
In biochemistry, a kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. As a result, kinase produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group. These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis.

The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis; a functional process that under degenerate conditions may result in a range of clinical manifestations including diabetes and cancer. Insulin signalling controls access to blood glucose in body cells. When insulin falls, especially in those with high insulin sensitivity, body cells begin only to have access to lipids that do not require transport across the membrane. So, in this way, insulin is the key regulator of fat metabolism as well. Biochemically, the insulin receptor is encoded by a single gene INSR, from which alternate splicing during transcription results in either IR-A or IR-B isoforms. Downstream post-translational events of either isoform result in the formation of a proteolytically cleaved α and β subunit, which upon combination are ultimately capable of homo or hetero-dimerisation to produce the ≈320 kDa disulfide-linked transmembrane insulin receptor.
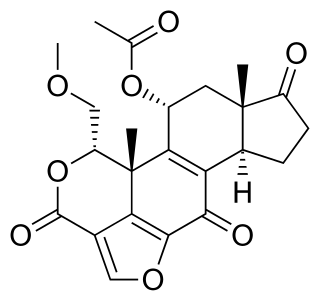
Wortmannin, a steroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii, is a non-specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration (IC50) of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly used PI3K inhibitor. It displays a similar potency in vitro for the class I, II, and III PI3K members although it can also inhibit other PI3K-related enzymes such as mTOR, DNA-PKcs, some phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) at high concentrations Wortmannin has also been reported to inhibit members of the polo-like kinase family with IC50 in the same range as for PI3K. The half-life of wortmannin in tissue culture is about 10 minutes due to the presence of the highly reactive C20 carbon that is also responsible for its ability to covalently inactivate PI3K. Wortmannin is a commonly used cell biology reagent that has been used previously in research to inhibit DNA repair, receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell proliferation.

Phosphoinositide phospholipase C is a family of eukaryotic intracellular enzymes that play an important role in signal transduction processes. These enzymes belong to a larger superfamily of Phospholipase C. Other families of phospholipase C enzymes have been identified in bacteria and trypanosomes. Phospholipases C are phosphodiesterases.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer.
Class II PI 3-kinases are a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that share a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity and method of activation.
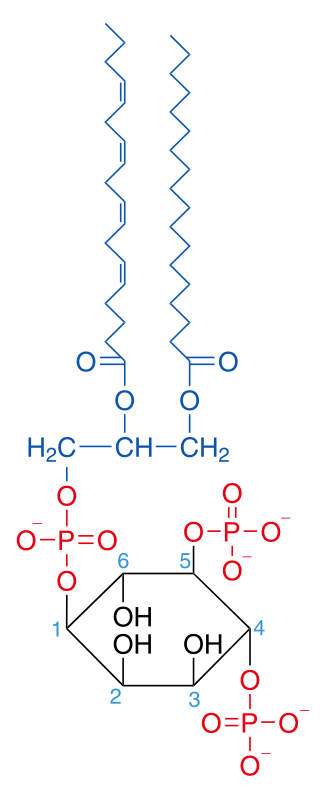
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)P2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins.

Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes, yet an important second messenger. The generation of PtdIns(3,4)P2 at the plasma membrane activates a number of important cell signaling pathways.

Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta isoform or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene.

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological cell signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes. One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized "on demand" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.
Phospholipase D (EC 3.1.4.4, lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase, PLD; systematic name phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase) is an anesthetic sensitive and mechanosensitive enzyme of the phospholipase superfamily that catalyses the following reaction

Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase is a kinase enzyme which acts to inactivate the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase by phosphorylating it using ATP.

John Kuriyan is the dean of basic sciences and a professor of biochemistry at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. He was formerly the Chancellor's Professor at the University of California, Berkeley in the departments of molecular and cell biology (MCB) and chemistry, a faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab's physical biosciences division, and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences and he has also been on the Life Sciences jury for the Infosys Prize in 2009, 2019 and 2020.

Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids.
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.

The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an intracellular signaling pathway important in regulating the cell cycle. Therefore, it is directly related to cellular quiescence, proliferation, cancer, and longevity. PI3K activation phosphorylates and activates AKT, localizing it in the plasma membrane. AKT can have a number of downstream effects such as activating CREB, inhibiting p27, localizing FOXO in the cytoplasm, activating PtdIns-3ps, and activating mTOR which can affect transcription of p70 or 4EBP1. There are many known factors that enhance the PI3K/AKT pathway including EGF, shh, IGF-1, insulin, and calmodulin. Both leptin and insulin recruit PI3K signalling for metabolic regulation. The pathway is antagonized by various factors including PTEN, GSK3B, and HB9.
Lewis C. Cantley is an American cell biologist and biochemist who has made significant advances to the understanding of cancer metabolism. Among his most notable contributions are the discovery and study of the enzyme PI-3-kinase, now known to be important to understanding cancer and diabetes mellitus. He is currently Meyer Director and Professor of Cancer Biology at the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City. He was formerly a professor in the Departments of Systems Biology and Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and the Director of Cancer Research at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, in Boston, Massachusetts. In 2016, he was elected Chairman of the Board for the Hope Funds for Cancer Research.
Leonard (Len) R Stephens FRS is a molecular biologist, senior group leader and associate director at the Babraham Institute.
PASLI disease is a rare genetic disorder of the immune system. PASLI stands for “p110 delta activating mutation causing senescent T cells, lymphadenopathy, and immunodeficiency.” The immunodeficiency manifests as recurrent infections usually starting in childhood. These include bacterial infections of the respiratory system and chronic viremia due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and/or cytomegalovirus (CMV). Individuals with PASLI disease also have an increased risk of EBV-associated lymphoma. Investigators Carrie Lucas, Michael Lenardo, and Gulbu Uzel at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the U.S. National Institutes of Health and Sergey Nejentsev at the University of Cambridge, UK simultaneously described a mutation causing this condition, which they called activated PI3K delta syndrome (APDS).
Phillip (Phill) Thomas Hawkins FRS is a molecular biologist, senior group leader at the Babraham Institute.













