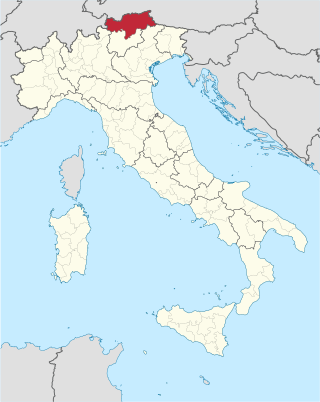
South Tyrol is an autonomous province in northern Italy. An English translation of the official German and Italian names could be the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, reflecting the multilingualism and different naming conventions in the area. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province is the northernmost of Italy, the second largest with an area of 7,400 square kilometres (2,857 sq mi), and has a total population of about 534,000 inhabitants as of 2021. Its capital and largest city is Bolzano.

Bolzano is the capital city of the province of Bolzano - South Tyrol, in Northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third largest in historical Tyrol. The greater metro area has about 250,000 inhabitants and is one of the urban centres within the Alps.

Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol is an autonomous region of Italy, located in the northern part of the country. The region has a population of 1.1 million, of whom 62% speak Italian as their mother tongue, 30% speak South Tyrolean German and several foreign languages are spoken by immigrant communities. Since the 1970s, most legislative and administrative powers have been transferred to the two self-governing provinces that make up the region: the province of Trento, commonly known as Trentino, and the province of Bolzano, commonly known as South Tyrol. In South Tyrol, German remains the sizeable majority language.

Brixen is a town and commune in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Bolzano.

Kaltern an der Weinstraße, often abbreviated to Kaltern or Caldaro, is a municipality and a village in South Tyrol in northern Italy. It is about 12 kilometres (7 mi) southwest of the city of Bolzano.

Neumarkt is a comune (municipality) and a village in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) south of the city of Bolzano. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia.
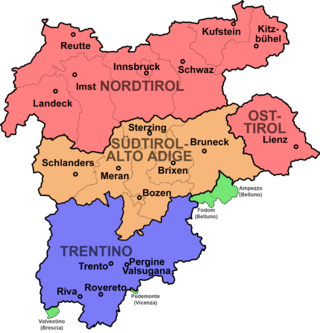
Modern-day South Tyrol, an autonomous Italian province created in 1948, was part of the Austro-Hungarian County of Tyrol until 1918. It was annexed by Italy following the defeat of the Central Powers in World War I. It has been part of a cross-border joint entity, the Euroregion Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino, since 2001.

Eppan an der Weinstraße, often abbreviated to Eppan or Appiano, is a comune (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about 8 kilometres (5 mi) southwest of the city of Bolzano.

Kurtatsch an der Weinstraße, often abbreviated to Kurtatsch or Cortaccia, is a comune (municipality) and a village in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of the city of Bolzano. Kurtatsch is one of the southernmost villages in the German-speaking area.
Kurtinig an der Weinstraße, often abbreviated to Kurtinig or Cortina, is a comune (municipality) and a village in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about 30 kilometres (19 mi) southwest of the city of Bolzano.
Margreid an der Weinstraße, often abbreviated to Margreid or Magrè, is a comune (municipality) and a village in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of the city of Bolzano.

Montan an der Weinstraße is a municipality with 1,701 inhabitants and a village in the South of South Tyrol in northern Italy, about 15 km south of Bolzano. The name Montan derives from the Latin mons ("mountain").

Tramin an der Weinstraße, often abbreviated to Tramin or Termeno, is a comune (municipality) in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about 20 kilometres southwest of the city of Bolzano. The name of the grape variety Gewürztraminer has its origins in Tramin.

Überetsch-Unterland is a district in the southern part of the Italian province of South Tyrol. It comprises the valley of the Adige river from Bolzano in the north to Salorno in the south.

In 1919, at the time of its annexation, the middle part of the County of Tyrol which is today called South Tyrol was inhabited by almost 90% German speakers. Under the 1939 South Tyrol Option Agreement, Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini determined the status of the German and Ladin (Rhaeto-Romanic) ethnic groups living in the region. They could emigrate to Germany, or stay in Italy and accept their complete Italianization. As a consequence of this, the society of South Tyrol was deeply riven. Those who wanted to stay, the so-called Dableiber, were condemned as traitors while those who left (Optanten) were defamed as Nazis. Because of the outbreak of World War II, this agreement was never fully implemented. Illegal Katakombenschulen were set up to teach children the German language.

Bolzano/Bozen railway station is the main station of Bolzano, capital of the autonomous province of South Tyrol, in northeastern Italy.
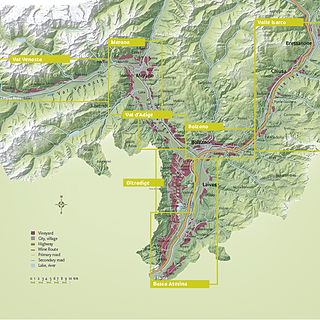
South Tyrol is an autonomous province located in northeast Italy producing wine. This Austro-Italian wine region is noted for the distinct Austrian influences on the wine industry, due to the region's long history under the rule of Austria-Hungary and Holy Roman Empires.
The South Tyrolean Unterland or Bozen Unterland is a section of the Etschtal valley stretching from the regional capital Bolzano (Bozen) down the Adige (Etsch) river to Tramin and Salorno (Salurn). The area is known for its history, particularly regarding Rhaetic, Roman, and Germanic archaeological sites; its bilingualism, and its viticulture; the Gewürztraminer grape originated here.

Laag is a frazione of the comune of Neumarkt in South Tyrol in the Italian region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located about 30 km northeast of the city of Trento and about 25 km south of the city of Bolzano. Laag is situated on the plain on the left side of the Adige river.

























