
The Union Jack or Union Flag is the de facto national flag of the United Kingdom. The Union Jack was also used as the official flag of several British colonies and dominions before they adopted their own national flags. The flag continues to have official status in Canada, by parliamentary resolution, where it is known as the Royal Union Flag. However, it is commonly referred to in Canada as the Union Jack.

An ensign is a maritime flag that is used for the national identification of a ship. It is the largest flag and is generally flown at the stern (rear) of the ship while in port. Depending on the ship's origin, it may sometimes be identical with a jack on the bow of the ship when in a port. Jacks are more common on warships than on merchant ships.

The flag of Scotland is the national flag of Scotland, which consists of a white saltire defacing a blue field. The Saltire, rather than the Royal Standard of Scotland, is the correct flag for all private individuals and corporate bodies to fly. It is also, where possible, flown from Scottish Government buildings every day from 8:00 am until sunset, with certain exceptions.

The Red Ensign or "Red Duster" is the civil ensign of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. It is one of the British ensigns, and it is used either plain or defaced with either a badge or a charge, mostly in the right half.

In British maritime law and custom, an ensign is the identifying flag flown to designate a British ship, either military or civilian. Such flags display the United Kingdom Union Flag in the canton, with either a red, white or blue field, dependent on whether the vessel is civilian, naval, or in a special category. These are known as the red, white, and blue ensigns respectively.

The flag of New Zealand, also known as the New Zealand Ensign, is based on the British maritime Blue Ensign – a blue field with the Union Jack in the canton or upper hoist corner – augmented or defaced with four red stars centred within four white stars, representing the Southern Cross constellation.
The history of the Royal Canadian Air Force begins in 1914, with the formation of the Canadian Aviation Corps (CAC) that was attached to the Canadian Expeditionary Force during the First World War. It consisted of one aircraft that was never called into service. In 1918, a wing of two Canadian squadrons called the Canadian Air Force (CAF) was formed in England and attached to the Royal Air Force, but it also would never see wartime service. Postwar, an air militia also known as the Canadian Air Force was formed in Canada in 1920. In 1924 the CAF was renamed the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) when it was granted the royal title by King George V. The RCAF existed as an independent service until 1968.

The several branches of the United States Armed Forces are represented by flags. Within the U.S. military, various flags fly on various occasions, and on various ships, bases, camps, and military academies.
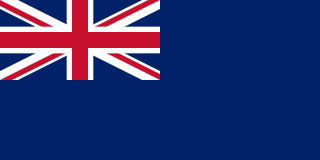
The Blue Ensign is a British ensign that may be used on vessels by certain authorised yacht clubs, Royal Research Ships and British merchant vessels whose master holds a commission in the Royal Naval Reserve or has otherwise been issued a warrant. Defaced versions with a badge or other emblem are used more broadly; in the United Kingdom by authorised government or private bodies; and internationally by nations or organisations previously a part of the British Empire.

The White Ensign, at one time called the St George's Ensign because of the simultaneous existence of a crossless version of the flag, is an ensign worn on British Royal Navy ships and shore establishments. It consists of a red St George's Cross on a white field, identical to the flag of England except with the Union Flag in the upper canton.

The Canadian Red Ensign served as a nautical flag and civil ensign for Canada from 1892 to 1965, and later as the de facto flag of Canada before 1965. The flag is a British Red Ensign, with the Royal Union Flag in the canton, emblazoned with the shield of the coat of arms of Canada.

A roundel is a circular disc used as a symbol. The term is used in heraldry, but also commonly used to refer to a type of national insignia used on military aircraft, generally circular in shape and usually comprising concentric rings of different colours. Other symbols also often use round shapes.

The Royal Australian Air Force Ensign is used by the Royal Australian Air Force and the Australian Air Force Cadets in Australia. It may also be flown on Air Force aircraft overseas. It is based on the Australian national flag, with the field changed to Air Force blue, and the southern cross tilted clockwise to make room for the RAAF roundel inserted in the lower fly quarter. The roundel is a red leaping kangaroo on white within a dark blue ring. The ensign was proclaimed as a Flag of Australia under section 5 of the Flags Act on 6 May 1982.

The Rhodesian Air Force (RhAF) was an air force based in Salisbury which represented several entities under various names between 1935 and 1980: originally serving the British self-governing colony of Southern Rhodesia, it was the air arm of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland between 1953 and 31 December 1963; of Southern Rhodesia once again from 1 January 1964; and of the unrecognised nation of Rhodesia following its Unilateral Declaration of Independence from Britain on 11 November 1965.

The national flag of Australia is based on the British Blue Ensign—a blue field with the Union Jack in the upper hoist quarter—augmented with a large white seven-pointed star and a representation of the Southern Cross constellation, made up of five white stars. Australia also has a number of other official flags representing its people and government bodies.

The flags of British India were varied, and the British Empire used several different banners during the period of its rule in the Indian subcontinent. Flags with the Star of India emblem in their design are often referred to as the Star of India flag, and were used to represent India itself and high offices in the government of India. The Viceroy's Union Flag banner, featuring the star emblem, was officially considered the "Flag of India," and the Red Ensign bearing the star was also used as an Indian flag, particularly at international events. The Royal Indian Navy also flew a blue jack flag bearing the Star of India. The East India Company, which ruled India prior to 1858, used a flag featuring the Union Jack with red and white stripes.

Military aircraft insignia are insignia applied to military aircraft to visually identify the nation or branch of military service to which the aircraft belong. Many insignia are in the form of a circular roundel or modified roundel; other shapes such as stars, crosses, squares, or triangles are also used. Insignia are often displayed on the sides of the fuselage, the upper and lower surfaces of the wings, as well as on the fin or rudder of an aircraft, although considerable variation can be found amongst different air arms and within specific air arms over time.

The Royal Canadian Air Force Ensign is the official flag which is used to represent the Royal Canadian Air Force. The Ensign has an air force blue field defaced with the Canadian Flag in the canton and the current Royal Canadian Air Force roundel in the fly.

The New Zealand White Ensign is a naval ensign used by ships of the Royal New Zealand Navy (RNZN) from 1968. Based on the Royal Navy's White Ensign, it features the Southern Cross from the New Zealand national flag in place of the Saint George's Cross. One of the earliest flags associated with the country, that used by the United Tribes of New Zealand, was a white ensign. This was replaced by the Union Flag when New Zealand became a British colony. A blue ensign with the Southern Cross was introduced for ships of the colonial government in 1867 and this soon became a de facto national flag. Ships in New Zealand naval service wore the Royal Navy's White Ensign until 1968 when the distinct New Zealand White Ensign was introduced. The ensign was implemented out of a desire to distinguish New Zealand vessels from those of the Royal Navy and this decision is regarded as an important step in the development of the RNZN.

The Rhodesian Air Force Ensign was used as the flag of the Rhodesian Air Force. The first flag was created in 1954 under the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, being updated following Southern Rhodesia exiting the Federation in 1963. It was updated further in 1970 when Rhodesia unilaterally declared themselves a republic.














































