This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2018) |

The Rachol Fort is a historical Portuguese era fort located in the village of Rachol, Salcette concelho , in the state of Goa on the west coast of India.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2018) |

The Rachol Fort is a historical Portuguese era fort located in the village of Rachol, Salcette concelho , in the state of Goa on the west coast of India.
It was originally erected by the Sultanate of Bijapur, then ruled by Ismail Adil Shah, to defend the left bank of the Zuari river. Conquered in AD 1520 by Krishnadevaraya, the emperor of the Vijayanagara Kingdom; he handed over this fort in the same year to the Portuguese Empire in exchange for protection of southern India against the northern India Mughal Empire. [1]
Occupied by Portuguese forces, it was renovated and rebuilt, and two bastions were added in AD 1604. Between the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries it had a hundred pieces of artillery, a significant number for those times.
After the siege that was imposed by the Maratha Empire leader Sambhaji in AD 1684, it was remodeled as decided by the Viceroy of Portuguese India, Dom Francisco de Tavora, 1st Count of Alvor, as epigraphic inscription, which reads:
THE COUNT OF ALVOR, VICEROY OF INDIA, ORDERED THIS FORTRESS'S RENOVATION AFTER DEFENDING THE SIEGE OF SAMBHAJI ON 22 APRIL 1684.
It underwent a new reform campaign in AD 1745, on the order of Pedro Miguel de Almeida Portugal e Vasconcelos, the first Marquis of Alorna.
The fort's cannons were later sent to other forts and abandoned as a military post. [2]
This fort is currently severely ruined, but one can still see the old gate of arms surmounted by the coat of arms of the Portuguese monarchy, and some sections of the walls and the moat.
Its gate has been a monument protected by the government of Goa, Daman and Diu since 1983.

Sambhaji Bhosale was the second Chhatrapati of the Maratha Empire, ruling from 1681 to 1689. He was the eldest son of Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha Empire. Sambhaji's rule was largely shaped by the ongoing wars between the Maratha Empire and the Mughal Empire, as well as other neighbouring powers such as the Siddis, Mysore and the Portuguese in Goa. After Sambhaji's death, his brother Rajaram I succeeded him as the next Chhatrapati.

The State of India, also referred as the Portuguese State of India or simply Portuguese India, was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a sea route to the Indian subcontinent by Vasco da Gama, a subject of the Kingdom of Portugal. The capital of Portuguese India served as the governing centre of a string of military forts and trade posts scattered all over the Indian Ocean.
Dom Diogo Rodrigues, Dom Diogo Roiz was a Portuguese explorer of the Indian Ocean who sailed as an ordinary helmsman under the command of Dom Pedro Mascarenhas around Goa. They sailed from the Cape of Good Hope eastward into little-known waters of the newly discovered route to Goa. Rodrigues island was named after him between 4 and 9 February 1528 because he had discovered it during his only return journey from Goa via Cochin to Lisbon, where he was elevated to the rank of a knight (cavaleiro) by John III of Portugal. He then returned to Goa and made a mark in the history of the Portuguese empire in the subcontinent around the mid-16th century.
The Mughal–Maratha Wars, sometimes referred to as a whole as the Deccan War, the Maratha War of Independence, or the Twenty-Seven Years' War were a set of wars fought between the Mughal Empire and the Maratha Empire from 1680 to 1707.

Reis Magos is a village located on the northern bank of the Mandovi River in Bardez, Goa, opposite to the capital city of Panjim. The village is famous for two of Goa’s famous structures; the Reis Magos Fort, and the Reis Magos Church – the first church in Bardez. Reis Magos is the Portuguese name for the Three Wise Men from the Bible.
The Maratha Conquests were a series of conquests in the Indian subcontinent which led to the building of the Maratha Empire. These conquests were started by Shivaji in 1659, from the victory at the Battle of Pratapgad against Bijapur. The expansion of the empire was limited and interrupted by the Mughal conquests of south India by Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. Marathas were forced to defend their territories against the overwhelmingly strong Mughal army in the 27 years long Deccan wars. They were able to defend their territories and gain an upper hand over Mughals in the sustained conflict.

Anjediva Island(Konkani: Anjadiv; Portuguese: Ilha de Angediva) is an Indian island in the Arabian Sea. It sits off the coast of Canacona. It is politically part of Goa state, geographically the nearest mainland is the coast of the Canara subregion of Karnataka state.
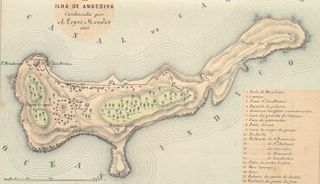
Fort Anjediva, built on the Anjadip Island, off the coast of the Indian state of Karnataka but under the administrative jurisdiction of the Indian state of Goa, was once under Portuguese rule. The island of Anjadip has an area of 1.5 square kilometres (0.58 sq mi).
Tivim pronounced Thivim, is a village in Nathivim in Bardez, in the North Goa district of Goa, India. It is an important gateway into North Goa as the home to the major railway station in North Goa. Tivim was also the ancestral village of the first global beauty queen of India, Ms. Reita Faria. More recently Prathamesh Maulingkar was crowned Mister Supranational 2018..
Bernardo Peres da Silva was a governor of Portuguese India. He was the first and only native Goan to be appointed to this post during the 451 years of Portuguese colonial and provincial governance. He was also one of the first elected representatives in the Portuguese Parliament from its overseas Indian colonies.

Corjuem Fort is a fortress situated 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) from the village of Aldona on the river island of Corjuem, Goa. It was a military fortress for the defense of Portuguese India. It is smaller than the other forts in Goa, but it gives a good view of the surrounding river and land. It is a protected monument under the Goa, Daman and Diu ancient monuments and archaeological sites and remains act.
Rachol is a village within an island of the same name in Salcete, Goa, in south-western India. It is located on the left bank of the Zuari River and is home to the famous Rachol Seminary. The famous Portuguese colonial fort of Rachol has been completely erased, leaving behind the traces of the moat and the main gate. The village has many heritage structures and is an important site to study the history of Salcete. The Church of Our Lady of Snows at Rachol is said to be the first church of Salcete and is called the Matriz of South Goa. Ilha de Rachol is a part of the village.

The Igreja de Nossa Senhora das Neves is a historical Catholic church in Rachol village, Salcete sub-district, on the southern banks of the Zuari river, in the South Goa district of Goa state, India. The church was built in the 1560's during the Goa Inquisition. It is situated in close proximity to the renowned Rachol Seminary. There is a church of the same name in the neighbouring village of Raia.
The Fortaleza de São Sebastião, also called the Tivim Fort, after the village where a part of the long wall structure was once located, is a fort that spans from the village of Tivim, to the area known as Colvale, in Goa, on the west coast of India. Currently, most of it is in ruins and barely visible. However, parts of the structure are in the process of being restored.

The Ponda Fort is located near Ponda, in the state of Goa on the west coast of India. The present structure is a modern reconstruction on this location and converted into a park. In 2017 the lower walls of the fort had collapsed, due to neglect and also due to the use of poor quality materials during a previous (1977) renovation. The original structure was constructed of stone and mud, and left bare, the new structure contains stone, concrete and is plastered and painted red.

The Maratha Navy was the naval wing of the armed forces of the Maratha Empire, which existed from around mid-17th century to mid-18th century in India.
The Mormugão fort was located on the southern tip of the mouth of the Zuari river in Mormugao in the state of Goa on the west coast of India.
The siege of Janjira (1682) was a military conflict fought between Maratha and Siddis of Janjira,the allies of Mughal Empire.Maratha Emperor Sambhaji personally besieged the fort of Murud-Janjira to stop Siddi's intrusions into Maratha Territories and to capture the strategically important fort Janjira.
Maratha Invasion of Goa (1683) or Sambhaji's Invasion of Goa refers to the invasion of Portuguese controlled portion of Old Goa and the northern areas of Konkan. The battles were fought between the Mahratta confederacy and the Portuguese in Goa and Bombay-Bassein, on various fronts in between 1682-1683. In 1682, 2 years after the death of Shivaji, Mahrattas began arming and fortifying their border with Portuguese held territories, and the Portuguese increasingly aligned themselves with the Moghal empire to avert the looming threat. This would set the background for a series of Mahratta hostilities in and around the present-day Goa (Gomantak) and Bombay (Mumbai) of the Konkan region. The Ponda Fort near the capital city of Velha Goa was a strategic Maratha position, hence Francisco de Távora (viceroy) led a botched attack on it in late 1683, attempting to prevent the raids. Sambhaji ordered reinforcements to press on the advantage of the Portuguese retreat at Ponda and elsewhere. He stormed the colony of Goa, Marathas temporarily occupied many forts there. The Maratha forces were preemptively mobilised, and the Portuguese situation eventually became dire. Sambhaji ransacked the north Konkan region for over a month, his forces also pillaged Salcette and Bardes areas in south Konkan. Sambhaji came very close to capturing the city of Old Goa, but his forces retreated from Goa, Damaon& Diu and the northern areas of Konkan division on 2 January 1684, to avoid the large Moghul armed force led by Bahadur Shah I (Muazzam).
Mughal invasion of Konkan (1684) was a part of the Deccan wars. It was a campaign launched by Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb to capture the Konkan region from the Maratha Empire under Sambhaji. The Mughal forces were led by Mu'azzam and Shahbuddin Khan. The harsh climate and the Maratha guerrilla strategy forced the numerically strong Mughal army into a slow retreat. The Maratha army suffered small losses in this unsuccessful campaign of Mughal Empire.In this war Mughals was badly defeated by Marathas.