Up to five species are commonly recognized in this genus.

Lithornithidae is an extinct, possibly paraphyletic group of early paleognath birds. They are known from fossils dating to the Upper Paleocene through the Middle Eocene of North America and Europe, with possible Late Cretaceous representatives. All are extinct today; the youngest specimen is the currently unnamed SGPIMH MEV1 specimen from the mid-Eocene Messel Pit site.
Lavocatavis is an extinct genus of prehistoric bird from the Eocene of Algeria. A fossilized femur was described from the Glib Zegdou Formation in 2011 and is the only known specimen of Lavocatavis. The species was designated L. africana.

Cariamiformes is an order of primarily flightless birds that has existed for over 50 million years. The group includes the family Cariamidae (seriemas) and the extinct families such as Phorusrhacidae, Bathornithidae, Idiornithidae and Ameghinornithidae. Extant members (seriemas) are only known from South America, but fossils of many extinct taxa are also found in other continents including Europe and North America. Though traditionally considered a suborder within Gruiformes, both morphological and genetic studies show that it belongs to a separate group of birds, Australaves, whose other living members are Falconidae, Psittaciformes and Passeriformes.

Australaves is a clade of birds, defined in 2012, consisting of the Eufalconimorphae as well as the Cariamiformes. They appear to be the sister group of Afroaves. This clade was defined in the PhyloCode by George Sangster and colleagues in 2022 as "the least inclusive crown clade containing Cariama cristata and Passer domesticus".

Eleutherornis cotei is an extinct flightless predatory cariamiform bird which lived during the Middle Eocene of France and Switzerland. Since the early 20th century, researchers have initially described the fossils of Eleutherornis as separate taxa, some remains as a species of Gastornis and others as an ancient ratite related to modern ostriches. However, subsequent analyses have questioned the original interpretations, and a thorough reexamination in 2013 indicated that all of these described remains represent the same species.

Telluraves is a recently defined clade of birds defined by their arboreality. Based on most recent genetic studies, the clade unites a variety of bird groups, including the australavians as well as the afroavians. This grouping was defined in the PhyloCode by George Sangster and colleagues in 2022 as "the least inclusive crown clade containing Accipiter nisus and Passer domesticus". They appear to be the sister group of the Phaethoquornithes.

Bathornis is an extinct lineage of birds related to modern day seriemas, that lived in North America about 37–20 million years ago. Like the closely related and also extinct phorusrhacids, it was a flightless predator, occupying predatory niches in environments classically considered to be dominated by mammals. It was a highly diverse and successful genus, spanning a large number of species that occurred from the Priabonian Eocene to the Burdigalian Miocene epochs.
Elaphrocnemus is a genus of extinct bird from the Eocene and Oligocene periods of Europe. Part of Cariamiformes, its closest living relatives are seriemas, though it differs significantly from them, being a better flyer.

Halcyornithidae is an extinct family of telluravian birds thought to be related to the Psittaciformes (parrots), Passeriformes (songbirds), and to the extinct Messelasturidae. Halcyornithids have been found in various Eocene formations in Europe and North America. Widespread and diverse in the Early Eocene of North America and Europe, halcyornithids are not found in locales later than the Middle Eocene. Halcyornithids were small, arboreal birds with zygodactyl feet, with two toes facing forwards and two facing back, a trait shared with other tree-dwelling families of Eocene birds like the Zygodactylidae and the messelasturids. The skull of halcyornithids features a ridge of bone above the eye called the supraorbital process, similar to birds of prey. The relationships of the halcyornithids to other birds remain uncertain. Halcyornithids have been proposed as relatives to owls and as a lineage closer to parrots than to songbirds. Most recently, halcyornithids have been identified as the sister group of the clade including parrots and songbirds. It is also possible that Halcyornithidae is paraphyletic with respect to the Messelasturidae.

















