
Elastin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELN gene. Elastin is a key component of the extracellular matrix in gnathostomes. It is highly elastic and present in connective tissue allowing many tissues in the body to resume their shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin to return to its original position when it is poked or pinched. Elastin is also an important load-bearing tissue in the bodies of vertebrates and used in places where mechanical energy is required to be stored.
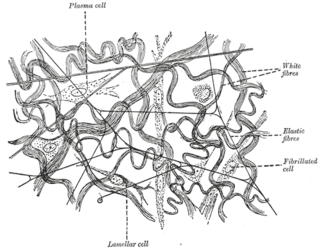
Elastic fibers are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan.

Penicillamine, sold under the brand name of Cuprimine among others, is a medication primarily used for the treatment of Wilson's disease. It is also used for people with kidney stones who have high urine cystine levels, rheumatoid arthritis, and various heavy metal poisonings. It is taken by mouth.
Necrobiosis is the physiological death of a cell, and can be caused by conditions such as basophilia, erythema, or a tumor. It is identified both with and without necrosis.

Cutis laxa or pachydermatocele is a group of rare connective tissue disorders in which the skin becomes inelastic and hangs loosely in folds.

The Koebner phenomenon or Köbner phenomenon, also called the Koebner response or the isomorphic response, attributed to Heinrich Köbner, is the appearance of skin lesions on lines of trauma. The Koebner phenomenon may result from either a linear exposure or irritation. Conditions demonstrating linear lesions after a linear exposure to a causative agent include: molluscum contagiosum, warts and toxicodendron dermatitis. Warts and molluscum contagiosum lesions can be spread in linear patterns by self-scratching ("auto-inoculation"). Toxicodendron dermatitis lesions are often linear from brushing up against the plant. Causes of the Koebner phenomenon that are secondary to scratching rather than an infective or chemical cause include vitiligo, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen nitidus, pityriasis rubra pilaris, and keratosis follicularis.
Anetoderma is a benign but uncommon disorder that causes localized areas of flaccid or herniated sac-like skin due to a focal reduction of dermal elastic tissue. Anetoderma is subclassified as primary anetoderma, secondary anetoderma, iatrogenic anetoderma of prematurity, congenital anetoderma, familial anetoderma, and drug-induced anetoderma.
Acquired perforating dermatosis is clinically and histopathologically similar to perforating folliculitis, also associated with chronic kidney failure, with or without hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, and/or diabetes mellitus, but not identical to Kyrle disease.
Kyrle disease is identified as a form of an acquired perforating disease. Other major perforating diseases are elastosis perforans serpiginosa and reactive perforating collagenosis. Recently, however, there is a controversy on categorizing Kyrle disease with perforating dermatosis or a subtype of acquired perforating collagenosis.
Reactive perforating collagenosis is a rare, familial, nonpuritic skin disorder characterized by papules that grow in a diameter of 4 to 6mm and develop a central area of umbilication to which keratinous material is lodged. The cause of reactive perforating collagenosis is unknown.

Perforating calcific elastosis is an acquired, localized cutaneous disorder, most frequently found in obese, multiparous, middle-aged women, characterized by lax, well-circumscribed, reticulated or cobble-stoned plaques occurring in the periumbilical region with keratotic surface papules.

Linear focal elastosis or elastotic striae is a skin condition that presents with asymptomatic, palpable or atrophic, yellow lines of the middle and lower back, thighs, arms and breasts.

Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa or Acrokeratoelastoidosis is a hereditary form of marginal keratoderma, and can be defined as a palmoplantar keratoderma. It is distinguished by tiny, firm pearly or warty papules on the sides of the hands and, occasionally, the feet. It is less common than the hereditary type of marginal keratoderma, keratoelastoidosis marginalis.

Aplasia cutis congenita is a rare disorder characterized by congenital absence of skin. Ilona J. Frieden classified ACC in 1986 into 9 groups on the basis of location of the lesions and associated congenital anomalies. The scalp is the most commonly involved area with lesser involvement of trunk and extremities. Frieden classified ACC with fetus papyraceus as type 5. This type presents as truncal ACC with symmetrical absence of skin in stellate or butterfly pattern with or without involvement of proximal limbs. It is the most common congenital cicatricial alopecia, and is a congenital focal absence of epidermis with or without evidence of other layers of the skin.
Annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma is a cutaneous condition characterized histologically by a dermal infiltrate of macrophages.

Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck (CCRN) is a minor and very rare congenital cutaneous condition characterized by branchial arch remnants that are considered to be the cervical variant of accessory tragus. It resembles a rudimentary pinna that in most cases is located in the lower anterior part of the neck.
Wrinkly skin syndrome(WSS) is a rare genetic condition characterized by sagging, wrinkled skin, low skin elasticity, and delayed fontanelle (soft spot) closure, along with a range of other symptoms. The disorder exhibits an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern with mutations in the ATP6V0A2 gene, leading to abnormal glycosylation events. There are only about 30 known cases of WSS as of 2010. Given its rarity and symptom overlap with other dermatological conditions, reaching an accurate diagnosis is difficult and requires specialized dermatological testing. Limited treatment options are available but long-term prognosis is variable from patient to patient, based on individual case studies. Some skin symptoms recede with increasing age, while progressive neurological advancement of the disorder causes seizures and mental deterioration later in life for some patients.
Verrucous perforating collagenoma is a very rare skin disorder which presents (clinically) with verrucous papules with a transepidermal elimination of collagen.

Favre–Racouchot syndrome is a solar elastotic disorder consisting of multiple open comedones that occurs in skin damaged by sunlight, especially under and lateral of the eyes. The comedones are widened openings for hair follicles and sebaceous glands filled with material.

Familial cutaneous collagenoma is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by the presence of multiple symmetric nodules on the trunk and upper arms in multiple members of the same family. The nodules are flesh-colored, asymptomatic, and they start appearing during adolescent years. It has been described in 10 families worldwide.












