Belliena is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1902.

Pancorius is a genus of Asian jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1902. They are similar to Hyllus.

Telamonia is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1887. They are colorful spiders, with patterns that vary considerably between sexes and species. Two longitudinal stripes along the abdomen are common, and the carapace is often colored. They have a slender opisthosoma and long legs.

Zenodorus is a genus of the jumping spiders distributed from the Moluccas to Australia, including several islands of the Pacific. It was once considered a junior synonym of Omoedus, but this was later rejected by Jerzy Prószyński in 2017. At least one species, Z. orbiculatus, specializes on hunting ants.

Idiopidae, also known as armored or spiny trapdoor spiders, is a family of mygalomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1889.

Nemesiidae is a family of mygalomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1889, and raised to family status in 1985. Before becoming its own family, it was considered part of "Dipluridae". The family is sometimes referred to as wishbone spiders due to the shape of their burrows.

Migidae, also known as tree trapdoor spiders, is a family of spiders with about 100 species in eleven genera. They are small to large spiders with little to no hair and build burrows with a trapdoor. Some species live in tree fern stems. They have a Gondwanan distribution, found almost exclusively on the Southern Hemisphere, occurring in South America, Africa, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand and New Caledonia.

Badumna is a genus of intertidal spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1890. They are harmless spiders that can be found around human structures and buildings. The most well-known species is B. insignis, also known as the "black house spider" or "black window spider".

Aname is a genus of mygalomorph spiders. It is endemic to Australia. The spiders, as well as some in closely related genera, are also known as wishbone spiders.
Aname diversicolor, the black wishbone spider, is a species of burrowing arachnid found in southern Australia.
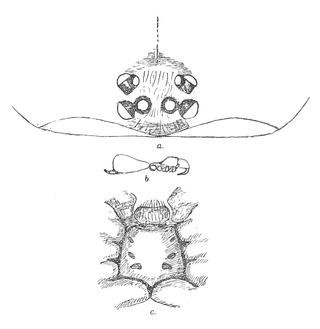
Cantuaria is a genus of South Pacific armored trapdoor spiders that was first described by Henry Roughton Hogg in 1902. From 1985 to 2006 it was merged with former genus Misgolas, now Arbanitis.
Blakistonia is a genus of Australian armoured trapdoor spiders that was first described by Henry Roughton Hogg in 1902.

Henry Roughton Hogg was a British amateur arachnologist and businessman who lived in both Australia and Britain.
Heteromigas is a genus of spiders in the family Migidae. It was first described in 1902 by Henry Roughton Hogg. As of 2016, it contains two Australian species.
Proshermacha is a genus of mygalomorph spiders in the family Anamidae. It is endemic to Australia, and was first described by Eugène Simon in 1908.
Arbanitis andrewsi is a species of armoured trap-door spider in the family Idiopidae, and is endemic to South Australia.
Hadronyche meridiana, also known as the Central Victorian funnel-web spider, is a species of funnel-web spider in the Atracidae family. It is endemic to Australia. It was described in 1902 by British arachnologist Henry Roughton Hogg.
Heteromigas dovei is a species of tree trapdoor spider in the Migidae family. It is endemic to Australia. It was described in 1902 by British arachnologist Henry Roughton Hogg.
Aname tasmanica is a species of mygalomorph spider in the Anamidae family. It is endemic to Australia. It was described in 1902 by British arachnologist Henry Roughton Hogg.
Idiosoma smeatoni is a species of mygalomorph spider in the Idiopidae family. It is endemic to Australia. It was described in 1902 by British arachnologist Henry Roughton Hogg. The specific epithet honours banker and amateur scientist Thomas Drury Smeaton who provided type specimens of the spiders to the South Australian Museum.









