Oenopota rubescens is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Mangeliidae,.
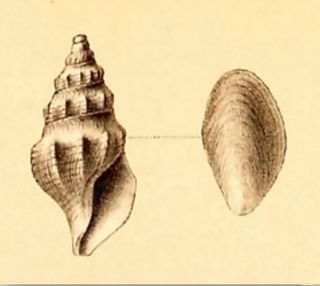
Aoteadrillia bulbacea is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Horaiclavidae.

Crassispira epicasta is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Pseudomelatomidae.

Crassispira erigone is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Pseudomelatomidae.

Clionella bornii is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Clavatulidae.

Calliclava aegina is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Drilliidae.
Ancistrobasis costulata is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.

Carenzia carinata is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.

Carenzia trispinosa is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.

Seguenzia elegans is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.
Quinnia ionica is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.

Seguenzia is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Seguenziidae.

Vetulonia paucivaricosa is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the superfamily Seguenzioidea.

Solariella amabilis is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Solariellidae.

Alvania fischeri is a species of minute sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Rissoidae.

Herpetopoma instrictum, common name the basket-like false top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Chilodontidae.
Rotellenzia lampra is a species of extremely small deep water sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.
Seguenzia cervola is a species of extremely small deep water sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.
Seguenzia giovia is a species of extremely small deep water sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.
Seguenzia stephanica is a species of extremely small deep water sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.













