
SMS Kaiser was the lead ship of the Kaiser class of dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy. Kaiser was built by the Imperial Dockyard at Kiel, launched on 22 March 1911 and commissioned on 1 August 1912. The ship was equipped with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets, and had a top speed of 23.4 knots. Kaiser was assigned to III Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet for the majority of World War I.

The Bayern class was a class of four super-dreadnought battleships built by the German Kaiserliche Marine. The class comprised Bayern, Baden, Sachsen, and Württemberg. Construction started on the ships shortly before World War I; Baden was laid down in 1913, Bayern and Sachsen followed in 1914, and Württemberg, the final ship, was laid down in 1915. Only Baden and Bayern were completed, due to shipbuilding priorities changing as the war dragged on. It was determined that U-boats were more valuable to the war effort, and so work on new battleships was slowed and ultimately stopped altogether. As a result, Bayern and Baden were the last German battleships completed by the Kaiserliche Marine.

SMSBaden was a Bayern-class dreadnought battleship of the German Imperial Navy built during World War I. Launched in October 1915 and completed in March 1917, she was the last battleship completed for use in the war; two of her sisters—Sachsen and Württemberg—were incomplete when the war ended. The ship mounted eight 38-centimeter (15 in) guns in four twin turrets, displaced 32,200 metric tons at full combat load, and had a top speed of 21 knots. Along with her sister Bayern, Baden was the largest and most powerfully armed battleship built by the Imperial Navy.

SMS Bayern was the lead ship of the Bayern class of dreadnought battleships in the German Kaiserliche Marine. The vessel was launched in February 1915 and entered service in July 1916, too late to take part in the Battle of Jutland. Her main armament consisted of eight 38 cm (15 in) guns in four turrets, which was a significant improvement over the preceding König's ten 30.5 cm (12 inch) guns. The ship was to have formed the nucleus for a fourth battle squadron in the High Seas Fleet, along with three of her sister ships. Of the other ships only one—Baden—was completed; the other two were canceled later in the war when production requirements shifted to U-boat construction.

SMS Seydlitz was a battlecruiser of the German Kaiserliche Marine, built in Hamburg. She was ordered in 1910 and commissioned in May 1913, the fourth battlecruiser built for the High Seas Fleet. She was named after Friedrich Wilhelm von Seydlitz, a Prussian general during the reign of King Frederick the Great and the Seven Years' War. Seydlitz represented the culmination of the first generation of German battlecruisers, which had started with the Von der Tann in 1906 and continued with the pair of Moltke-class battlecruisers ordered in 1907 and 1908. Seydlitz featured several incremental improvements over the preceding designs, including a redesigned propulsion system and an improved armor layout. The ship was also significantly larger than her predecessors—at 24,988 metric tons, she was approximately 3,000 metric tons heavier than the Moltke-class ships.

SMS König was the first of four König-class dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy during World War I. König was named in honor of King William II of Württemberg. The battleship was armed with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets and could steam at a top speed of 21 knots. Laid down in October 1911, the ship was launched on 1 March 1913. The construction of König was completed shortly after the outbreak of World War I; she was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 9 August 1914.

SMS Derfflinger was a battlecruiser of the German Kaiserliche Marine built in the early 1910s during the Anglo-German naval arms race. She was the lead ship of her class of three ships; her sister ships were Lützow and Hindenburg. The Derfflinger-class battlecruisers were larger and featured significant improvements over the previous German battlecruisers, carrying larger guns in a more efficient superfiring arrangement. Derfflinger was armed with a main battery of eight 30.5 cm (12 in) guns, compared to the 28 cm (11 in) guns of earlier battlecruisers. She had a top speed of 26.5 knots and carried heavy protection, including a 30-centimeter (11.8 in) thick armored belt.

SMS Moltke was the lead ship of the Moltke-class battlecruisers of the German Imperial Navy, named after the 19th-century German Field Marshal Helmuth von Moltke. Commissioned on 30 September 1911, the ship was the second battlecruiser of the Imperial Navy. Moltke, along with her sister ship Goeben, was an enlarged version of the previous German battlecruiser design, Von der Tann, with increased armor protection and two more main guns in an additional turret. Compared to her British rivals—the Indefatigable class—Moltke and her sister Goeben were significantly larger and better armored.

SMS Von der Tann was the first battlecruiser built for the German Kaiserliche Marine, as well as Germany's first major turbine-powered warship. At the time of her construction, Von der Tann was the fastest dreadnought-type warship afloat, capable of reaching speeds in excess of 27 knots. She was designed in response to the British Invincible class. While the German design had slightly lighter guns—28 cm (11 in), compared to the 30.5 cm (12 in) Mark X mounted on the British ships—Von der Tann was faster and significantly better-armored. She set the precedent of German battlecruisers carrying much heavier armor than their British equivalents, albeit at the cost of smaller guns.

SMS Kronprinz was the last dreadnought battleship of the four-ship König class of the German Imperial Navy. The battleship was laid down in November 1911 and launched on 21 February 1914. She was formally commissioned into the Imperial Navy on 8 November 1914, just over 3 months after the start of World War I. The name Kronprinz refers to Crown Prince Wilhelm, and in June 1918, the ship was renamed Kronprinz Wilhelm in his honor. The battleship was armed with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets and could steam at a top speed of 21 knots.

The Derfflinger class was a class of three battlecruisers of the Imperial German Navy. The ships were ordered for the 1912–13 Naval Building Program of the German Imperial Navy as a reply to the Royal Navy's two new Lion-class battlecruisers that had been launched a few years earlier. The preceding Moltke class and the incrementally improved Seydlitz represented the end of the evolution of Germany's first generation of battlecruisers. The Derfflinger class had considerable improvements, including a larger primary armament, all of which was mounted on the centerline. The ships were also larger than the preceding classes. The Derfflinger class used a similar propulsion system, and as a result of the increased displacement were slightly slower.

Franz Ritter von Hipper was an admiral in the German Imperial Navy. Franz von Hipper joined the German Navy in 1881 as an officer cadet. He commanded several torpedo boat units and served as watch officer aboard several warships, as well as Kaiser Wilhelm II's yacht SMY Hohenzollern. Hipper commanded several cruisers in the reconnaissance forces before being appointed commander of the I Scouting Group in October 1913.

SMS Markgraf was the third dreadnought battleship of the four-ship König class. She served in the Imperial German Navy during World War I. The battleship was laid down in November 1911 and launched on 4 June 1913. She was formally commissioned into the Imperial Navy on 1 October 1914, just over two months after the outbreak of war in Europe. Markgraf was armed with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets and could steam at a top speed of 21 knots. Markgraf was named in honor of the royal family of Baden. The name Markgraf is a rank of German nobility and is equivalent to the English Margrave, or Marquess.

SMS Grosser Kurfürst was the second dreadnought battleship of the four-ship König class. Grosser Kurfürst served in the Imperial German Navy during World War I. The battleship was laid down in October 1911 and launched on 5 May 1913. She was formally commissioned into the Imperial Navy on 30 July 1914, days before the outbreak of war between Germany and the United Kingdom. Her name means Great Elector, and refers to Frederick William I, the Prince-elector of Brandenburg. Grosser Kurfürst was armed with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets and could steam at a top speed of 21 knots.

SMS Prinzregent Luitpold was the fifth and final vessel of the Kaiser class of dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy. Prinzregent Luitpold's keel was laid in October 1910 at the Germaniawerft dockyard in Kiel. She was launched on 17 February 1912 and was commissioned into the navy on 19 August 1913. The ship was equipped with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets, and had a top speed of 21.7 knots.

SMS König Albert was the fourth vessel of the Kaiser class of dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy. König Albert's keel was laid on 17 July 1910 at the Schichau-Werke dockyard in Danzig. She was launched on 27 April 1912 and was commissioned into the fleet on 31 July 1913. The ship was equipped with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets, and had a top speed of 22.1 knots. König Albert was assigned to III Battle Squadron and later IV Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet for the majority of her career, including World War I.

SMS Ostfriesland was the second vessel of the Helgoland class of dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy. Named for the region of East Frisia, Ostfriesland's keel was laid in October 1908 at the Kaiserliche Werft dockyard in Wilhelmshaven. She was launched on 30 September 1909 and was commissioned into the fleet on 1 August 1911. The ship was equipped with twelve 30.5 cm (12 in) guns in six twin turrets, and had a top speed of 21.2 knots. Ostfriesland was assigned to the I Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet for the majority of her career, including World War I.

SMS Oldenburg was the fourth vessel of the Helgoland class of dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy. Oldenburg's keel was laid in March 1909 at the Schichau-Werke dockyard in Danzig. She was launched on 30 June 1910 and was commissioned into the fleet on 1 May 1912. The ship was equipped with twelve 30.5 cm (12 in) guns in six twin turrets, and had a top speed of 21.2 knots. Oldenburg was assigned to I Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet for the majority of her career, including World War I.
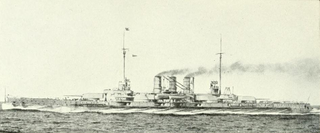
SMS Thüringen was the third vessel of the Helgoland class of dreadnought battleships of the German Kaiserliche Marine (Imperial Navy}. Thüringen's keel was laid in November 1908 at the AG Weser dockyard in Bremen. She was launched on 27 November 1909 and commissioned into the fleet on 1 July 1911. The ship was equipped with twelve 30.5 cm guns in six twin turrets, and had a top speed of 21 knots. Thüringen was assigned to I Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet for the majority of her career, including World War I.






















