
Maurits Cornelis Escher was a Dutch graphic artist who made woodcuts, lithographs, and mezzotints that used mathematics as an inspiration. Despite wide popular interest, Escher was for most of his life neglected in the art world, even in his native Netherlands. He was 70 before a retrospective exhibition was held. In the late twentieth century, he became more widely appreciated, and in the twenty-first century he has been celebrated in exhibitions around the world.

In visual perception, an optical illusion is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that arguably appears to differ from reality. Illusions come in a wide variety; their categorization is difficult because the underlying cause is often not clear but a classification proposed by Richard Gregory is useful as an orientation. According to that, there are three main classes: physical, physiological, and cognitive illusions, and in each class there are four kinds: Ambiguities, distortions, paradoxes, and fictions. A classical example for a physical distortion would be the apparent bending of a stick half immerged in water; an example for a physiological paradox is the motion aftereffect. An example for a physiological fiction is an afterimage. Three typical cognitive distortions are the Ponzo, Poggendorff, and Müller-Lyer illusion. Physical illusions are caused by the physical environment, e.g. by the optical properties of water. Physiological illusions arise in the eye or the visual pathway, e.g. from the effects of excessive stimulation of a specific receptor type. Cognitive visual illusions are the result of unconscious inferences and are perhaps those most widely known.

A Shepard tone, named after Roger Shepard, is a sound consisting of a superposition of sine waves separated by octaves. When played with the bass pitch of the tone moving upward or downward, it is referred to as the Shepard scale. This creates the auditory illusion of a tone that seems to continually ascend or descend in pitch, yet which ultimately gets no higher or lower.

The Penrose triangle, also known as the Penrose tribar, the impossible tribar, or the impossible triangle, is a triangular impossible object, an optical illusion consisting of an object which can be depicted in a perspective drawing, but cannot exist as a solid object. It was first created by the Swedish artist Oscar Reutersvärd in 1934. Independently from Reutersvärd, the triangle was devised and popularized in the 1950s by psychiatrist Lionel Penrose and his son, prominent Nobel Prize-winning mathematician Sir Roger Penrose, who described it as "impossibility in its purest form". It is featured prominently in the works of artist M. C. Escher, whose earlier depictions of impossible objects partly inspired it.

An impossible object is a type of optical illusion that consists of a two-dimensional figure which is instantly and naturally understood as representing a projection of a three-dimensional object but cannot exist as a solid object. Impossible objects are of interest to psychologists, mathematicians and artists without falling entirely into any one discipline.

The Necker cube is an optical illusion that was first published as a rhomboid in 1832 by Swiss crystallographer Louis Albert Necker. It is a simple wire-frame, two dimensional drawing of a cube with no visual cues as to its orientation, so it can be interpreted to have either the lower-left or the upper-right square as its front side.

Gestalt psychology, gestaltism, or configurationism is a school of psychology that emerged in the early twentieth century in Austria and Germany as a theory of perception that was a rejection of basic principles of Wilhelm Wundt's and Edward Titchener's elementalist and structuralist psychology.

The impossible cube or irrational cube is an impossible object invented by M.C. Escher for his print Belvedere. It is a two-dimensional figure that superficially resembles a perspective drawing of a three-dimensional cube, with its features drawn inconsistently from the way they would appear in an actual cube.

The Müller-Lyer illusion is an optical illusion consisting of three stylized arrows. When viewers are asked to place a mark on the figure at the midpoint, they tend to place it more towards the "tail" end. The illusion was devised by Franz Carl Müller-Lyer (1857–1916), a German sociologist, in 1889.
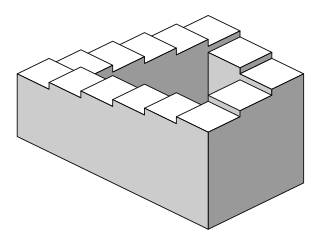
The Penrose stairs or Penrose steps, also dubbed the impossible staircase, is an impossible object created by Oscar Reutersvärd in 1937 and later independently discovered and made popular by Lionel Penrose and his son Roger Penrose. A variation on the Penrose triangle, it is a two-dimensional depiction of a staircase in which the stairs make four 90-degree turns as they ascend or descend yet form a continuous loop, so that a person could climb them forever and never get any higher. This is clearly impossible in three-dimensional Euclidean geometry but possible in some non-Euclidean geometry like in nil geometry.

Oscar Reutersvärd was a Swedish graphic artist, who in 1934 pioneered the art of 3D drawings that may initially appear feasible, yet cannot be physically constructed. He is sometimes described as "the father of the impossible figure", although there are much older examples, e.g. Hogarth's Satire on False Perspective.
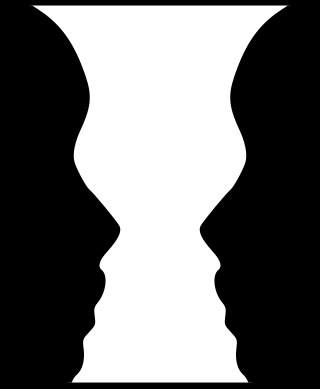
Figure–ground organization is a type of perceptual grouping that is a vital necessity for recognizing objects through vision. In Gestalt psychology it is known as identifying a figure from the background. For example, black words on a printed paper are seen as the "figure", and the white sheet as the "background".
Multistable perception is a perceptual phenomenon in which an observer experiences an unpredictable sequence of spontaneous subjective changes. While usually associated with visual perception, multistable perception can also be experienced with auditory and olfactory percepts.

Ambiguous images or reversible figures are visual forms that create ambiguity by exploiting graphical similarities and other properties of visual system interpretation between two or more distinct image forms. These are famous for inducing the phenomenon of multistable perception. Multistable perception is the occurrence of an image being able to provide multiple, although stable, perceptions.

Roger Newland Shepard was an American cognitive scientist and author of the "universal law of generalization" (1987). He was considered a father of research on spatial relations. He studied mental rotation, and was an inventor of non-metric multidimensional scaling, a method for representing certain kinds of statistical data in a graphical form that can be comprehended by humans. The optical illusion called Shepard tables and the auditory illusion called Shepard tones are named for him.

Rubin's vase is a famous set of ambiguous or bi-stable two-dimensional forms developed around 1915 by the Danish psychologist Edgar Rubin.

Ascending and Descending is a lithograph print by the Dutch artist M. C. Escher first printed in March 1960. The original print measures 14 in × 11+1⁄4 in. The lithograph depicts a large building roofed by a never-ending staircase. Two lines of identically dressed men appear on the staircase, one line ascending while the other descends. Two figures sit apart from the people on the endless staircase: one in a secluded courtyard, the other on a lower set of stairs. While most two-dimensional artists use relative proportions to create an illusion of depth, Escher here and elsewhere uses conflicting proportions to create the visual paradox.

The Spinning Dancer, also known as the Silhouette Illusion, is a kinetic, bistable, animated optical illusion originally distributed as a GIF animation showing a silhouette of a pirouetting female dancer. The illusion, created in 2003 by Japanese web designer Nobuyuki Kayahara, involves the apparent direction of motion of the figure. Some observers initially see the figure as spinning clockwise and some counterclockwise. Additionally, some may see the figure suddenly spin in the opposite direction.
Kōkichi Sugihara is a Japanese mathematician and artist known for his three-dimensional optical illusions that appear to make marbles roll uphill, pull objects to the highest point of a building's roof, and make circular pipes look rectangular. His illusions, which often involve videos of three-dimensional objects shown from carefully chosen perspectives, won first place at the Best Illusion of the Year Contest in 2010, 2013, 2018,and 2020 and second place in 2015 and 2016.

The Shepard elephant, also known as L'egs-istential Quandary or the impossible elephant is an optical illusion, of the type impossible object, based on figure-ground confusion. As its creator Roger Shepard explains:
The elephant…belongs to a class of objects that are truly impossible in that the object itself cannot be globally segregated from the nonobject or background. Parts of the object become the background, and vice versa.

















