Contents
This is a list of visual illusions.
| Name | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Active shutter 3D system |  | Active shutter 3D system is a technique for displaying stereoscopic 3D images. It works by only presenting the image intended for the left eye while blocking the right eye's view, then presenting the right-eye image while blocking the left eye, and repeating this so rapidly that the interruptions do not interfere with the perceived fusion of the two images into a single 3D image. |
| Afterimage illusion |  | An afterimage or ghost image is a visual illusion involving an image continuing to appear in one's vision after the exposure to the original image has ceased. |
| Afterimage on empty shape (also known as color dove illusion) |  | This type of illusion is designed to exploit graphical similarities. |
| Ambiguous image |  | These are images that can form two separate pictures. For example, the image shown forms a rabbit and a duck. |
| Ambigram |  | A calligraphic design that has multiple or symmetric interpretations. |
| Ames room illusion |  | An Ames room is a distorted room that is used to create a visual illusion. |
| Ames trapezoid window illusion |  | A window is formed in the shape of a trapezium. It is often hung and spun around to provide the illusion that the window rotates through less than 180 degrees. |
| Asahi illusion |  | A flower-like figure with petals is arranged in a circle, which are dark on the outside and lighter in transitions toward the middle. The inner part of the background is perceived as significantly brighter than the outer background. |
| Autokinetic effect | The autokinetic effect, or autokinesis, occurs when a stationary image appears to move. | |
| Autostereogram |   | An autostereogram is a single-image stereogram (SIS), designed to create the visual illusion of a three-dimensional (3D) scene from a two-dimensional image in the human brain. An ASCII stereogram is an image that is formed using characters on a keyboard. Magic Eye is an autostereogram book series. |
| Barberpole illusion |  | The barber pole illusion is a visual illusion that reveals biases in the processing of visual motion in the human brain. |
| Benham's top |  | When a disk that has lines or colours on it is spun, it can form arcs of colour. |
| Beta movement | | Movement that appears to occur when fixed pictures turn on and off. |
| Bezold Effect |  | An apparent change of tone of a colour due to the alteration of the colour of the background. |
| Blivet |  | Also known as "poiuyt" or "devil's fork", this illusion is an impossible image because in reality the shape cannot exist. |
| Café wall illusion |  | This illusion is a pattern in which the mortar or grout between different coloured bricks or tiles on a wall appear to form non-parallel, straight lines, despite the lines being parallel (and straight). Its name comes from a café wall that produced the illusion. |
| Catoptric cistula |  | A catoptric cistula is a box with insides made of mirrors so as to distort images of objects put into the box. |
| Checker shadow illusion | 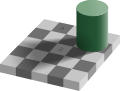  | The checker shadow illusion shows that when a shadow is cast onto a checked board, the colours of squares A and B in the photos appear to be different, when in fact they are the same. |
| Chubb illusion |  | The Chubb illusion is an optical illusion or error in visual perception in which the apparent contrast of an object varies substantially to most viewers depending on its relative contrast to the field on which it is displayed. |
| Chromostereopsis |  | Chromostereopsis is a visual illusion whereby the impression of depth is conveyed in two-dimensional color images, usually of red–blue or red–green colors. |
| Color constancy |  | Colour constancy is an example of subjective constancy and a feature of the human color perception system which ensures that the perceived color of objects remains relatively constant under varying illumination conditions. A green apple for instance looks green to us at midday, when the main illumination is white sunlight, and also at sunset, when the main illumination is red. |
| Color phi phenomenon | The color phi phenomenon is a perceptual illusion in which a disembodied perception of motion is produced by a succession of still images. | |
| Contingent perceptual aftereffect | Contingent aftereffects are illusory percepts that are apparent on a test stimulus after exposure to an induction stimulus for an extended period. | |
| Convergence micropsia | Convergence micropsia is a type of micropsia characterized by the reduction in apparent size of objects viewed when the eyes are more converged than they need to be for the distance of the object from the eyes. | |
| Cornsweet illusion |  | An illusion where two colours can obviously be seen to be different when placed directly beside each other; however, when the two colours are separated by a thick black line, they appear to be of the same hue. |
| Crater illusion |  | A type of multistable illusion where an image of a concave object, rotated so that the light source is below, may sometimes appear convex, and vice versa. This phenomenon is because light sources tend to shine from above the subject. |
| Delboeuf illusion |  | An optical illusion of relative size perception. The two black circles are exactly the same size; however, the one on the left seems larger. |
| Disappearing Model | A trompe-l'œil body painting by Joanne Gair. | |
| The dress |  | An optical illusion resulting from the brain's attempt to discount coloured tinting from daylight and other sources. [1] The dress was a viral phenomenon, which was either seen as blue and black or as white and gold. Its true colours were eventually confirmed to be blue and black. [2] |
| Ebbinghaus illusion | 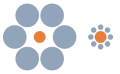 | The Ebbinghaus illusion, or Titchener circles, is an optical illusion of relative size perception. The two orange circles are exactly the same size; however, the one on the right appears larger. |
| Ehrenstein illusion |  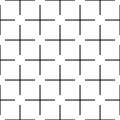 | The Ehrenstein illusion is an optical illusion studied by the German psychologist Walter Ehrenstein in which the sides of a square placed inside a pattern of concentric circles take an apparent curved shape. |
| Fata Morgana (mirage) |  | Visible in a narrow band right above the horizon, Fata Morgana mirages significantly distort the object or objects on which they are based, often such that the object is completely unrecognizable. A Fata Morgana may be seen on land or at sea, in polar regions, or in deserts. It may involve almost any kind of distant object, including boats, islands, and the coastline. |
| Fechner color | The Fechner color effect is an illusion of color seen when looking at certain rapidly changing or moving black-and-white patterns. They are also called pattern induced flicker colors (PIFCs). | |
| Figure-ground (perception) |  | Figure–ground organization is a type of perceptual grouping that is a vital necessity for recognizing objects through vision. In Gestalt psychology it is known as identifying a figure from the background. |
| Filling-in | 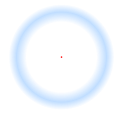 | Filling-in phenomena are those responsible for the completion of missing information across the physiological blind spot, and across natural and artificial scotomata. |
| Flash lag illusion |  | The flash lag illusion is a visual illusion wherein a flash and a moving object that appear in the same location are perceived to be displaced from one another. |
| Forced perspective |  | Application used in film and architecture to create the illusion of larger, more distant objects. |
| Fraser spiral illusion |  | The Fraser spiral illusion, or false spiral, or the twisted cord illusion, was first described by the British psychologist Sir James Fraser in 1908. The overlapping black arc segments appear to form a spiral; however, the arcs are a series of concentric circles. |
| Gravity hill |  | A gravity hill is a place where the layout of the surrounding land produces an illusion, making a slight downhill slope appear to be an uphill slope. See also: List of gravity hills |
| Grid illusion |   | A grid illusion is any kind of grid that deceives a person's vision. |
| Hering illusion |  | The Hering illusion (1861): When two straight and parallel lines are presented in front of radial background (like the spokes of a bicycle), the lines appear as if they were bowed outwards. |
| Hollow-Face illusion |  | The Hollow-Face illusion is an optical illusion in which the perception of a concave mask of a face appears as a normal convex face. |
| Horizon dip |  | Horizon dip, also known as a "sea dip": The horizon appears to rise from a dip in the middle distance. |
| Hybrid image |  | A Hybrid image is an optical illusion developed at MIT in which an image can be interpreted in one of two different ways depending on viewing distance. |
| Illusory contours |  | Illusory contours or subjective contours are a form of visual illusion where contours are perceived without a luminance or color change across the contour. |
| Impossible object |  | A two-dimensional image of an impossible three-dimensional object, such as the impossible cube from M.C. Escher's 1958 print Belvedere |
| Irradiation illusion |  | The irradiation illusion is an illusion of visual perception in which a light area of the visual field looks larger than an otherwise identical dark area. |
| Isometric illusion |  | An isometric illusion (also called an ambiguous figure or inside/outside illusion) is a type of optical illusion, specifically one due to multistable perception. |
| Jastrow illusion |  | The Jastrow illusion is an optical illusion discovered by the American psychologist Joseph Jastrow in 1889. |
| Kanizsa triangle |  | The Kanizsa triangle is an optical illusion first described by the Italian psychologist Gaetano Kanizsa in 1955. It is a triangle formed of illusory contours. |
| Kinetic Depth Effect | The Kinetic depth effect is the phenomenon whereby the three-dimensional structural form of a silhouette can be perceived when the object is moving. In the absence of other visual depth cues, this might be the only perception mechanism available to infer the object's shape. Additionally the direction of motion can reverse due to the existence of multiple 3D visual solutions. | |
| Koffka ring |  | The Koffka ring is a geometric optical illusion discovered by the german psychologist Kurt Koffka. |
| Leaning tower illusion | The Leaning tower illusion is an optical illusion that presents two identical images of the Leaning Tower of Pisa side by side. | |
| Lilac chaser |  | Lilac chaser is a visual illusion, also known as the Pac-Man illusion. |
| Lunar terminator illusion | The lunar terminator illusion is an optical illusion where the apparent source of sunlight illuminating the moon does not correspond with the actual position of the sun. | |
| Mach bands |  | Mach bands is an optical illusion named after the physicist Ernst Mach. |
| McCollough effect |  | The McCollough effect (1965) is a phenomenon of human visual perception in which colorless gratings appear colored contingent on the orientation of the gratings. It is an aftereffect requiring a period of induction to produce it. |
| Missing square puzzle |   | The missing square puzzle is an optical illusion used in mathematics classes to help students reason about geometrical figures. |
| Moon illusion |  | The Moon illusion is an optical illusion in which the Moon appears larger near the horizon than it does while higher up in the sky. |
| Motion aftereffect | The motion aftereffect (MAE) is a visual illusion experienced after viewing a moving visual stimulus for a time (tens of milliseconds to minutes) with stationary eyes, and then fixating a stationary stimulus. The stationary stimulus appears to move in the opposite direction to the original (physically moving) stimulus. | |
| Motion illusion | 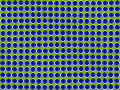 | Motion illusion refers to any optical illusion in which a static image appears to be moving due to the cognitive effects of interacting color contrasts, object shapes, and position. |
| Müller-Lyer illusion |  | The Müller-Lyer illusion is an optical illusion consisting of a stylized arrow. |
| Multistable perception | Multistable perception is a perceptual phenomenon in which an observer experiences an unpredictable sequence of spontaneous subjective changes. | |
| Necker cube |  | The Necker cube is an optical illusion first published in 1832 by Swiss crystallographer Louis Albert Necker. |
| Numerosity adaptation effect |  | The numerosity adaptation effect is a perceptual phenomenon in numerical cognition which demonstrates non-symbolic numerical intuition and exemplifies how numerical percepts can impose themselves upon the human brain automatically. |
| Orbison illusion | 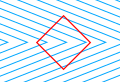 | The Orbison illusion is an optical illusion that was first described by the psychologist William Orbison in 1939. |
| Oppel-Kundt illusion | | The Oppel-Kundt illusion is an optical illusion named after German physicists Johann Joseph Oppel (first mentioned this phenomenon in 1860) and August Kundt (first performed a systematic study of the illusion in 1863). |
| Pareidolia | 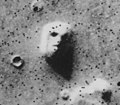 | Pareidolia is the tendency for perception to impose a meaningful interpretation on a nebulous stimulus, usually visual, so that one detects an object, pattern, or meaning where there is none. Pareidolia is a specific but common type of apophenia (the tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things or ideas) |
| Penrose stairs | 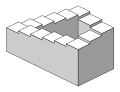 | The Penrose stairs were created by Lionel Penrose and his son Roger Penrose. [3] A variation on the Penrose triangle, it is a two-dimensional depiction of a staircase in which the stairs make four 90-degree turns as they ascend or descend yet form a continuous loop, so that a person could climb them forever and never get any higher. |
| Penrose triangle |  | The Penrose triangle was first created by the Swedish artist Oscar Reutersvärd in 1934. The mathematician Roger Penrose independently devised and popularised it in the 1950s, describing it as "impossibility in its purest form". |
| Pepper's ghost | Pepper's ghost is an illusion technique, used in theatre, cinema, amusement parks, museums, television, and concerts, in which an image of an object offstage is projected so that it appears to be in front of the audience. | |
| Perceived visual angle |  | In human visual perception, the visual angle, denoted θ, subtended by a viewed object sometimes looks larger or smaller than its actual value. |
| Peripheral drift illusion |  | A motion illusion (1979/1999) generated by the presentation of a sawtooth luminance grating in the visual periphery. |
| Phantogram |  | Phantograms, also known as Phantaglyphs, Op-Ups, free-standing anaglyphs, levitated images, and book anaglyphs, are a form of optical illusion. |
| Phi phenomenon | The term phi phenomenon is used in a narrow sense for an apparent motion that is observed if two nearby optical stimuli are presented in alternation with a relatively high frequency. | |
| Poggendorff illusion |  | The Poggendorff illusion (1860) involves the misperception of the position of one segment of a transverse line that has been interrupted by the contour of an intervening structure (here a rectangle). |
| Ponzo illusion |  | In the Ponzo illusion (1911) two identical lines across a pair of converging lines, similar to railway tracks, are drawn. The upper line looks longer because we interpret the converging sides according to linear perspective as parallel lines receding into the distance. In this context, we interpret the upper line as though it were farther away, so we see it as longer – a farther object would have to be longer than a nearer one for both to produce retinal images of the same size. |
| Pulfrich effect | The Pulfrich effect is the effect that covering one eye with transparent but darkened glass can cause purely lateral motion to appear to have a depth component even though in reality it doesn't; even a completely flat scene such as one shown on a television screen can appear to exhibit some three-dimensional motion, but this is an illusion because darkening the scene for one eye causes the photoreceptors in that eye to respond more slowly. | |
| Rubin vase |  | Rubin vase (1915): an ambiguous or bi-stable (i.e., reversing) two-dimensional form. |
| Sander illusion | | In Sander's parallelogram (1926) the diagonal line bisecting the larger, left-hand parallelogram appears to be considerably longer than the diagonal line bisecting the smaller, right-hand parallelogram, but is in fact the same length. |
| Silencing |  | Silencing is an illusion in which a set of objects that change in luminance, hue, size, or shape appear to stop changing when they move. |
| Size–weight illusion | The size–weight illusion is also known as the Charpentier illusion or Charpentier–Koseleff illusion. | |
| Stepping feet illusion | | The stepping feet illusion is influenced by the contrast between moving objects and their background. |
| Stroboscopic effect | | The stroboscopic effect is a visual phenomenon caused by aliasing that occurs when continuous rotational or other cyclic motion is represented by a series of short or instantaneous samples (as opposed to a continuous view) at a sampling rate close to the period of the motion. |
| Swept-plane display | Swept-plane display is a structure from motion technique with which one can create the optical illusion of a volume of light, due to the persistence of vision property of human visual perception. | |
| Ternus illusion | The Ternus illusion (1926/1938) is based upon apparent motion. | |
| Thaumatrope |  | A thaumatrope is a toy that was popular in Victorian times. |
| Trompe-l'œil |  | Trompe-l'œil is an artistic term for the highly realistic optical illusion of three-dimensional space and objects on a two-dimensional surface. |
| Troxler's fading | Troxler's fading: When one fixates on a particular point for even a short period of time, an unchanging stimulus away from the fixation point will fade away and disappear. | |
| Vanishing puzzle |  | A vanishing puzzle is a mechanical optical illusion showing different numbers of a certain object when parts of the puzzle are moved around. [4] |
| Vertical–horizontal illusion |  | The Vertical-horizontal illusion is the tendency for observers to overestimate the length of a vertical line relative to a horizontal line of the same length. |
| Vista paradox |  | The Vista paradox is a natural optical illusion where an object seen through an aperture appears to shrink in apparent size as the observer approaches the aperture. |
| Visual tilt effects |  | The tilt illusion (TI) is the phenomenon that the perceived orientation of a test line or grating is altered by the presence of surrounding lines or grating with a different orientation. The tilt aftereffect (TAE) is the phenomenon that the perceived orientation is changed after prolonged inspection of another oriented line or grating. |
| Wagon-wheel effect |  | The wagon-wheel effect is an optical illusion in which a spoked wheel appears to rotate differently from its true rotation. |
| White's illusion |  | White's illusion is a brightness illusion in which certain stripes of a black-and-white grating are replaced by gray rectangles of the same color, luminance, and opacity. The brightness of the gray rectangles appears to be closer to the brightness of the top and bottom bordering stripes. |
| Wundt illusion |  | The two red vertical lines are both straight, but they may look as if they are bowed inwards to some observers. The distortion is induced by the crooked lines on the background |
| Zoetrope |  | A zoetrope is a pre-film animation device that produces the illusion of motion, by displaying a sequence of drawings or photographs showing progressive phases of that motion. |
| Zöllner illusion |  | The Zöllner illusion is a classic optical illusion named after its discoverer, German astrophysicist Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner. |