
Chuquicamata is the largest open pit copper mine in terms of excavated volume in the world. It is located in the north of Chile, just outside Calama, at 2,850 m (9,350 ft) above sea level. It is 215 km (134 mi) northeast of Antofagasta and 1,240 km (770 mi) north of the capital, Santiago. Flotation and smelting facilities were installed in 1952, and expansion of the refining facilities in 1968 made 500,000 tons annual copper production possible in the late 1970s. Previously part of Anaconda Copper, the mine is now owned and operated by Codelco, a Chilean state enterprise, since the Chilean nationalization of copper in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Its depth of 850 metres (2,790 ft) makes it the second deepest open-pit mine in the world, after Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah, United States.
Quadra FNX Mining Ltd was a Vancouver, British Columbia-based company that produced copper, nickel, platinum, palladium, gold, cobalt, and molybdenum with operations in Nevada, Arizona, Chile, Greenland, and the Sudbury Basin, Ontario, Canada.

Kennecott Utah Copper LLC (KUC), a division of Rio Tinto Group, is a mining, smelting, and refining company. Its corporate headquarters are located in South Jordan, Utah. Kennecott operates the Bingham Canyon Mine, one of the largest open-pit copper mines in the world in Bingham Canyon, Salt Lake County, Utah. The company was first formed in 1898 as the Boston Consolidated Mining Company. The current corporation was formed in 1989. The mine and associated smelter produce 1% of the world's copper.

The Nevada Northern Railway was a railroad in the U.S. state of Nevada, built primarily to reach a major copper producing area in White Pine County, Nevada. The railway, constructed in 1905-06, extended northward about 140 miles (230 km) from Ely to connections with the Western Pacific Railroad at Shafter and Southern Pacific Railroad at Cobre. In 1967 NN reported 40 million net ton-miles of revenue freight on 162 miles (261 km) of line.

Porphyry copper deposits are copper ore bodies that are formed from hydrothermal fluids that originate from a voluminous magma chamber several kilometers below the deposit itself. Predating or associated with those fluids are vertical dikes of porphyritic intrusive rocks from which this deposit type derives its name. In later stages, circulating meteoric fluids may interact with the magmatic fluids. Successive envelopes of hydrothermal alteration typically enclose a core of disseminated ore minerals in often stockwork-forming hairline fractures and veins. Because of their large volume, porphyry orebodies can be economic from copper concentrations as low as 0.15% copper and can have economic amounts of by-products such as molybdenum, silver, and gold. In some mines, those metals are the main product.

KGHM Polska Miedź S.A., commonly known as KGHM, is a Polish multinational corporation that employs around 34,000 people around the world and has been a major copper and silver producer for more than 50 years. In 1991, the company was established as a state enterprise and since 1997, their shares have been traded on the Warsaw Stock Exchange. Currently, KGHM operates 9 open-pit and underground mines located in Poland, Canada, the USA and Chile and is actively advancing 4 projects. KGHM produces key global resources including copper, copper sulphate, gold, silver, nickel, nickel sulphate, molybdenum, rhenium, lead, sulphuric acid, selenium, platinum group metals. KGHM is based in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in Lubin, Poland.

The Bingham Canyon Mine, more commonly known as Kennecott Copper Mine among locals, is an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City, Utah, in the Oquirrh Mountains. The mine is the largest man-made excavation, and deepest open-pit mine in the world, which is considered to have produced more copper than any other mine in history – more than 19,000,000 short tons. The mine is owned by Rio Tinto Group, a British-Australian multinational corporation. The copper operations at Bingham Canyon Mine are managed through Kennecott Utah Copper Corporation which operates the mine, a concentrator plant, a smelter, and a refinery. The mine has been in production since 1906, and has resulted in the creation of a pit over 0.75 miles (1,210 m) deep, 2.5 miles (4 km) wide, and covering 1,900 acres. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1966 under the name Bingham Canyon Open Pit Copper Mine. The mine experienced a massive landslide in April 2013 and a smaller slide in September 2013.
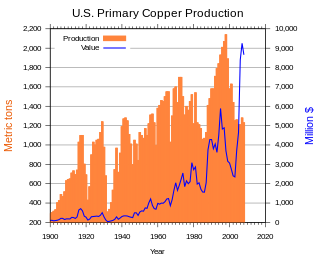
Copper mining in the United States has been a major industry since the rise of the northern Michigan copper district in the 1840s. In 2017 the United States produced 1.27 million metric tonnes of copper, worth $8 billion, making it the world's fourth largest copper producer, after Chile, China, and Peru. Copper was produced from 23 mines in the US. Top copper producing states in 2014 were Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Minor production also came from Idaho, and Missouri. As of 2014, the US had 45 million tonnes of known remaining reserves of copper, the fifth largest known copper reserves in the world, after Chile, Australia, Peru, and Mexico.

Gold mining in the United States has taken place continually since the discovery of gold at the Reed farm in North Carolina in 1799. The first documented occurrence of gold was in Virginia in 1782. Some minor gold production took place in North Carolina as early as 1793, but created no excitement. The discovery on the Reed farm in 1799 which was identified as gold in 1802 and subsequently mined marked the first commercial production.
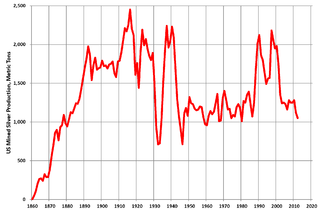
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.
Silver mining in Colorado has taken place since the 1860s. In the past, Colorado called itself the Silver State.
Silver mining in Nevada, a state of the United States, began in 1858 with the discovery of the Comstock Lode, the first major silver-mining district in the United States. Nevada calls itself the "Silver State." Nevada is the nation's second-largest producer of silver, after Alaska. In 2014 Nevada produced 10.93 million troy ounces of silver, of which 6.74 million ounces were as a byproduct of the mining of gold. The largest byproducers were the Hycroft Mine, the Phoenix Mine, the Midas Mine and Round Mountain.
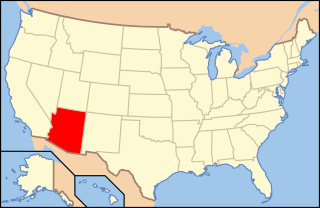
Copper mining in Arizona, a state of the United States, has been a major industry since the 19th century. In 2007 Arizona was the leading copper-producing state in the US, producing 750 thousand metric tons of copper, valued at $5.54 billion. Arizona's copper production was 60% of the total for the United States. Copper mining also produces gold and silver as byproducts. Byproduct molybdenum from copper mining makes Arizona the nation's second-largest producer of that metal. Although copper mineralization was found by the earliest Spanish explorers of Arizona, the territory was remote, and copper could seldom be profitably mined and shipped. Early Spanish, Mexican, and American prospectors searched for gold and silver, and ignored copper. It was not until the completion of the Southern Pacific Railroad in 1876 that copper became broadly economic to mine and ship to market.

Gold mining in Nevada, a state of the United States, is a major industry, and one of the largest sources of gold in the world. In 2018 Nevada produced 5,581,160 troy ounces, representing 78% of US gold and 5.0% of the world's production. Total gold production recorded from Nevada from 1835 to 2017 totals 205,931,000 troy ounces (6,405.2 t), worth US$322.6 billion at 2020 values. Much of Nevada's gold production comes from large open pit mining using heap leaching recovery.

El Teniente is an underground copper mine located in the Chilean Andes, 2,300 m (7,500 ft) above mean sea level. It is in the commune of Machalí in Cachapoal Province, Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins Region, near the company town of Sewell. This was established for the workers and their families.

The Skouries mine is a high-grade gold-copper porphyry deposit located in the Chalkidiki peninsula in northern Greece. It is currently under development by Eldorado Gold and is planned to be an open pit and underground mine. Production is targeted in 2019.

Molybdenum mining in the United States produced 65,500 metric tons of molybdenum in 2014, worth US$1.8 billion. The US was the world's second-largest molybdenum producer, after China, and provided 25% of the world's supply of molybdenum.























