
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

A dermatofibroma, or benign fibrous histiocytomas, is a benign nodule in the skin, typically on the legs, elbows or chest of an adult. It is usually painless.

Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and also usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis.
Diabetic dermopathy is a type of skin lesion usually seen in people with diabetes mellitus. It is characterized by dull-red papules that progress to well-circumscribed, small, round, atrophic hyperpigmented skin lesions usually on the shins. It is the most common of several diabetic skin conditions, being found in up to 30% of diabetics. Similar lesions can occasionally be found in non-diabetics usually following trauma or injury to the area; however, more than 4 lesions strongly suggests diabetes.
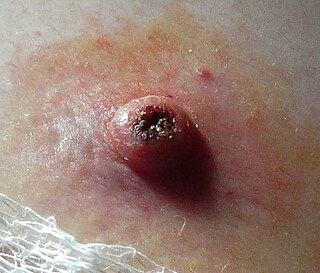
Keratoacanthoma (KA) is a common low-grade rapidly-growing skin tumour that is believed to originate from the hair follicle and can resemble squamous cell carcinoma.

Angiokeratoma is a benign cutaneous lesion of capillaries, resulting in small marks of red to blue color and characterized by hyperkeratosis. Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum refers to Fabry's disease, but this is usually considered a distinct condition.

Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common, sometimes chronic skin condition which presents as reddish bumps on the skin arranged in a circle or ring. It can initially occur at any age, though two-thirds of patients are under 30 years old, and it is seen most often in children and young adults. Females are two times as likely to have it as males.
Lichen spinulosus is a rare skin disorder characterized by follicular keratotic papules that are grouped into large patches. It is a variant of keratosis pilaris named for its resemblance to a patch of lichen.

Angiofibroma (AGF) is a descriptive term for a wide range of benign skin or mucous membrane lesions in which individuals have:
- benign papules, i.e. pinhead-sized elevations that lack visible evidence of containing fluid;
- nodules, i.e. small firm lumps usually >0.1 cm in diameter; and/or
- tumors, i.e. masses often regarded as ~0.8 cm or larger.

Parakeratosis is a mode of keratinization characterized by the retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum. In mucous membranes, parakeratosis is normal. In the skin, this process leads to the abnormal replacement of annular squames with nucleated cells. Parakeratosis is associated with the thinning or loss of the granular layer and is usually seen in diseases of increased cell turnover, whether inflammatory or neoplastic. Parakeratosis is seen in the plaques of psoriasis and in dandruff.
Kyrle disease is identified as a form of an acquired perforating disease. Other major perforating diseases are elastosis perforans serpiginosa and reactive perforating collagenosis. Recently, however, there is a controversy on categorizing Kyrle disease with perforating dermatosis or a subtype of acquired perforating collagenosis.

Perforating calcific elastosis is an acquired, localized cutaneous disorder, most frequently found in obese, multiparous, middle-aged women, characterized by lax, well-circumscribed, reticulated or cobble-stoned plaques occurring in the periumbilical region with keratotic surface papules.

Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa is a familial condition characterized by multiple keratotic papules on the dorsum of the hands and feet, palms, soles, in which electron microscopy shows rarified, abnormal elastic tissue.
Galli–Galli disease is a rare inherited condition that has close resemblance clinically to Dowling-Degos' disease, but is histologically distinct, characterized by skin lesions that are 1- to 2-mm slightly keratotic red to dark brown papules which are focally confluent in a reticulate pattern. The disease is also characterized by slowly progressive and disfiguring reticulate hyperpigmentation of the flexures, clinically and histopathologically diagnostic for Dowling-Degos disease but also associated with suprabasal, nondyskeratotic acantholysis.

Warty dyskeratoma, also known as an Isolated dyskeratosis follicularis, is a benign epidermal proliferation with distinctive histologic findings that may mimic invasive squamous cell carcinoma and commonly manifests as an umbilicated lesion with a keratotic plug, WD have some histopathologic similarities to viral warts but it's not caused by HPV and the majority of these lesions display overall histopathologic features consistent with a follicular adnexal neoplasm. Usually limited to the head, neck, scalp or face and vulva. Lesions are generally solitary and sporadic and may be associated with a follicular unit. Oral involvement, particularly the hard palate, and genital involvement have been reported. it can also be thought of as one of the manifestations of focal acantholytic dyskeratosis, an epidermal reaction pattern that can be seen in several disorders, including Darier's disease and Grover's disease. But the main Difference between Darier disease and Warty dyskeratoma, is that Darier disease inherited dermatosis consisting of multiple keratotic papules on the face, trunk, and extremities, while WD occurs as an isolated, noninherited, single keratotic nodule mainly confined to the head and neck as mentioned earlier.
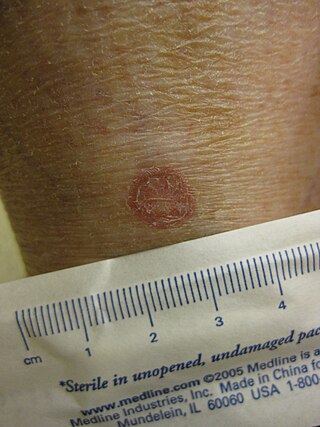
Porokeratosis is a specific disorder of keratinization that is characterized histologically by the presence of a cornoid lamella, a thin column of closely stacked, parakeratotic cells extending through the stratum corneum with a thin or absent granular layer.
Waxy keratosis of childhood is a keratotic, flesh-colored papule that is either sporadic or familial, and may be generalized or segmental.

Majocchi's granuloma is a skin condition characterized by deep, pustular plaques, and is a form of tinea corporis. It is a localized form of fungal folliculitis. Lesions often have a pink and scaly central component with pustules or folliculocentric papules at the periphery. The name comes from Domenico Majocchi, who discovered the disorder in 1883. Majocchi was a professor of dermatology at the University of Parma and later the University of Bologna. The most common dermatophyte is called Trichophyton rubrum.
Perforating granuloma annulare is a skin condition of unknown cause, usually appearing on the dorsal hands, presenting as papules with a central keratotic core.

Isthmicoma are a cutaneous condition characterized by flat, keratotic papules of the head and neck, skin lesions that are usually solitary.













