
The Alytidae are a family of primitive frogs. Their common name is painted frogs or midwife toads. Most are endemic to Europe, but three species occur in northwest Africa, and a species formerly thought to be extinct is found in Israel.

Weald Clay or the Weald Clay Formation is a Lower Cretaceous sedimentary rock unit underlying areas of South East England, between the North and South Downs, in an area called the Weald Basin. It is the uppermost unit of the Wealden Group of rocks within the Weald Basin, and the upper portion of the unit is equivalent in age to the exposed portion of the Wessex Formation on the Isle of Wight. It predominantly consists of thinly bedded mudstone. The un-weathered form is blue/grey, and the yellow/orange is the weathered form, it is used in brickmaking.

Eopelobates is an extinct genus of frogs in the family Pelobatidae. Closely related to the living European spadefoot toad, it is known from the Eocene of western North America, and the Eocene–Pliocene of Europe. It is suggested that the distribution over both Europe and North America is due to dispersal during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum.
Saltenia is an extinct genus of frogs. It was assigned to the family Pipidae by R. L. Carroll in 1988 and again in 2005 by A. M. Báez and T. Harrison. The single described species, Saltenia ibanezi, is thought to have lived in South America in the Late Cretaceous.
Almasaurus is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Latiscopidae. It is known from several skulls and some postcranial material found from the Argana Formation in Morocco, which dates back to the Late Triassic.
Baurubatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric frogs found in the Maastrichtian Marília Formation of Brazil, formerly considered to be related to the extant family Ceratophryidae. However, a detailed assessment of the anatomy and relationships of the single known fossil of Baurubatrachus demonstrated that it is not part of Ceratophryidae and might be part of a much ancient group of Neobatrachia.
Nevobatrachus gracilis is the only species in the extinct genus Nevobatrachus, a genus of prehistoric frogs. The original generic name of this frog was Cordicephalus Nevo (1968); however, this generic name turned out to be preoccupied by a cestode genus Cordicephalus Wardle, McLeod & Stewart (1947), which remains nomenclaturally available in spite of being considered a junior synonym of the diphyllobothriid genus Pyramicocephalus. Mahony (2019) coined a replacement name Nevobatrachus. Fossils of N. gracilis were found in a lacustrine deposit in Makhtesh Ramon called "Amphibian Hill" and it is believed they lived during the Lower Cretaceous.
Eoscapherpeton is an extinct genus of giant salamander, known from the Late Cretaceous of Central Asia. Fossils have been found in the Cenomanian aged Khodzhakul Formation and Dzharakuduk Formation, Turonian aged Bissekty Formation and the Coniacian-Santonian aged Aitym Formation of Uzbekistan, the Santonian aged Yalovach Formation of Tajikistan, and the Santonian-lower Campanian aged Bostobe Formation and Campanian aged Darbasa Formation of Kazakhstan.

Eodiscoglossus is an extinct genus of prehistoric frogs. It is known from the type species E. santonjae from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) El Castellar Formation of Spain, as well as a referred species E. oxoniensis known from the Forest Marble Formation of the UK and an indeterminate species from the Dzunbain Formation of Mongolia. It was a small primitive frog, with a length of only 27 mm (1.1 in) from the premaxilla to the ischium. Formerly considered to be closely related to discoglossids, E. santonjae is now regarded as close to the root of the crown group of modern frogs in a position more derived than New Zealand frogs and tailed frogs, but more basal than costatans like alytids and other more advanced frogs like neobatrachians. The morphology of E. santonjae suggests a generalist and unspecialised movement habit. The referral of E. oxoniensis to Eodiscoglossus has been questioned, as it is much earlier than the type species and it is based on homoplasic and plesiomorphic characteristics inherited from a common ancestor, so there is no clear evidence of a close relation.
Lithobatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric amphibian. It was described in 1929 by Hampton Wildman Parker based on a poorly preserved specimen that was first described as Hyla europaea by Gladwyn Kingsley Noble the year before. The two engaged in a debate whether the new genus was warranted. It might belong to the family Palaeobatrachidae, but this remains ambiguous.

Liaobatrachus is a genus of prehistoric frog, the first fossil specimen of which was recovered from the Yixian Formation of Liaoning Province, China. It was the first Mesozoic era frog ever found in China. The species Callobatrachus sanyanensis,Mesophryne beipiaoensis and Yizhoubatrachusmacilentus were classified as species of Liaobatrachus in one study, but this has been rejected by other authors. The genus has been considered a nomen dubium by some authors due to the poor preservation of the holotype specimen. Fossils were found in the Sihetun locality of the western part of Liaoning province, in the lower part of the Yixian Formation, and date to approximately 124.6 Ma. Another specimen was collected near Heitizigou, 25 kilometres (16 mi) south of Beipiao. The specimen has a snout–vent length of 69 millimetres (2.7 in). Liaobatrachus is considered to be the most basal member of Discoglossidae based on phylogenetic analysis.
Vulcanobatrachus is an extinct genus of fossil frog. The genus contains the single species Vulcanobatrachus mandelai found at Marydale, South Africa, described in 2005 and named after Nelson Mandela. The genus owes its name to the fact that fossils were recovered from an extinct volcanic crater lake of Late Cretaceous age. The fossil frogs are assumed to have died following a limnic eruption (a degassing event possibly of CO2) by the volcano.
Wealdenbatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric frog known from the Lower Cretaceous of Uña, Spain, which is part of the La Huérguina Formation Its anatomy and relationships have recently been revisited, finding that this frog might be a proficient jumper, and that it was a primitive frog close to the ancestry of all modern frogs.
Pachycentrata is an extinct genus of prehistoric amphibian.
Theatonius is an extinct genus of Cretaceous amphibians known from North America. Originally described from the Lance Formation, Wyoming, it is now also known from Utah, Montana, and New Jersey.
Spathiurus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that lived during the Cenomanian in the Sannine Formation of Lebanon.

Plethodus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish. It is the type genus of the family Plethodidae.
Thoraciliacus rostriceps is an extinct species of frog from the Cretaceous period and the only species of the genus Thoraciliacus, which is classified in the unranked clade Pipimorpha. A recent phylogenetic analysis confirmed this conclusion, and further suggested that Thoraciliacus rostriceps is more closely related to Pipidae and Shelaniinae than to Palaeobatrachus. Fossils of T. rostriceps were found in Makhtesh Ramon, Negev Desert, Israel and it is believed they lived during the Barremian. Other fossils have been found near Marydale, South Africa in an Upper Cretaceous lake.

Pipoidea are a clade of frogs, that contains the most recent common ancestor of living Pipidae and Rhinophrynidae as well as all its descendants. It is broadly equivalent to Xenoanura.
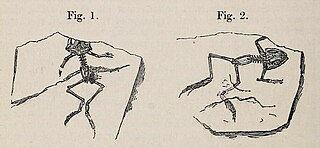
Indobatrachus is an extinct genus of frog known from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to Early Paleocene of India. It contains a single species, Indobatrachus pusillus.








