
In pathology, the reticulin stain is a popular staining method in histology. It is used to visualize reticular fiber and used extensively in liver histo pathology. [1]

In pathology, the reticulin stain is a popular staining method in histology. It is used to visualize reticular fiber and used extensively in liver histo pathology. [1]

Anatomical pathology (Commonwealth) or anatomic pathology (U.S.) is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination of organs and tissues. Over the 20th century, surgical pathology has evolved tremendously: from historical examination of whole bodies (autopsy) to a more modernized practice, centered on the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer to guide treatment decision-making in oncology. Its modern founder was the Italian scientist Giovanni Battista Morgagni from Forlì.

Cytopathology is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1928. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments, in contrast to histopathology, which studies whole tissues. Cytopathology is frequently, less precisely, called "cytology", which means "the study of cells".

A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments.

Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver disease. Steatosis can also occur in other organs, including the kidneys, heart, and muscle. When the term is not further specified, it is assumed to refer to the liver.

Histopathology is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments.

In pathology, a Councilman body, also known as a Councilman hyaline body or apoptotic body, is an eosinophilic globule of apoptotic hepatocyte cell fragments. Ultimately, the fragments are taken up by macrophages or adjacent parenchymal cells. They are found in the liver of individuals suffering from acute viral hepatitis, yellow fever, and other viral syndromes.

Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) is a staining method used to detect polysaccharides and mucosubstances in tissues. The reaction of periodic acid oxidizes vicinal diols in these sugars, usually breaking up the bond between two adjacent carbons not involved in the glycosidic linkage or ring closure in the ring of monosaccharide units that are part of the long polysaccharides and creating a pair of aldehydes at the two free tips of each broken monosaccharide ring. The oxidation condition has to be sufficiently regulated so as to not further oxidize the aldehydes. These aldehydes then react with the Schiff reagent to give a purple-magenta color. A suitable basic stain is often used as a counterstain.

Pneumocystosis is a fungal infection that most often presents as Pneumocystis pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS or poor immunity. It usually causes cough, difficulty breathing and fever, and can lead to respiratory failure. Involvement outside the lungs is rare but, can occur as a disseminated type affecting lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, eyes, kidneys, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract or other organs. If occurring in the skin, it usually presents as nodular growths in the ear canals or underarms.

Oil Red O (Solvent Red 27, Sudan Red 5B, C.I. 26125, C26H24N4O) is a lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) diazo dye used for staining of neutral triglycerides and lipids on frozen sections and some lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of a red powder with an absorbance maximum at 518 nanometers.

Papanicolaou stain is a multichromatic (multicolored) cytological staining technique developed by George Papanicolaou in 1942. The Papanicolaou stain is one of the most widely used stains in cytology, where it is used to aid pathologists in making a diagnosis. Although most notable for its use in the detection of cervical cancer in the Pap test or Pap smear, it is also used to stain non-gynecological specimen preparations from a variety of bodily secretions and from small needle biopsies of organs and tissues. Papanicolaou published three formulations of this stain in 1942, 1954, and 1960.

Hematoxylin and eosin stain is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E.

In histopathology, a Mallory body, Mallory–Denk body (MDB), or Mallory's hyaline is an inclusion found in the cytoplasm of liver cells. Mallory bodies are damaged intermediate filaments within the liver cells.

Hepatocellular adenoma is a rare, benign liver tumor. It most commonly occurs in people with elevated systemic levels of estrogen, classically in women taking estrogen-containing oral contraceptive medication.
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy is a rare life-threatening complication of pregnancy that occurs in the third trimester or the immediate period after delivery. It is thought to be caused by a disordered metabolism of fatty acids by mitochondria in the fetus, caused by long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. This leads to decreased metabolism of long chain fatty acids by the feto-placental unit, causing subsequent rise in hepatotoxic fatty acids in maternal plasma. The condition was previously thought to be universally fatal, but aggressive treatment by stabilizing the mother with intravenous fluids and blood products in anticipation of early delivery has improved prognosis.

Periodic acid–Schiff–diastase stain is a periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain used in combination with diastase, an enzyme that breaks down glycogen. PAS-D is a stain often used by pathologists as an ancillary study in making a histologic diagnosis on paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. PAS stain typically gives a magenta color in the presence of glycogen. When PAS and diastase are used together, a light pink color replaces the deep magenta. Differences in the intensities of the two stains can be attributed to different glycogen concentrations and can be used to semiquantify glycogen in samples. In practice, the tissue is deparaffinized, the diastase incubates, and the PAS stain is applied.

The canals of Hering, or intrahepatic bile ductules, are part of the outflow system of exocrine bile product from the liver. Liver stem cells are hypothesized to inhabit the canals.

Felix Victor Birch-Hirschfeld was a German pathologist who was a native of Kluvensieck bei Rendsburg.
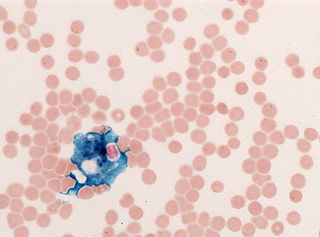
In histology, histopathology, and clinical pathology, Perls Prussian blue is a commonly used method to detect the presence of iron in tissue or cell samples. Perls Prussian Blue derives its name from the German pathologist Max Perls (1843–1881), who described the technique in 1867. The method does not involve the application of a dye, but rather causes the pigment Prussian blue to form directly within the tissue. The method stains mostly iron in the ferric state which includes ferritin and hemosiderin, rather than iron in the ferrous state.

In histopathology, feathery degeneration, formally feathery degeneration of hepatocytes, is a form of liver parenchymal cell death associated with cholestasis.

Critical green inclusions, also known as green neutrophilic inclusions and informally, death crystals or crystals of death, are amorphous blue-green cytoplasmic inclusions found in neutrophils and occasionally in monocytes. They appear brightly coloured and refractile when stained with Wright-Giemsa stain. These inclusions are most commonly found in critically ill patients, particularly those with liver disease, and their presence on the peripheral blood smear is associated with a high short-term mortality rate.