
Mantis shrimp are carnivorous marine crustaceans of the order Stomatopoda. Stomatopods branched off from other members of the class Malacostraca around 340 million years ago. Mantis shrimp typically grow to around 10 cm (3.9 in) in length, while a few can reach up to 38 cm (15 in). A mantis shrimp's carapace covers only the rear part of the head and the first four segments of the thorax. Varieties range in colour from shades of brown to vivid colours, with more than 520 species of mantis shrimp known. They are among the most important predators in many shallow, tropical and subtropical marine habitats. However, despite being common, they are poorly understood, as many species spend most of their lives sheltering in burrows and holes.

Yohoia is an extinct genus of megacheiran arthropod from the Cambrian period that has been found as fossils in the Burgess Shale formation of British Columbia, Canada. The type species, Yohoia tenuis, was described in 1912 by Walcott, who considered it an anostracan crustacean. 711 specimens of Yohoia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 1.35% of the community. In 2015, Conway Morris et al. reported another species, Y. utahana, from the Marjum Formation, Utah.

Oratosquilla oratoria, the Japanese mantis shrimp, is a species of mantis shrimp found in the western Pacific. It is widely harvested in Japan and eaten as sushi. Like other members of its order it has a powerful spear, which it uses to hunt invertebrates and small fish. It grows to a length of 185 millimetres (7.3 in), and lives at depths of 10–100 metres (33–328 ft).

Megacheira is an extinct class of predatory arthropods defined by their possession of spined "great appendages". Their taxonomic position is controversial, with studies either considering them stem-group euarthropods, or stem-group chelicerates. The homology of the great appendages to the cephalic appendages of other arthropods is also controversial. Uncontested members of the group were present in marine environments worldwide from the lower to middle Cambrian.
Aeschronectida is an extinct order of mantis shrimp-like crustaceans which lived in the Mississippian subperiod in what is now Montana. They exclusively lived in the Carboniferous, or the age of amphibians. They have been found mostly in the U.S. and in the British Isles, in 1979 species were found in the Madera Formation in New Mexico. Aeschronectida was first identified appearing in Continental Europe in around 2014. While sharing similar characteristics to Stomatopoda, they lack certain physical characteristics of that taxon. The first species of Aeschronectida is accredited to Frederick R. Schram. They diverge substantially from typical hoplocaridan morphology by having more unmodified thoracopods. It's theorized that these thoracopods evolved to become more specialized, making them potential ancestors to Stomatopoda.

The Jamaican ibis, Jamaican flightless ibis or clubbed-wing ibis is an extinct bird species of the ibis subfamily uniquely characterized by its club-like wings. It is the only species in the genus Xenicibis, and one of only two flightless ibis genera, the other being the genus Apteribis which was endemic to Hawaii's islands of Maui Nui.

Crustaceans are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are a part of the subphylum Crustacea, a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans.
Triassosculda is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp from the Early Triassic aged Paris biota of Idaho. Its discovery bridged a 100-million-year gap in mantis shrimp evolution from the late Carboniferous to the Jurassic. Its only species is T. ahyongi.

Tyrannosculda is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp which lived during the Late Jurassic in southern Germany. It was named in 2021, with T. laurae as the type and only species. Several fossil specimens are known, representing various growth stages.
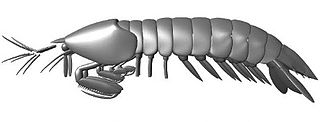
Tyrannophontes is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived during the late Carboniferous period in what is now the Mazon Creek fossil beds of Illinois. It is the only genus in the family Tyrannophontidae. The type species, T. theridion, was described in 1969 by Frederick Schram. A second, much larger species, T. gigantion, was also named by Schram in 2007. Two other species were formerly assigned to the genus, but have since been reclassified.

Daidal is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived during the Carboniferous period. It is the only genus in the family Daidalidae. Three species are currently placed within the genus. Fossils of the type species, D. acanthocercus, have been found in the Bear Gulch Limestone of Montana. A second species, D. pattoni, is known from the Lower Limestone Formation of Scotland, and the third species, D. schoellmanni, was discovered in Westphalia, Germany. The genus has been proposed to be polyphyletic, with D. pattoni possibly being an earlier diverging lineage, though more specimens and research are needed to confirm this.

Sculda is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp known from the late Jurassic to late Cretaceous of Germany and Lebanon. Although several species have been assigned to it, some are now deemed dubious or moved to different genera. It was a moderate-sized crustacean, measuring no more than 50 mm (2.0 in) long. Sculda would have lived in a marine environment and been a predatory animal, likely smashing its prey with the widened segment of its raptorial appendages before cutting it with the sharp appendage tips.
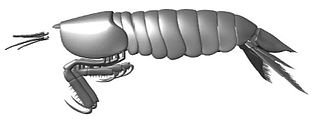
Gorgonophontes is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived during the late Carboniferous period in what is now the United States and Belgium. It contains two named species. The type species, G. peleron, was described in 1984 by Frederick Schram based on 100 specimens found in Nebraska and Iowa. A second species, G. fraiponti, was first named from multiple specimens found near Liège in 1922 and later reassigned to the genus.
Chabardella is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp which lived during the Late Carboniferous in France. It was named in 2009, with C. spinosa as the type and only species.
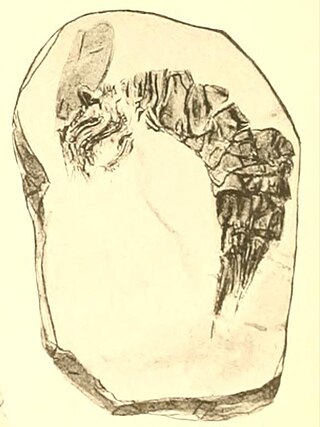
Bairdops is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived during the Early Carboniferous period in what is now Scotland and the United States. Two named species are currently assigned to it. The type species, B. elegans, has been collected from several Dinantian-aged localities in Scotland, and was first described in 1908 by British geologist Ben Peach as a species of Perimecturus. The generic name was coined decades later in 1979 by American paleontologist Frederick Schram, and honors William Baird. A later species, B. beargulchensis, was named in 1978 after the Serpukhovian-aged Bear Gulch Limestone of Montana where it was discovered. The two species were originally deemed close relatives based on their physical similarities, but several cladistic analyses published since 1998 have suggested the genus may be polyphyletic.

Perimecturus is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived during the Early Carboniferous period in what is now Scotland and the United States. The first known specimens were collected near the River Esk in Glencartholm, Scotland, and the genus was named in 1908 by Ben Peach, making it the second genus of Paleozoic mantis shrimp to be described. While many species have been classified in the genus since then, taxonomic revisions in the late 20th and 21st centuries have reassigned most of these to different genera, leaving two named species currently assigned to this genus. The type species, P. parki, was first named in 1882 as a species of Anthrapalaemon and is known from the Viséan-aged Glencartholm Volcanic Beds of Scotland. Fossils of a later species, P. rapax, have been found in the Bear Gulch Limestone of Montana and were first described by Frederick Schram.

Gorgonophontidae is a family of fossil mantis shrimps which lived from the Moscovian to Gzhelian stages of the Carboniferous period. It was erected in 2007 as a monotypic group by Frederick Schram to contain only the type genus Gorgonophontes. A second genus, Chabardella, was assigned to the family in 2009. Fossils of gorgonophontids have been found in France, Belgium and the United States. The family may be polyphyletic.
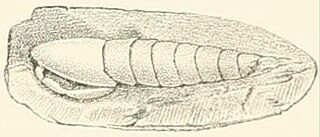
Archaeocaris is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived in North America during the Early Carboniferous period. Though it was placed as a member of the family Perimecturidae until 2008, it is currently deemed the only genus in the family Archaeocarididae, and contains two species. The type species, A. vermiformis, was described by Fielding Bradford Meek in 1872 from specimens collected at the base of the Waverly Group in Kentucky. A second species, A. graffhami, was named by Harold Kelly Brooks in 1962 based on a fossil found in the Caney Shale of Oklahoma, with additional remains later found in the Pilot Shale of Nevada.
Nodosculda is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived in North America during the late Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous period, between 105 and 100 million years ago. The only species is Nodosculda fisherorum, known from several specimens uncovered in the Paw Paw Formation of Texas.
Ursquilla is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp that lived in Israel and Jordan during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous period. It contains a single species, Ursquilla yehoachi.














