
Schinia arcigera, the arcigera flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in North America from Nova Scotia to Florida, west to Arizona and Idaho, north to Saskatchewan.

Schinia jaguarina, the jaguar flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found on North America's Great Plains from Saskatchewan and Alberta south to Texas, eastward on coast to Florida and westward in south to Arizona. In Mexico it is found down to Mexico City.

The bleeding flower moth is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found from North Carolina to Florida, west to Texas, north to Montana. There is also a disjunct population in Ontario.

Schinia florida, the primrose moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae described by Achille Guenée in 1852. Its range includes most of temperate North America aside from the west coast.

Schinia bina, the bina flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from Mexico City to central Florida, and as far north as Saskatchewan and Manitoba in Canada.

Schinia lucens, the leadplant flower moth or false indigo flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Herbert Knowles Morrison in 1875. It is found in the central and western United States.

Schinia roseitincta is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Leon F. Harvey in 1875. It is found in the northern United States and in Canada.
Schinia verna, or the Verna's flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba.

Schinia acutilinea, the angled gem or acute-lined flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1878. It is found in the dry southern portions of Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, south across the plains and Great Basin to southern Arizona and California.

Schinia gracilenta, the slender flower moth or iva flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Jacob Hübner in 1818. It is found from the US states of New York to Florida and Nebraska to Arizona. The species is listed as endangered in Connecticut.

Schinia chrysella is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found throughout the central United States south to Monterry, Mexico.

Schinia septentrionalis, the northern flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1858. It is found in North America from Missouri to Quebec to South Carolina and Louisiana. Records include Colorado, Oklahoma, South Dakota and Texas. It is listed as threatened in the US state of Connecticut.

Schinia pulchripennis, or the common flower moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae that is distributed throughout North America, including California and Nevada.

The rabbitbush flower moth is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found from central Arizona and New Mexico, north to Colorado, south-western Wyoming and Utah, west to Nevada and California, and north to Oregon, Idaho and Washington.
Schinia sexata is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in North America, where it is known only from southern Manitoba, Canada.

Schinia alencis is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found from south-eastern Colorado to south-eastern Arizona east to western Oklahoma, northern Texas to south-western and south-eastern Texas.

Schinia psamathea is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is known from east-central Georgia southwestward to the Panhandle of Florida, southeastern Alabama, and southwestern Mississippi. It seems to prefer sandy soils either in dune type habitats or near sandy beaches.
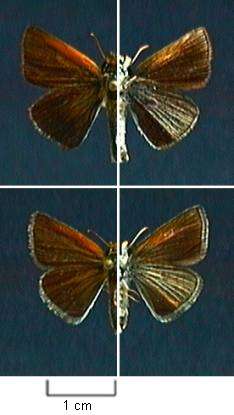
Oarisma poweshiek, the Poweshiek skipperling, is a North American butterfly in the family Hesperiidae (skippers), subfamily Hesperiinae. The range of this species in Canada is restricted to southeastern Manitoba, and in the United States it historically ranged from the Dakotas to the southern Lower Peninsula of Michigan.
Gustav Wilhelm Belfrage (1834–1882) was an American insect collector. He was born in Stockholm, Sweden, but travelled to the United States in 1860 where he settled in Bosque County, Texas.

Leon F. Harvey was an American entomologist, physician, and dentist. He was a founding member of the Buffalo Society of Natural Sciences, serving as its first treasurer and later as its president.
















