
Gatwick Express is an express rail passenger service between ‹See TfM›London Victoria, Gatwick Airport, Haywards Heath and Brighton in South East England. It is the brand name used by the Govia Thameslink Railway train operating company on the Gatwick Express route of the Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern franchise.

Heathrow Express is a high-frequency airport rail link operating between London Heathrow Airport and ‹See TfM›London Paddington. Opened in 1998, trains run non-stop, with a journey time of 15 minutes. The service is operated jointly by Great Western Railway and Heathrow Express Operating Company, a wholly owned subsidiary of Heathrow Airport Holdings. Around 16,000 passengers use the service each day.

Rail transport in Switzerland is noteworthy for the density of its network, its coordination between services, its integration with other modes of transport, timeliness and a thriving domestic and trans-Alp freight system. It is made necessary by strong regulations on truck transport, and is enabled by properly coordinated intermodal logistics.

BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad in the United States. One of six North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 36,000 employees, 33,400 miles (53,800 km) of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

The Metro Blue Line is a 12-mile (19.3 km) light rail line in Hennepin County, Minnesota, that is part of the Metro network. It travels from downtown Minneapolis to Minneapolis–Saint Paul International Airport and the southern suburb of Bloomington. Formerly the Hiawatha Line prior to May 2013, the line was originally named after the Milwaukee Road's Hiawatha passenger train and Hiawatha Avenue, reusing infrastructure from the former and running parallel to the latter for a portion of the route. The line opened June 26, 2004, and was the first light rail service in Minnesota. An extension, Bottineau LRT, is planned to open in 2028.

Gatwick Airport railway station is on the Brighton Main Line in West Sussex, England. It serves Gatwick Airport, 26 miles 47 chains (42.8 km) down the line from ‹See TfM›London Bridge via Redhill. The platforms are about 70 metres (230 ft) to the east of the airport's South Terminal, with the ticket office above the platforms and station entrances and exits directly connected to the terminal. The station is also connected to the airport's North Terminal by the Airport Shuttle people-mover. Gatwick Airport was the busiest station in South East England region from 2017 to 2018. There have been two stations at Gatwick, sited about 0.85 miles (1.37 km) from each other. It is the busiest station in both West Sussex and South East England, and the sixth busiest station in the UK outside of London.

The Italian railway system is one of the most important parts of the infrastructure of Italy, with a total length of 24,567 km (15,265 mi) of which active lines are 16,832 km (10,459 mi). The network has recently grown with the construction of the new high-speed rail network. Italy is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Italy is 83.

Reading railway station is a major transport hub in the town of Reading in Berkshire, England, it is 36 miles (58 km) west of London Paddington. It is sited on the northern edge of the town centre, near to the main retail and commercial areas and the River Thames. It is the busiest station in Berkshire, and the third busiest in South East England.

The North Downs Line is a railway line in South East England. It runs for 45 miles 40 chains (73.2 km) from Reading in Berkshire to Redhill in Surrey. It is named after the North Downs, a range of chalk hills that runs parallel to the eastern part of the route. The name was introduced in 1989 by Network SouthEast, the then operator. The North Downs Line serves the settlements in the Blackwater Valley as well as the towns of Guildford, Dorking and Reigate. It acts as an orbital route around the south and southwest of London and has direct connections to the Great Western Main Line at Reading, the Waterloo-Reading line at Wokingham, the Alton line at Ash, the Portsmouth Direct Line at Guildford and the Brighton Main Line at Redhill.

Luton Airport Parkway station is on the Midland Main Line in England, serving south Luton and Luton Airport in Bedfordshire. The station is situated in Luton's Park Town district, being 29.27 miles (47.11 km) from London St Pancras between Harpenden to the south and Luton to the north. Its three-letter station code is LTN, also the IATA code for the airport.

Luton railway station is located in the town centre of Luton, Bedfordshire, England. The station is about three minutes' walk from The Mall Shopping Centre. It is situated on the Midland Main Line and is operated by Thameslink.
An airport rail link is a service providing passenger rail transport between an airport and a nearby city. Direct links operate straight from the airport terminal to the city, while other links require an intermediate use of a people mover or shuttle bus. Advantages for the passenger include faster travel times and easy connections with other public transport. Advantages for the airport include increased patronage and enhanced accessibility for staff. Additionally, authorities have benefitted from less highway congestion, less pollution, and more business opportunities.

Stourbridge Town is a railway station in the town of Stourbridge, West Midlands, England. It is situated at the end of a short branch line linking the station with Stourbridge Junction, 0.8 miles away, where passengers can change for mainline train services. It is said to be the shortest operational branch railway line in Europe.

Luton is a town in the United Kingdom less than 30 miles (50 km) north of the centre of London, and has good transport links via the motorway network and the National Rail system. Luton is also home to Luton Airport, one of the major feeder airports for London and the southeast. The town is also served by buses run by Arriva Herts & Essex and other operators and has a guided busway. As a Unitary Authority, Luton Borough Council is responsible for local highways and public transport in the borough.
Urban andsuburban rail plays a key role in public transport in many of the major cities of the United Kingdom. Urban rail refers to the train service between city centres and suburbs or nearby towns that acts as a main mode of transport for travellers on a daily basis. They consist of several railway lines connecting city centre stations of major cities to suburbs and surrounding towns.

Zermatt railway station is a metre gauge railway station serving the car-free mountaineering and ski resort of Zermatt, in the Canton of Valais, Switzerland. It is the southern terminus of the BVZ Zermatt-Bahn (BVZ), which connects Zermatt with standard gauge lines at Visp and Brig. Since 1 January 2003, the BVZ has been owned and operated by the Matterhorn Gotthard Bahn (MGB), following a merger between the BVZ and the Furka Oberalp Bahn (FO). The station is across the street from Zermatt GGB railway station, the valley terminus of the Gornergrat Railway.

Govia Thameslink Railway (GTR) is a British train operating company that operates the TSGN rail franchise. Within the franchise, GTR runs trains under the sub-brands: Thameslink, Great Northern, Southern, and Gatwick Express. GTR is a subsidiary of Govia, which is itself a joint venture between the British Go-Ahead Group (65%) and French company Keolis (35%).

The Luton DART is an airport rail link in Luton, Bedfordshire, England, which connects Luton Airport Parkway station and Luton Airport using a Cable Liner automated people mover system. DART is an acronym for Direct Air–Rail Transit. The line, which opened in March 2023, replaces the shuttle bus service, with the aim of reducing road congestion and reducing journey times from London St Pancras to the airport terminal to 32 minutes.
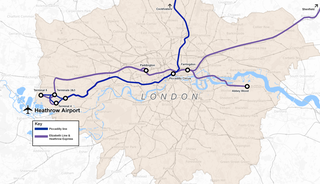
Over the years, a number of transport proposals have been made to improve public access to Heathrow Airport, near London in the United Kingdom.

The Gatwick Airport Shuttle Transit is a 0.75-mile (1.21 km) long elevated automated people mover that links the North and South Terminals at London's Gatwick Airport. The line is ground-side, and besides linking the two terminals also serves to link the North terminal to the airport railway station. Although sometimes colloquially, but erroneously, known as a "monorail", the transit vehicles are carried on rubber tyres running on a concrete track with twin running surfaces and are steered by separate guide rails.


















