
Mosasaurs are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes.
Tylosaurus is a genus of russellosaurine mosasaur that lived about 92 to 66 million years ago during the Turonian to Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils have been found primarily around North Atlantic Ocean including in North America, Europe, and Africa.

The Mosasaurinae are a subfamily of mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the subfamily are informally and collectively known as "mosasaurines" and their fossils have been recovered from every continent except for South America.

Globidens is an extinct genus of mosasaurid oceanic lizard classified as part of the Globidensini tribe in the Mosasaurinae subfamily. Globidens belongs to the family Mosasauridae, which consists of several genera of predatory marine lizards of various sizes that were prevalent during the Late Cretaceous. Specimens of Globidens have been discovered in Angola, Brazil, Colombia, Morocco, Syria and the United States. Among mosasaurs, Globidens is probably most well known for the highly rounded, globe-like teeth that give it its name.

Prognathodon is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Mosasaurinae subfamily, alongside genera like Mosasaurus and Clidastes. Prognathodon has been recovered from deposits ranging in age from the Campanian to the Maastrichtian in the Middle East, Europe, New Zealand, and North America.
Clidastes is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Mosasaurinae subfamily, alongside genera like Mosasaurus and Prognathodon. Clidastes is known from deposits ranging in age from the Coniacian to the early Campanian in the United States.
Carinodens is an extinct genus of Cretaceous marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. "Carinodens" means "keel teeth" and was named in 1969 as a replacement name for Compressidens, "compressed teeth", which was already in use for a gadilidan scaphopod mollusk.

Schizorhiza is an extinct genus of schizorhizid sclerorhynchoid that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains one valid species, Schizorhiza stromeri. It lived from the Campanian to Maastrichtian, and its fossils have been found in Africa, the Middle East, North America, and South America.
Stratodus is a genus of giant prehistoric aulopiform fish found in Cretaceous-aged marine strata of Kansas, Alabama, Morocco, Israel, and Niger, South Dakota, Jordan. It has also been found in the Tamaguélelt Formation of Mali, dating to the Lower Eocene, indicating that Stratodus survived the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event. This sleek fish has an upper jaw filled with multiple rows of tiny teeth and was the largest aulopiform, reaching 5 meters in length.

Saurocephalus is an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes within the family Saurodontidae. The genus was first described in 1824 and contains six or seven species, including the type species S. lanciformis. Saurocephalus first appeared during the early Valanginian and continued on to the Maastrichtian, where it nearly went extinct. However, the recent discovery of S. lanciformis remains from the earliest Paleocene indicates that it just barely survived into the Cenozoic. This would make it the last surviving ichthyodectiform.

Wadi Harrana is a seasonal stream (wadi) in the eastern Jordanian Badia, about sixty kilometers southeast of the city of Amman. It runs eastwards from the edge of the Jordanian Highlands to the Azraq oasis.

Gigantatypus is an extinct late Maastrichtian sea turtle that lived in the southern regions of the Tethys Ocean about 100–120 kilometres (62–75 mi) off the north eastern margins of Cretaceous Africa immediately before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction events . Fossil remains of Gigantatypus are so far only represented in sediments from the Muwaqqar Chalk-Marl Formation of Jordan. Estimated at over 3.5 metres (11 ft) in length, members of this genus reached remarkably large proportions equivalent to that of or possibly even exceeding Archelon Wieland, 1896, considered as the largest marine turtles to ever roam the oceans of the world. Although Gigantatypus apparently did not survive the K/T boundary, which also was the fate of other gigantic marine turtles such as protostegids, other genera of Cheloniidae, though significantly smaller, survived the mass extinction and continued on until the present day.
Harranahynchus is an extinct genus of schizorhizid sawskate that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains one valid species, Harranahynchus minutadens. It is known from relatively complete cranial and body fossils found in the Muwaqqar Chalk Marl Formation of Jordan, dating back to the late Maastrichtian. Its rostral denticles are extremely small and are arranged in batteries like its close relative Schizorhiza. It has an estimated length of around 2 m (6.6 ft).

Nyctosauridae is a family of specialized soaring pterosaurs of the late Cretaceous Period of North America, Africa, and possibly other continents including South America. It was named in 1889 by Henry Alleyne Nicholson and Richard Lydekker.

The Kristianstad Basin is a Cretaceous-age structural basin and geological formation in northeastern Skåne, the southernmost province of Sweden. The basin extends from Hanöbukten, a bay in the Baltic Sea, in the east to the town of Hässleholm in the west and ends with the two horsts Linderödsåsen and Nävlingeåsen in the south. The basin's northern boundary is more diffuse and there are several outlying portions of Cretaceous-age sediments. During the Cretaceous, the region was a shallow subtropical to temperate inland sea and archipelago.
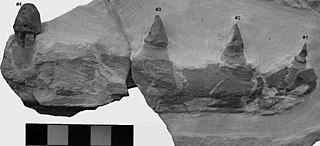
Harranasaurus is an extinct genus of globidensin mosasaur from Jordan. The genus contains one known species, H. khuludae from the Muwaqqar Chalk Marl Formation of Jordan.

Inabtanin is an extinct genus of azhdarchoid pterosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Muwaqqar Formation of Jordan. The genus contains a single species, I. alarabia, known from a partial skeleton. Inabtanin represents one of the most complete pterosaur taxa known from the Afro-Arabia region.
The Muwaqqar Chalk-Marl Formation or Muwaqqar Formation is a Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) and early Paleogene-aged geological formation in Jordan, cropping out across the Jordanian Highlands from north to south. It is the geological formation containing Jordan's famous oil shales, which are among the largest in the world. Some outcrops of the formation contain extremely well-preserved fossils, making it a lagerstätte.

Postredectes is an extinct genus of ichthyodectid ray-finned fish from the Late Cretaceous Muwaqqar Chalk-Marl Formation of Jordan. The type species is P. harranaensis.













