
The Florissant Formation is a sedimentary geologic formation outcropping around Florissant, Teller County, Colorado. The formation is noted for the abundant and exceptionally preserved insect and plant fossils that are found in the mudstones and shales. Based on argon radiometric dating, the formation is Eocene in age and has been interpreted as a lake environment. The fossils have been preserved because of the interaction of the volcanic ash from the nearby Thirtynine Mile volcanic field with diatoms in the lake, causing a diatom bloom. As the diatoms fell to the bottom of the lake, any plants or animals that had recently died were preserved by the diatom falls. Fine layers of clays and muds interspersed with layers of ash form "paper shales" holding beautifully-preserved fossils. The Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument is a national monument established to preserve and study the geology and history of the area.

A bone bed is any geological stratum or deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe especially dense collections such as Lagerstätte. It is also applied to brecciated and stalagmitic deposits on the floor of caves, which frequently contain osseous remains.
The most recent understanding of the evolution of insects is based on studies of the following branches of science: molecular biology, insect morphology, paleontology, insect taxonomy, evolution, embryology, bioinformatics and scientific computing. It is estimated that the class of insects originated on Earth about 480 million years ago, in the Ordovician, at about the same time terrestrial plants appeared. Insects are thought to have evolved from a group of crustaceans. The first insects were landbound, but about 400 million years ago in the Devonian period one lineage of insects evolved flight, the first animals to do so. The oldest insect fossil has been proposed to be Rhyniognatha hirsti, estimated to be 400 million years old, but the insect identity of the fossil has been contested. Global climate conditions changed several times during the history of Earth, and along with it the diversity of insects. The Pterygotes underwent a major radiation in the Carboniferous while the Endopterygota underwent another major radiation in the Permian.
Megapaloelodus is an extinct genus of stem flamingo of the family Palaelodidae. Megapaloelodus is primarily known from Miocene America, from South Dakota and Oregon in the north to Argentina in the south, but the species Megapaloelodus goliath was found in Europe. Additionally, one unnamed species was discovered in Miocene sediments from Namibia. Due to a lack of skull material, little can be said about the ecology of Megapaloelodus. Species of this genus are typically larger than those of Palaelodus and appear to have inhabited similar brackish lake environments. Additionally, they may have been capable of "locking" their legs in a standing position.

Rainbow Basin is a geological formation in the Calico Peaks range, located approximately 8 miles (13 km) north of Barstow in the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California.
The geology of Illinois includes extensive deposits of marine sedimentary rocks from the Palaeozoic, as well as relatively minor contributions from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic. Ice age glaciation left a wealth of glacial topographic features throughout the state.
The Chañares Formation is a Carnian-age geologic formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, located in La Rioja Province, Argentina. It is characterized by drab-colored fine-grained volcaniclastic claystones, siltstones, and sandstones which were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment. The formation is most prominently exposed within Talampaya National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site within La Rioja Province.

Palaelodidae is a family of extinct birds in the group Phoenicopteriformes, which today is represented only by the flamingos. They were widespread during the Neogene, with fossil remains found on all continents other than Antarctica. The oldest remains referred to this group appeared in the fossil record during the Oligocene in Egypt and Belgium, before palaelodids reached their peak diversity during the Miocene. Following this the group declined in the early Pliocene before going extinct on most continents. However, remains found near Cooper Creek in the Lake Eyre Basin indicate that palaelodids managed to survive in Australia until the Pleistocene. Currently three genera are recognized by scientists: Adelalopus, Palaelodus and Megapaloelodus. Most fossil remains stem from Europe and have been assigned to the type species, Palaelodus ambiguus. Due to the fragmentary nature of most of these species, little is known about their ecology. They appear to have preferred brackish lakes and lagoons. Palaelodus has previously been thought to be a wader or diver, but recent research indicates that they were better suited for swimming and possibly fed on insect larvae and other aquatic invertebrates. At least Megapaloelodus appears to have adaptations for "locking" their legs in a standing position.

The Barstow Formation is a series of limestones, conglomerates, sandstones, siltstones and shales exposed in the Mojave Desert near Barstow in San Bernardino County, California.

Archaebranchinecta barstowensis is a species of fairy shrimp (Anostraca) that inhabited California during the Middle Miocene. Its fecal material is abundant in the concretions from the Barstow Formation. A limited number of whole specimens have been found, and they represent the "best-preserved fossil anostracan known to date". The closest relative of A. barstowensis appears to be Archaebranchinecta pollicifera from the surroundings of Lake Titicaca, and the two have been separated from the genus Branchinecta as the new genus Archaebranchinecta.
Anthony Ricardo Fiorillo is Executive Director of the New Mexico Museum of Natural History & Science, as well as a senior fellow at the Institute for the Study of Earth and Man at Southern Methodist University. For many years he was vice president of research & collections and chief curator at the Perot Museum of Nature & Science. A native of Connecticut, he received his bachelor's at the University of Connecticut, his master's at the University of Nebraska and a Ph.D. in Vertebrate Paleontology from the University of Pennsylvania.

The Klondike Mountain Formation is an Early Eocene (Ypresian) geological formation located in the northeast central area of Washington state. The formation is composed of volcanic rocks in the upper unit and volcanic plus lacustrine (lakebed) sedimentation in the lower unit. the formation is named for the type location designated in 1962, Klondike Mountain northeast of Republic, Washington. The formation is a lagerstätte with exceptionally well-preserved plant and insect fossils has been found, along with fossil epithermal hot springs.
Calicovatellus is an extinct genus of dytiscid beetle in the subfamily Hydroporinae. As of 2018, one species is recognized, Calicovatellus petrodytes. It was found in the Barstow Formation in southern California and dates to the Miocene.

Paleontology in Wisconsin refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The state has fossils from the Precambrian, much of the Paleozoic, some a parts of the Mesozoic and the later part of the Cenozoic. Most of the Paleozoic rocks are marine in origin. Because of the thick blanket of Pleistocene glacial sediment that covers the rock strata in most of the state, Wisconsin’s fossil record is relatively sparse. In spite of this, certain Wisconsin paleontological occurrences provide exceptional insights concerning the history and diversity of life on Earth.

The Waldron Shale is a geologic formation in Indiana. It preserves fossils dating back to the Silurian period. These fossils comprise at least three different benthic communities primarily living in the inter-reef, deep waters that were stable for much of the Wenlockian epoch. Many of these fossils are found most frequently around microbioherms constructed by small encrusting organisms which protected other species from the effects of storms.

The Punchbowl Formation is a sedimentary sandstone geologic formation in the northern San Gabriel Mountains, above the Antelope Valley in Los Angeles County, southern California.
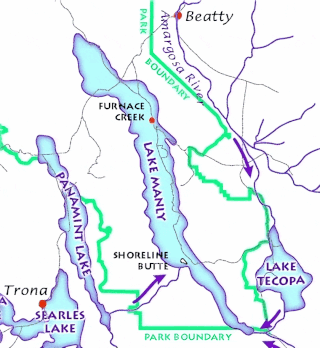
Lake Tecopa is a former lake in Inyo County, southern California. It developed during the Miocene and the Pleistocene within a tectonic basin close to the border with Nevada. Fed by the Amargosa River and some neighbouring washes, it eventually culminated to a surface area of 235 square kilometres (91 sq mi) around 186,000 years ago and left sediments. Afterwards, the Amargosa River cut a gorge out of the lake and into Death Valley with its Lake Manly, draining the lake. The present-day towns of Shoshone, California and Tecopa, California lie within the basin of the former lake.

The geology of California is highly complex, with numerous mountain ranges, substantial faulting and tectonic activity, rich natural resources and a history of both ancient and comparatively recent intense geological activity. The area formed as a series of small island arcs, deep-ocean sediments and mafic oceanic crust accreted to the western edge of North America, producing a series of deep basins and high mountain ranges.
Maria Antonieta Lorente is a geologist who specializes in stratigraphy and biostratigraphy.
The Ngorora Formation is a geological formation in Kenya preserving fossils dating to the Miocene. The uppermost member of the formation shows sign of a faunal turnover that occurred around 11 to 10.5 million years ago, coinciding with faunal changes elsewhere in the world. This turnover includes the arrival of the horse Hipparion in East Africa. The Ngorora Formation was initially mapped by G.R. Chapman in collaboration with the East African Geological Research Unit (EAGRU) and formally described by Bishop & Chapman in 1970. Major fossil finds were made in the early 1970s, with expeditions to the area recovering thousands of mammal, fish and mollusc remains alongside less common fossil material of birds and reptiles.











