
General elections were held in Sweden on 17 and 18 September 1932. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 104 of the 230 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag. The party returned to government after six years in opposition, marking the beginning of 44 years of near-uninterrupted rule. This was also the first time the socialist parties received an overall majority of the elected parties' popular vote, although the Hansson cabinet still required cross-aisle co-operation to govern since the centre-right parties won 118 out of 230 seats.
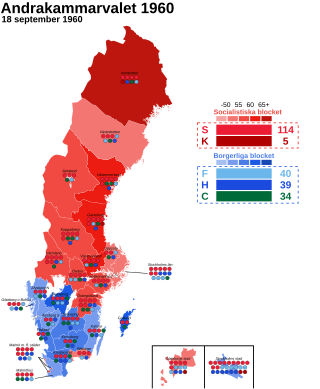
General elections were held in Sweden on 18 September 1960. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 114 of the 232 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag.
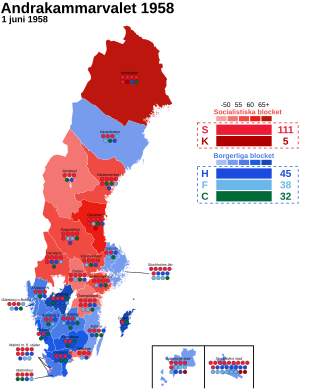
Early general elections were held in Sweden on 1 June 1958, after the defeat of the Social Democratic government's proposals for a new pensions system in a parliamentary vote. The Social Democrats remained the largest party, winning 111 of the 231 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag, and Tage Erlander's third government was returned to power. In accordance with the law, the new Chamber was elected only to complete the previous Chamber's term, which was due to end in 1960.
Early parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 25 and 26 October 1959. Following the electoral reforms made after the June elections, the Independence Party won 16 of the 40 seats in the Lower House of the Althing.

Early general elections were held in Sweden between 27 March and 7 April 1914, after the Riksdag had been prematurely dissolved by the Cabinet of Hjalmar Hammarskjöld. The General Electoral League emerged as the largest party, winning 86 of the 230 seats in the Andra kammaren. As of 2022, this is the last time a Swedish election has not seen the Social Democrats win a plurality of seats.

Early general elections were held in Sweden 5 and 13 September 1914, the second that year. Although the General Electoral League received the most votes, the Swedish Social Democratic Party emerged as the largest party, winning 87 of the 230 seats in the Andra kammaren, and have managed to remain so in every subsequent Swedish election.

Presidential elections were held in Cyprus for the first time on 13 December 1959. Only two candidates contested the election; Makarios III, who was backed by EOKA, and Ioannis Clerides, a member of the Democratic Union who was also supported by AKEL. The result was a victory for Makarios III, who received 67% of the vote, although he did not take office until 16 August 1960. Voter turnout was 91.2%.
Sweden held a general election on 20 September 1964.
Sweden held an early general election to fulfil the four-year term between the regular 1956 and 1960 elections. Although the centre-right received more votes, the leftist parties won one more seat. The election was held on 1 June.
Sweden held a general election on 21 September 1952.
Sweden held a general election on 19 September 1948. This was the country's first election since the dissolution of the wartime unity government in 1945, which had consisted of the Social Democrats and all three centre-right parties. The election resulted in the Social Democrats maintaining their 46% share of the vote, securing their position in government. Meanwhile, the centre-right parties made gains at the expense of the Communists, who suffered a significant decline in the overall vote. The People's Party achieved the largest gains of any party, becoming the largest opposition party.
Sweden held a general election on 17 September 1944. Due to the wartime coalition government the bloc balance mainly determined that Per-Albin Hansson remained as Prime Minister, with the four-party coalition remaining in office with 215 out of 230 seats. Among the traditional blocs, the left bloc won 130 and the right bloc 100.
Sweden held a general election on 15 September 1940.
Sweden held a general election around 19 September 1924. This was the second election under universal suffrage. In spite of a majority for the non-socialist parties, Social Democrat Hjalmar Branting was able to form a government, although his successor eventually saw the government fall and being replaced by a right-leaning Electoral League government.
Sweden held a general election around 15 September 1928 to the second chamber.
Sweden held a general election around 17 September 1932.
Sweden held a general election on 20 September 1936.
Sweden held a general election throughout September 1921.
Sweden held a general election throughout September 1914.
Sweden held a general election in September 1920. The election was the last before universal suffrage was introduced the following year. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 75 of the 230 seats in the Second Chamber of the Riksdag. In spite of this, the non-socialist parties got a sizeable majority in the chamber.





